Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guide 2
Guide 2
Uploaded by
Maio EspinosaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Guide 2
Guide 2
Uploaded by
Maio EspinosaCopyright:
Available Formats
Margarita Díaz Torres
31 BB
Guide:
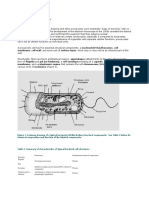
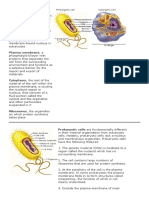
Types of cells:
Eukaryotic:
They are divided into multiple linear chromosomes. Organized with proteins into a
complex structure.
Pant Cell (chloroplast, cell wall central vacuole) and Animal Cell (Contains
cytoskeleton, the plasma membrane that encases the cell)
Differences:
The eukaryotic cells have nucleus and organelles
Cell wall
They are more complex
They are bigger because they can mi multi-cellular organisms.
Prokaryotic:
Do not have a nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelles. In
other words, all their intracellular water-soluble components (proteins, DNA and
metabolites) are located together in the same area enclosed by cell membrane
Achaea (lack of peptidoglycan) and Bacteria (cell wall composed of peptidoglycan)
Differences:
Don’t have nucleus.
They are small.
All of them have cell wall (made of peptiduglicane).
No organelles.
They can have a flagellum.
Plasmatic membrane more resistance.
Transcription: DNA to RNA
Translation: RNA to protein
Margarita Díaz Torres
31 BB
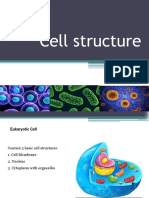
Organelles:
Plasma membrane: Regulate what passes into and out of
cell, cell-to-cell recognition, connection and adhesion, cell
communication.
Nucleus: Instructions for proteins synthesis and cell
reproduction, contains genetic information.
Ribosome: Sites of proteins synthesis.
Endoplasmic Reticulum: Intracellular compartment forms
transport vesicles; participates in lipid synthesis of membrane or
secreted proteins.
Golgi apparatus: Packages proteins for export from cell;
forms secretory vesicles.
Lysosomes: Digest the trash.
Mitochondria: Transform carbohydrates to energy.
Chloroplasts: Synthesize carbohydrates (photosynthesis)
Cell Wall: Protection and support.
Margarita Díaz Torres
31 BB
The Cell Theory:
Cells are the basic unit of structure of all living things. (Possible by advances in
microscopy) New cells are formed from other existing cells and the cell is a
fundamental unit of structure, physiology, and organization in a living organisms.
You might also like
- Initial ResearchDocument8 pagesInitial ResearchAnim MANo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesCell - The Unit of Lifelpc4944No ratings yet
- CELL Study MaterialDocument12 pagesCELL Study MaterialShyamasree SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Mitosis and Meiosis 2007 For UPLOADDocument44 pagesCell Structure Mitosis and Meiosis 2007 For UPLOADJason RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCell As A Unit of LifeRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- BIOL107 - Different Cell TypesDocument4 pagesBIOL107 - Different Cell TypesJahsuah OrillanedaNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesMariam Qais100% (1)
- The CellDocument77 pagesThe CellSTEM 11-B Sharina Joyce CanozaNo ratings yet
- Procaryotic Cell ArchitectureDocument18 pagesProcaryotic Cell ArchitectureWindi Dawn SallevaNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Document8 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Saurav SoniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Student Copy ZoologyDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Student Copy Zoologyapi-530699294No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 March 2009Document36 pagesLecture 1 March 2009api-19824406No ratings yet
- Biology Study Material - Xi - 22-23-Compressed - 0Document14 pagesBiology Study Material - Xi - 22-23-Compressed - 0gana63693No ratings yet
- CH 1: Evolution, The Themes of Biology, and Scientific InquiryDocument27 pagesCH 1: Evolution, The Themes of Biology, and Scientific InquiryZackNo ratings yet
- Abbu Laba Di BaDocument5 pagesAbbu Laba Di Bammamerto2005No ratings yet
- CELLDocument8 pagesCELLRajendra Chikkamath100% (1)
- Biyani's Think Tank: Cell Biology & GeneticsDocument81 pagesBiyani's Think Tank: Cell Biology & GeneticsAkshay chandrakarNo ratings yet
- Keerthana H PDocument22 pagesKeerthana H PVidya shree GNo ratings yet
- CellDocument16 pagesCellanantchouhdary1709No ratings yet
- Official Chapter 2 Student Copy ZoologyDocument5 pagesOfficial Chapter 2 Student Copy Zoologyapi-528700386No ratings yet
- Class 9 Fundamental Unit of Life (Notes)Document5 pagesClass 9 Fundamental Unit of Life (Notes)Udaya RakavanNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsDocument4 pagesGroup 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsClaire Angelie Ruaya100% (1)
