Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Departmental Budgets
Uploaded by
Barack Mike0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesfor data anaytics
Original Title
Departmental budgets
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentfor data anaytics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesDepartmental Budgets
Uploaded by
Barack Mikefor data anaytics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
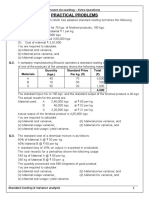
2 DEPARTMENTAL/OPERATING BUDGETS
Are budgets for different departments/operations in manufacturing entities.
Examples include:
Sales budget
Production budget
Material usage
Material purchases budget
Labor cost budget.
ILLUSTRATION: QUESTION 4 (b)
**** Sales budget
Shows the antipated sales units and sales value
For the sake of question, assume that SP per unit is 2,000 and 1,500 respectively for products M and K.
Product: Sales units SP per unit Sales Revenue
M 2,000 2,000 4,000,000.00
K 1,500 1,500 2,250,000.00
6,250,000.00
i) Production budget(Units only)
Shows units planned to be produced to satisfy sales demand
OS + Pdn - Sales = CS
Pdn = Sales+ CS - OS
Product:
M K
Sales 2,000 1,500 Input: Material
Closing stock 200 150 Labor
Opening stock 100 200
Pdn units 2,100 1,450
ii) Material usage budget
Material:
Exe Zed
Kgs Litres
Product:
M 4200 2100
K 4350 5800
Material usage 8550 7900
iii) Material purchases budget
Shows the planned material purchase quantity and value/cost satisfy the planned usage as per the usage budget ab
OS + Purchases - Usage = CS
Purchases = Usage+ CS-OS
Material:
Exe Zed
Usage 8550 7900
Closing stock 855 790
Opening stock 300 1000
Purchases(Qntity) 9105 7690
Material cost/Qntity 100 70
Total material cost 910,500.00 538,300.00
iv) Labor cost budget
Shows labor quantity(Time) and cost to satisfy planned production
Labour:
Skilled Semi-skilled
Product:
M 8400 4200
K 2900 7250
Labor hours required 11300 11450
Labor rate per hour 120 80
Labor cost 1,356,000.00 916,000.00
ucts M and K.
s per the usage budget above.
You might also like
- BudgetsDocument8 pagesBudgetsBarack MikeNo ratings yet
- Institute of Cost and Management Accountants of PakistanDocument11 pagesInstitute of Cost and Management Accountants of PakistanAsad RiazNo ratings yet
- AFAR Set BDocument11 pagesAFAR Set BRence Gonzales0% (2)
- Mba MGT ACCT (ILLUSTRATION QUESTIONS)Document13 pagesMba MGT ACCT (ILLUSTRATION QUESTIONS)biggykhairNo ratings yet
- Byproduct Mission MCQDocument3 pagesByproduct Mission MCQRohit ThandarNo ratings yet
- Cost SheetDocument10 pagesCost Sheetchukku2803No ratings yet
- Problem in Activity Based CostingDocument3 pagesProblem in Activity Based CostingLee Thomas Arvey FernandoNo ratings yet
- MAF Assignment QuestionDocument13 pagesMAF Assignment QuestionKietHuynhNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument30 pagesSummaryAkira Marantal Valdez0% (1)
- Spoiled Goods Are Goods That Have Been Damaged Through Imperfect Machining or IllustrationDocument3 pagesSpoiled Goods Are Goods That Have Been Damaged Through Imperfect Machining or IllustrationBuff FaloNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Question BankDocument28 pagesCost Accounting Question BankdeepakgokuldasNo ratings yet
- Working CapitalDocument2 pagesWorking CapitalPayal bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Job Order Costing Practice and Lecture QuestionDocument10 pagesJob Order Costing Practice and Lecture QuestionManaal HussainNo ratings yet
- Solution.: ST ND RD THDocument4 pagesSolution.: ST ND RD THhaggaiNo ratings yet
- MGT Acc 2019 SolutionDocument9 pagesMGT Acc 2019 SolutionSayeed AhmadNo ratings yet
- MGT Acc 2019 SolutionDocument9 pagesMGT Acc 2019 SolutionSayeed AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Midterm Examdocx PDF FreeDocument5 pagesCost Accounting Midterm Examdocx PDF FreeHannah Denise BatallangNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument29 pagesCost Accountingsino akoNo ratings yet
- Test Series: November, 2021 Mock Test Paper - 2 Intermediate (New) : Group - I Paper - 3: Cost and Management AccountingDocument9 pagesTest Series: November, 2021 Mock Test Paper - 2 Intermediate (New) : Group - I Paper - 3: Cost and Management AccountingAJNo ratings yet
- Asian Academy For Excellence Foundation, Inc.: Practical Accounting 2-Cost CPA Review O2017Document6 pagesAsian Academy For Excellence Foundation, Inc.: Practical Accounting 2-Cost CPA Review O2017didi chenNo ratings yet
