0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views26 pagesMS 6229
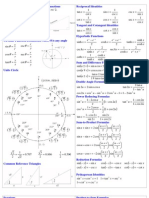
The document describes a course on trigonometry, coordinate geometry, and vectors. It includes the mode of assessment, which consists of tests, assignments, and a semester exam. The learning outcomes are solving problems using trigonometry, applying coordinate geometry, and applying vector operations. The course contents cover topics in trigonometry, coordinate geometry, and vectors. Trigonometry topics include conversions between degrees and radians, trig functions, identities, and solving triangles. Coordinate geometry covers locating points, lines, circles, and conic sections. Vectors includes definitions, operations, and applications to planes.
Uploaded by
Michael NammanjeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views26 pagesMS 6229
The document describes a course on trigonometry, coordinate geometry, and vectors. It includes the mode of assessment, which consists of tests, assignments, and a semester exam. The learning outcomes are solving problems using trigonometry, applying coordinate geometry, and applying vector operations. The course contents cover topics in trigonometry, coordinate geometry, and vectors. Trigonometry topics include conversions between degrees and radians, trig functions, identities, and solving triangles. Coordinate geometry covers locating points, lines, circles, and conic sections. Vectors includes definitions, operations, and applications to planes.
Uploaded by
Michael NammanjeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd