Professional Documents
Culture Documents
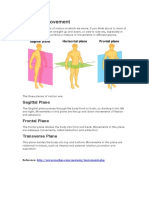
Body Movement
Uploaded by
Jhenia Mae Eulb0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views5 pagesOriginal Title
BODY MOVEMENT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views5 pagesBody Movement
Uploaded by
Jhenia Mae EulbCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
BODY MOVEMENT
If a blind child does not receive special training in this
area, he may not know how his body can move and this
movement may be awkward. When he walks he may
have either poor posture. Or the upper part of his body
may be rigid. The child might not know how to bend at
the waist or may walk with his feet far apart .
EXAMPLE OF BODY MOVEMENT
FLEXION - is the bending or the condition of being bent,
especially the bending of a limb or joint
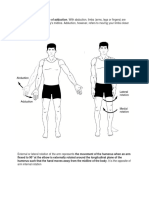
ADDUCTION - is the movement of body part toward the
body’s midline for fingers or toes.
ROTATION – is movement in which something, or a bone
whole limb, pivots or revolves around a single long axis.
PRONATION – is the forearm is a rotational movement
where the hand and upper arm are turned inward.
Pronation of a foot refers to turning of the sole outward.
So that weight is borne on the medial part of the foot.
SHOULDER JOINT – is formed where the humerus fit into
the scapula like a ball and socket .
CIRCUMDUCTION – means the circular movement of a
body part, such as a ball and socket joint or the eye. It
consists of a combination of flexion, extension, adduction
and abduction.
RADIAL DEVIATION – the wrist is complex series of joint
that are formed around the carpal bones and the radius
and ulna. The wrist is capable of three set of distinct
movement.
ULNAR DEVIATION – also known as ulnar drift, is a hand
deformity in which the swelling of the
metacarpophalangeal joint causes the fingers to become
displaced, tending toward the little finger.
OPPOSITION – is that in which thumb swing so that it
comes face to face with one or another of the fingers,as
in grasphing a needle or a ball.This movement is called
opposition.
EVERSION - is the movement of the sole of the foot away
from the median plane. Inversion is the movement of the
sole toward the median plane.
INVERSION – refers to movement that tilt the sole of the
foot away from inversion is the movement of the median
plane. Inversion is the movement of the sole towards the
median plane.
DEPRESSION – refers to movement in a superior
direction. Depression refers to movement in an inferior
direction, the opposite of elevation.
ELEVATION – is the upper movement of structures of the
body. The movement of elevation is the opposite of the
movement of depression.
PROTRACTION – is movement of a body part in the
anterior direction being drawn forward . The movement
of protraction is the opposite of the movement of
retraction.
SUPINATION – is a movement where the hand and upper
arm are turned inward. Pronation of the foot refers to
turning of the sole outwards, so that weight is borne on
the medial part of the foot.
HYPEREXTENSION – is an excessive joint movement in
which the angle formed by the bones of a particular joint
is opened, or straightened beyond its normal, healthy,
range of motion.
DORSIFLEXION – is the movement which decreases the
angle between the sole of the foot and the back of the
leg.
PLANTAR FLEXION – movement of the foot in which the
foot or toes flex downward the sole compare
dorsiflexion.
EXTERNAL ROTATION – is rotation away from the centre
of the body. Internal and external rotation of the arms
occurs at the shoulders, causing the elbow to rate.
You might also like
- Preseason Strength Training For Rugby Union - The General and Speci C Preparatory PhasesDocument9 pagesPreseason Strength Training For Rugby Union - The General and Speci C Preparatory PhasesHani Assi100% (1)
- Planes and Types of MovementDocument9 pagesPlanes and Types of Movementapi-341899824No ratings yet
- MAX-HYPE ELITE Ebook V3Document75 pagesMAX-HYPE ELITE Ebook V3Алексей Семенов100% (2)
- Atlas of Human Anatomy On MRIDocument140 pagesAtlas of Human Anatomy On MRIYanti Sihombing100% (3)
- Ankle Sprain Rehab 1Document3 pagesAnkle Sprain Rehab 1John NixonNo ratings yet
- Eastern Visayas State UniversityDocument58 pagesEastern Visayas State UniversityJoahna Mariz AbogadieNo ratings yet
- A. Kinesiology of HumanDocument7 pagesA. Kinesiology of HumanleyluuuuuhNo ratings yet
- Lumbar SpondylosisDocument59 pagesLumbar SpondylosisKURBULDKNo ratings yet
- Maternal Anatomy WilliamsDocument60 pagesMaternal Anatomy WilliamsZari Novela100% (2)