- Bacc232 .309 Management Accounting Assignment 1Document13 pagesBacc232 .309 Management Accounting Assignment 1TarusengaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - 1 - IllustrationDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - 1 - IllustrationYonas BamlakuNo ratings yet
- Budgeting Review QuestionDocument5 pagesBudgeting Review QuestionFrankNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out 4 - ABC and Support Cost AllocationDocument2 pagesHand-Out 4 - ABC and Support Cost AllocationJerric CristobalNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Revision QuestionsDocument3 pagesCost Accounting Revision QuestionsMutambu MwetaNo ratings yet
- Ex3 Accounting For FOHDocument7 pagesEx3 Accounting For FOHLemuel ReñaNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Midterm ExamDocument5 pagesCost Accounting Midterm ExamNerizza TrinidadNo ratings yet
- CAF-3 CMAModelpaperDocument5 pagesCAF-3 CMAModelpaperAsad ZahidNo ratings yet
- Variable and Absorption CostingDocument52 pagesVariable and Absorption CostingcruzchristophertangaNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous - 01Document8 pagesAsynchronous - 01Joshua SantiagoNo ratings yet
- b5 Special Solving Set 5Document6 pagesb5 Special Solving Set 5MSHANA ALLYNo ratings yet
- Activity Based Costing-ExerciseDocument4 pagesActivity Based Costing-ExerciseKevin James Sedurifa OledanNo ratings yet
- TC9 (A)Document12 pagesTC9 (A)Cean MhangoNo ratings yet
- A - Mock PSPM Set 2Document6 pagesA - Mock PSPM Set 2IZZAH NUR ATHIRAH BINTI AZLI MoeNo ratings yet
- Practical Problems: Fybsc - Semester Ii - Management Accounting - Extra QuestionsDocument4 pagesPractical Problems: Fybsc - Semester Ii - Management Accounting - Extra QuestionsRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Accounting & Finance Assignment 1 - Updated 1.0Document15 pagesAccounting & Finance Assignment 1 - Updated 1.0lavania100% (1)
- Cost AccDocument27 pagesCost AccAngel PulvinarNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting AssignmentDocument6 pagesCost Accounting AssignmentCharles BarcelaNo ratings yet
- Job Order Costing: Illustrative ProblemsDocument30 pagesJob Order Costing: Illustrative ProblemsPatrick LanceNo ratings yet
- @ProCA - Inter Contract Costing Past Exam QuestionsDocument10 pages@ProCA - Inter Contract Costing Past Exam QuestionscallbvipinjainNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Adc Bcom Part 2 Solved Past Paper 2016Document8 pagesCost Accounting Adc Bcom Part 2 Solved Past Paper 2016Imran JuttNo ratings yet
- To Record Raw Materials Purchased On AccountDocument4 pagesTo Record Raw Materials Purchased On AccountKathleen MercadoNo ratings yet
- AFIN210 Midterm Exam 2017Document5 pagesAFIN210 Midterm Exam 2017William C ManelaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Just in Time SystemDocument5 pagesQuiz 1 Just in Time SystemMicah CarpioNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Chapter 3Document5 pagesCost Accounting Chapter 3Jenefer DianoNo ratings yet
- Unit - Ii Cost and Management AccountingDocument17 pagesUnit - Ii Cost and Management AccountingRamakrishna RoshanNo ratings yet
- SM CSE ACT 301 Final AssessmentDocument4 pagesSM CSE ACT 301 Final AssessmentArifur Rahaman 182-15-2111No ratings yet
- FIFODocument5 pagesFIFOYanna YahNo ratings yet
- Assignment Cover Sheet: Northrise UniversityDocument6 pagesAssignment Cover Sheet: Northrise UniversitySapcon ThePhoenixNo ratings yet
- Mock Test 2021 PMDocument5 pagesMock Test 2021 PMBao Thy PhoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6,7Document2 pagesExercise 6,7Damian Sheila MaeNo ratings yet
- Just in Time and Backflush Costing With Illustrative Problem Docx Compress 1Document7 pagesJust in Time and Backflush Costing With Illustrative Problem Docx Compress 1Danica Kaye MorcellosNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Scanner - 240218 - 174108Document15 pagesCost Accounting Scanner - 240218 - 174108ViratNo ratings yet
- Job OrderDocument2 pagesJob Orderrose llarNo ratings yet
- Quiz Absorption and Variable CostingDocument2 pagesQuiz Absorption and Variable CostingPISONANTA KRISETIANo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document4 pagesAssignment 2Sahil KumarNo ratings yet
- Test Series: March, 2022 Mock Test Paper - 1 Intermediate: Group - I Paper - 3: Cost and Management AccountingDocument7 pagesTest Series: March, 2022 Mock Test Paper - 1 Intermediate: Group - I Paper - 3: Cost and Management AccountingMusic WorldNo ratings yet