- Animal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalDocument6 pagesAnimal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalJohnson Macayan FernándezNo ratings yet
- Bio Lecture 2 Cell StructureDocument46 pagesBio Lecture 2 Cell StructureLương Bang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document46 pagesLecture 2Phạm ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell StructureDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell StructurePRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument2 pagesCellsmalikaiman1015No ratings yet
- General Principles of Cell OrganisationDocument3 pagesGeneral Principles of Cell Organisation22194No ratings yet
- Botany Full PDF EMDocument72 pagesBotany Full PDF EMAbinaya PalaniNo ratings yet
- Cell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesDocument8 pagesCell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesHarismita AlagurajNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology and Genetics Notes On All Lectures PDFDocument62 pagesCell Biology and Genetics Notes On All Lectures PDFMR ManalangNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Notes Prokaryotic CellsDocument4 pagesIB Biology Notes Prokaryotic CellsayushfmNo ratings yet
- CellDocument22 pagesCellrapidalerthubNo ratings yet
- A Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingDocument4 pagesA Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingJONAVIE DEMALATANo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 006 Chapter 3Document7 pagesZoology Notes: 006 Chapter 3humanupgrade100% (1)
- Biochem Lecture 2Document3 pagesBiochem Lecture 2Samier AlihuddinNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes: NucleoidDocument3 pagesProkaryotes: NucleoidHubdar Ali KolachiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Overview of The Cellular Basis of LifeDocument3 pagesLesson 1 - Overview of The Cellular Basis of LifeYLADE, ERICCA ANDREANo ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Human CellDocument12 pagesHuman CellCrystal GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nature of CellsDocument7 pagesNature of CellsAdrian Lee VannorsdallNo ratings yet
- Cellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsDocument9 pagesCellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsPiriyatharshini RamanathNo ratings yet
- 8 Cell NotesDocument7 pages8 Cell NotesAbhijeet AmetaNo ratings yet
- The Cell: by DR - Hikmat Fatima HashmiDocument53 pagesThe Cell: by DR - Hikmat Fatima Hashmibeverly brittoNo ratings yet
- Biology Cell Presentation in Green White Illustrative StyleDocument61 pagesBiology Cell Presentation in Green White Illustrative Stylecorazondelatorre12345No ratings yet
- 3 Cytology Membran JunctionDocument48 pages3 Cytology Membran JunctionSamNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class IX Biology Fundament Unit of Life Chapter NotesDocument7 pagesCBSE Class IX Biology Fundament Unit of Life Chapter NotesDremaraanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Cell and Molecular Biology 1Document38 pagesLecture 1 Cell and Molecular Biology 1Martin HangasNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument35 pagesCell Structure2W10No ratings yet
- Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cell ResearchDocument10 pagesEukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cell ResearchlektiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-08 Cell: Structure and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-08 Cell: Structure and FunctionsHasharaNo ratings yet
- Functions of Organelles in CellDocument23 pagesFunctions of Organelles in CellZahid ShehzarNo ratings yet
- Initial Research: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesInitial Research: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsKatyFosdike1No ratings yet
- 2022-1-Tinjauan Umum Sel - Struktur SelDocument56 pages2022-1-Tinjauan Umum Sel - Struktur SelVe LinNo ratings yet
- DNA, The Genetic MaterialDocument6 pagesDNA, The Genetic MaterialMarinelle TumanguilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Student Copy ZoologyDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Student Copy Zoologyapi-523871804No ratings yet
- Biology Unit 2 Revision: Topic 3 - Voice of The GenomeDocument6 pagesBiology Unit 2 Revision: Topic 3 - Voice of The GenomeYasinKureemanNo ratings yet
- Biology Eukaryote Prokaryote CellDocument8 pagesBiology Eukaryote Prokaryote CellmIZZshaNaNo ratings yet
- WR (Oncologic Nursing)Document28 pagesWR (Oncologic Nursing)manu_gutierrez08No ratings yet