- Application of Bobath COnceptDocument61 pagesApplication of Bobath COnceptArun Kumar PTNo ratings yet
- Flexion and Extension: Rica Angelyn J. Atienza ABM-1CDocument4 pagesFlexion and Extension: Rica Angelyn J. Atienza ABM-1CRica Angelyn AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Case Report ScoliosisDocument67 pagesCase Report ScoliosisNurul Husna RashidNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument457 pagesIlovepdf MergedMar LoyolaNo ratings yet
- P.E CutieeeDocument16 pagesP.E CutieeeRachel SolisNo ratings yet
- HopeDocument3 pagesHopeAce CabreraNo ratings yet
- Movement of The JointsDocument13 pagesMovement of The JointsMAD MADNo ratings yet
- Pe 101Document7 pagesPe 101Betheemae R. MatarloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology For PrintingDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology For PrintingElaiza DomingoNo ratings yet
- Export DocumentDocument18 pagesExport DocumentAce OfranciaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terms of MovementsDocument7 pagesAnatomical Terms of MovementsElika YuukiNo ratings yet
- The Different Anatomical Types of MovementsDocument2 pagesThe Different Anatomical Types of MovementshayleyoursoulNo ratings yet
- Basic Bodily MovementsDocument13 pagesBasic Bodily MovementsKristelle LlegaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Rhythm (Bantilo, Ma. Karen V.)Document24 pagesFundamental Rhythm (Bantilo, Ma. Karen V.)Ma Karen V BantiloNo ratings yet
- Anatomicial PositonDocument19 pagesAnatomicial PositonMariel GuzonNo ratings yet
- JOINTMOVEMERNTSDocument23 pagesJOINTMOVEMERNTSheavenyurs2004No ratings yet
- Planes of The BodyDocument2 pagesPlanes of The Bodysunlightshines germono13No ratings yet
- Mcmillan, 1987) - in A Normal Walk The Toes Are: Key Facts About The Anatomical Terminology Anatomical PositionDocument2 pagesMcmillan, 1987) - in A Normal Walk The Toes Are: Key Facts About The Anatomical Terminology Anatomical PositionCarla NatividadNo ratings yet
- pathfit-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagespathfit-WPS OfficeEphrem MedallaNo ratings yet
- Pathfit ReviewerDocument3 pagesPathfit Reviewerwidafo7816No ratings yet
- Anatomcial PositonDocument18 pagesAnatomcial PositonAicelle GayapNo ratings yet
- Module 1 PE1 LectureDocument11 pagesModule 1 PE1 LectureCedie EnrileNo ratings yet
- Pe 1Document11 pagesPe 1Patrickjohn GelilioNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terms of MovementDocument12 pagesAnatomical Terms of MovementRIANE JADE CADALIG PENATNo ratings yet
- Body MovementsDocument9 pagesBody MovementsSyifa Salsabilla100% (1)
- Week 17Document4 pagesWeek 17Rizielyn TorresNo ratings yet
- The Different Types of Anatomical MovementDocument4 pagesThe Different Types of Anatomical MovementChromagrafxNo ratings yet
- Synovial Joints Allow For Many Types of Movement Including GlidingDocument5 pagesSynovial Joints Allow For Many Types of Movement Including Glidingaccounts 3 lifeNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Position Direction and TermsDocument6 pagesAnatomical Position Direction and TermsB Palaruan Christian NoelNo ratings yet
- Abduction: RetractionDocument3 pagesAbduction: RetractionChristel BobosNo ratings yet
- Joints and MovementsDocument18 pagesJoints and Movementssiddhi meenaNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of The FootDocument6 pagesBiomechanics of The FootAnonymous OAEuN9NE1s0% (1)
- Movement PhasesDocument19 pagesMovement PhasesAcethetic PlaysNo ratings yet
- PE1 Introduction To MovementsDocument4 pagesPE1 Introduction To MovementsDaniela AnsayNo ratings yet
- AnphDocument7 pagesAnphMarineth DeleonNo ratings yet
- Movements in Sports BiomechanicsDocument27 pagesMovements in Sports BiomechanicsHockey Deeoak980No ratings yet
- Anatomical Terms of Movements or MotionDocument2 pagesAnatomical Terms of Movements or MotionThe BrodieNo ratings yet
- Basic Movement 3Document4 pagesBasic Movement 3Miles AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminology Group 3Document22 pagesAnatomical Terminology Group 3Jim Roger Malabo LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Flexion and ExtensionDocument9 pagesFlexion and ExtensionGlydell MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Mapeh Dance Steps BasicDocument8 pagesMapeh Dance Steps Basicsci PantallanoNo ratings yet
- Fundamental RhythmsDocument17 pagesFundamental RhythmsbinnieNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of MovementsDocument12 pagesFundamentals of MovementsJhanin BuenavistaNo ratings yet
- Pe AngielaaaaDocument13 pagesPe AngielaaaaFiona Erica Aliangan BuellaNo ratings yet