- Problem 2-14 Product Cost Sunk Cost Direct LaborDocument8 pagesProblem 2-14 Product Cost Sunk Cost Direct LaborarijitmajeeNo ratings yet
- Acct1 8Document5 pagesAcct1 8kutipan raraNo ratings yet
- BDA EXCEL ASSIGMENT-RosemaryDocument2 pagesBDA EXCEL ASSIGMENT-RosemaryBarack MikeNo ratings yet
- Payment Data Summary Form - Vision Institute Copy2Document2 pagesPayment Data Summary Form - Vision Institute Copy2Barack MikeNo ratings yet
- Loan Amortisation ScheduleDocument7 pagesLoan Amortisation ScheduleBarack MikeNo ratings yet
- MA and Cost Estimation IntrodcutionDocument4 pagesMA and Cost Estimation IntrodcutionBarack MikeNo ratings yet
- Cost Estimation IllustrationDocument1 pageCost Estimation IllustrationBarack MikeNo ratings yet
- Cash BudgetDocument3 pagesCash BudgetBarack MikeNo ratings yet
- AgribusinessDocument234 pagesAgribusinessPurna DhanukNo ratings yet
- Bear Stearns and The Seeds of Its DemiseDocument15 pagesBear Stearns and The Seeds of Its DemiseJaja JANo ratings yet
- BFP Operational Procedures Manualc PDFDocument18 pagesBFP Operational Procedures Manualc PDFdichosohubert548No ratings yet
- Topic 4 Database MarketingDocument16 pagesTopic 4 Database MarketingHanna Charissa AvendanoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Financial ManagementDocument8 pagesStrategic Financial Managementdivyakashyapbharat1No ratings yet
- Current LogDocument5 pagesCurrent LogCorey Frazier100% (1)
- Marks of A Successful EntrepreneurDocument4 pagesMarks of A Successful Entrepreneuremilio fer villaNo ratings yet
- Digital Marketing Class NotesDocument58 pagesDigital Marketing Class Notestina tanwarNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - HGDG - PD and PIMMEDocument40 pagesSession 3 - HGDG - PD and PIMMEDr. Jose N. Rodriguez Memorial Medical Center100% (1)
- Strengthening Internal Brand Equity With Brand Ambassador Programs: Development and Testing of A Success Factor ModelDocument16 pagesStrengthening Internal Brand Equity With Brand Ambassador Programs: Development and Testing of A Success Factor ModelmelianNo ratings yet
- ACC201 Financial AccountingDocument47 pagesACC201 Financial AccountingG JhaNo ratings yet
- Session 13 - NPDIDocument8 pagesSession 13 - NPDIPRALHAD DASNo ratings yet
- Little Leaf's Microgreens Price Calculator 2021Document26 pagesLittle Leaf's Microgreens Price Calculator 2021Carl RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Samsung DissertationDocument6 pagesSamsung DissertationPayToWritePaperSingapore100% (1)
- Project Management Chapter 1 Gray N LarsonDocument12 pagesProject Management Chapter 1 Gray N LarsonDendy Wibisono94% (18)
- 高顿财经ACCA acca.gaodun.cn: Advanced Performance ManagementDocument13 pages高顿财经ACCA acca.gaodun.cn: Advanced Performance ManagementIskandar BudionoNo ratings yet
- PPE SolutionDocument6 pagesPPE SolutionHuỳnh Thị Thu BaNo ratings yet
- MCOM - 101 - Project ManagementDocument192 pagesMCOM - 101 - Project ManagementKhâñ ÄäshîNo ratings yet
- Internal Auditing.2022Document19 pagesInternal Auditing.2022One AshleyNo ratings yet
- Student Fees Guide Book Final Year 2022Document98 pagesStudent Fees Guide Book Final Year 2022lindokuhlemashaba877No ratings yet
- Request For QuotationDocument4 pagesRequest For QuotationMajestyNo ratings yet
- Rotec: Gas Turbine MaintenanceDocument10 pagesRotec: Gas Turbine MaintenanceThanapaet RittirutNo ratings yet
- Aide-Memoire Inspection IndDocument10 pagesAide-Memoire Inspection Indmorcos mikhailNo ratings yet
- Differential CostsDocument3 pagesDifferential Costskahit anoNo ratings yet
- JLN Pending, Kuching 1 30/11/22Document4 pagesJLN Pending, Kuching 1 30/11/22Jue tingsNo ratings yet
- Managing Audit Data: ©2019 John Wiley & Sons Australia LTDDocument51 pagesManaging Audit Data: ©2019 John Wiley & Sons Australia LTDMëŕĕ ĻöľõmãNo ratings yet
- Secretos Indicador TDI MMMDocument22 pagesSecretos Indicador TDI MMMLuiz Vinhas100% (2)
- Strategic MarketingDocument84 pagesStrategic MarketingKameshNo ratings yet
- Kyambogo University Provisional Diploma/ Certificate Entry Scheme Private Admission List 2019 2020Document7 pagesKyambogo University Provisional Diploma/ Certificate Entry Scheme Private Admission List 2019 2020The Campus Times0% (1)
- Acg Module 9 Thc5-LathDocument10 pagesAcg Module 9 Thc5-LathMeishein FanerNo ratings yet