- Pe Reading Materials and Activity Sheet FinalDocument14 pagesPe Reading Materials and Activity Sheet FinalMARY JOY MARTIREZNo ratings yet
- MovementsDocument2 pagesMovementsJulie Ann ParicaNo ratings yet
- Iii. Fundamental MovementsDocument27 pagesIii. Fundamental Movementsmain.23001392No ratings yet
- Types of Body Movements Anatomy and Physiology IDocument12 pagesTypes of Body Movements Anatomy and Physiology ICryzxia Bhene YuloNo ratings yet
- PEREZ ANGELO BSE FILIPINO1-GEPEMOVE-locomotor Non Locomotor MovementsDocument3 pagesPEREZ ANGELO BSE FILIPINO1-GEPEMOVE-locomotor Non Locomotor MovementsZach ChukachucksNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Anatomical Position and Movements of Joints PDFDocument16 pages1.3 Anatomical Position and Movements of Joints PDFPradosh Kumar PanigrahyNo ratings yet
- Locomotor and Non Locomotor MovementDocument11 pagesLocomotor and Non Locomotor MovementTrewan SeroNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Midterm PathfitDocument2 pagesReviewer Midterm PathfitMelendez, Abegail T.No ratings yet
- Basic MovementsDocument17 pagesBasic MovementsRodRigo Mantua Jr.No ratings yet
- MCT Chapter 2Document8 pagesMCT Chapter 2Kenneth BocterNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know YourselfDocument11 pagesGetting To Know YourselfNnleinomNo ratings yet
- Advanced Anatomy 2nd. Ed.: Body MovementsDocument23 pagesAdvanced Anatomy 2nd. Ed.: Body Movementseyob yirsaw basaznewNo ratings yet
- Locomotor MovementDocument4 pagesLocomotor MovementCenizal Shine100% (1)
- Lesson-3 P.EDocument37 pagesLesson-3 P.ECandice SanchezNo ratings yet
- Sas 3 PDFDocument10 pagesSas 3 PDFgekkonoojiNo ratings yet
- E LearningDocument2 pagesE LearningJhenia Mae EulbNo ratings yet
- Arts AppreciationDocument8 pagesArts AppreciationJhenia Mae EulbNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument2 pagesCase StudyJhenia Mae EulbNo ratings yet
- Case Study JhenDocument20 pagesCase Study JhenJhenia Mae EulbNo ratings yet
- Kai Greene Leg Workout PDFDocument2 pagesKai Greene Leg Workout PDFHarith SimonNo ratings yet
- Late Swing or Early Stance? A Narrative Review of Hamstring Injury Mechanisms During High Speed RunningDocument9 pagesLate Swing or Early Stance? A Narrative Review of Hamstring Injury Mechanisms During High Speed Runninggaston9reyNo ratings yet
- Rumus Kalimat InterogatifDocument11 pagesRumus Kalimat InterogatifMrs. KhannaNo ratings yet
- PNFDocument7 pagesPNFAdrian Diago TevesNo ratings yet
- وضعيات التصوير الشعاعي 1Document30 pagesوضعيات التصوير الشعاعي 1عبدالرحمن الاريانيNo ratings yet
- Storz MP100 BookletDocument9 pagesStorz MP100 BookletGuan JiangNo ratings yet
- Arthrology: DR N. ChikumbaDocument50 pagesArthrology: DR N. ChikumbaNatty ChikumbaNo ratings yet
- Ligamento Cruzado Doble FasciculoDocument16 pagesLigamento Cruzado Doble FasciculoAuusto CórdobaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Tables - Bones of The Thorax: Bone Structure Description Notes RibDocument3 pagesAnatomy Tables - Bones of The Thorax: Bone Structure Description Notes Ribyachiru121No ratings yet
- Joe Delaney - Full Body ProgrammeDocument23 pagesJoe Delaney - Full Body Programmeenes canNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture PointsDocument46 pagesAcupuncture PointsM. P. Schaefer100% (1)
- Weights Excercise Workout Card v.3Document1 pageWeights Excercise Workout Card v.3morenojeeNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document25 pagesActivity 3April CaringalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy McqsDocument20 pagesAnatomy McqsKishore SainaneeNo ratings yet
- TRABAJO CALENTAMIENTO 4ºeso EnglishDocument5 pagesTRABAJO CALENTAMIENTO 4ºeso EnglishAdriana Menendez NovoNo ratings yet
- Drivecure Healthcare PVT LTD: S. No Product Name Produ CT Cod e HSN Code GST (%)Document4 pagesDrivecure Healthcare PVT LTD: S. No Product Name Produ CT Cod e HSN Code GST (%)DRIVECURENo ratings yet
- NCM 116 Rle Special Activity (Positioning)Document2 pagesNCM 116 Rle Special Activity (Positioning)alexander abasNo ratings yet
- Core Stability: The MusclesDocument5 pagesCore Stability: The MusclesNazifi ShamsudinNo ratings yet
- Rehab Guidelines For Reverse Shoulder ArthroplastyDocument7 pagesRehab Guidelines For Reverse Shoulder Arthroplastydeepak100% (1)
- ISAKMetry - Edilberto - Aguiar - Restricted - 11-13-2022 - Edilberto AguiarDocument3 pagesISAKMetry - Edilberto - Aguiar - Restricted - 11-13-2022 - Edilberto Aguiar012 timeNo ratings yet
- Concept Map TemplateDocument4 pagesConcept Map TemplateaamenaNo ratings yet