Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bot - New Families
Uploaded by
atiyabegum282Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bot - New Families
Uploaded by
atiyabegum282Copyright:
Available Formats
SRI CHAITANYA Jr.
KALASALA, VAISHNAVI CAMPUS, BACHUPALLY
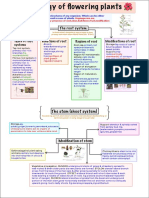
Characteristics MALVACEAE FABACEAE/PAPILIONOIDEAE ASTERACEAE/COMPOSITAE POACEAE /GRAMINAE
One of the sub family of Family of
It is known as mustard family. It is known as mallow family.
leguminosae. It is also Also called sun flower family. Advanced cerearls
Mainly Mainly
General description termed as pea family. family. Largest family distributed through ubiquitous
distributed in tropics distributed in tropics
Distributed all over out the world in occurance
and substropics and substropics
the world. largest monocot family
Annual herbs
Habit Annual or perennial herbs Herbs, shrubs and trees. Trees, shrubs, herbs. (Helianthus, Annual or perennial Herbs
Tagetus, Dahlia)
Tap root, fusiform/
Tap root but in
napiform tuberous roots may Tap root with Fibrous roots, stilt roots in maize,
Root Profusely branched tap root. Dahlia fasiculated
found. root nodules. jowar, sugarcane
roots/fibrous roots
Usually herbaceous, erect, much branched
Herbaeous stem with (brancing rare in Grasses have hollow stem at
Erect, branched with Erect or climber,
Stem pungent watery fluid. Dahlia and Helianthus) solid, sometimes internodes. stem is
star-shaped trichormes. herbaceous.
Have stellate hairs. with milky latex. In Helianthus jointed called culm
tuberous stem stores food
Alternate, pinnately Usually alternate but occasionally opposite
Simple, alternate Leaves are narrow
Simple rarely compound, compound or simple (as Helianthus)
palmately lobed, alternate Leaf base is
Leaves alternate, sessile leaves, reticulate or in Whorl (Eupatorium),
stipulate, reticulate sheath like Venation is
exstipulate, reticulate venation. venation, pulvinate leaf base exstipulate, petiolate, simple
venation. parallel, Contain silica, hence hard
stipulate. or compound venation reticulate.
Head or capitulum with involucre of bracts
Usually two types of
florets are found in inflorescence viz,
zygomorphic, ligulate or ray
Solitary terminal or Spike of spikelets
florets and actinomorphic tubular or disc
Inflorescence Corymobse raceme or corymb. axillary cymose or Racemose, (panicle in Dalbergia) In maize, female -spadix,
florets. In inflorescence,
raceme. Male-spike, Wheat-compoud spike
ray florets are found towards the
periphery (they are older in nature)
and disc florets are distributed near
centre (thus younger)
Bracteate, sessile
Bisexual, actinomorphic Sessile, Bracteate,
Bisexual, bracteate, Bisexual, zygomorphic, actinomorphic (disc
(may be zygomorphic), bisexual, unisexual in maize,
actinomorphic, bracteate or ebracteate, florets) or zygomorphic
Flower hypogynous, Zygomorphic hypogynous
complete pentamerous, pentamerous, hypogynous, (ray florets) epigynous
bracteate/ebracteaete, Sterile bracts called glumes are
hypogynous. complete and pentamerous.
tetramerous. present
Characteristics BRASSICACEAE/ CRUCIFERAE MALVACEAE FABACEAE/PAPILIONOIDEAE ASTERACEAE/COMPOSITAE POACEAE /GRAMINAE
epicalyx formed by bracteoles
Perianth: Highly reduced, 2 in
is present below the calyx and
Four, free, polysepalous in two Five, gamolous 5 modified into hairs or pappus. number, reduced to pin head like
Calyx is protective in nature. Sepals
whorls, 2+2 valvate aestivation imbricate/valvate aestivation Persistent, help in fruit dispersal lodicules. In bamboo, 3 are
5, fused, gamosepalous,
present
valvate aestivation
Five, polypetalous,
papilionaceous (posterior 5, Gamopetalous,
Four, polypetalous Five, petals free, but
standard, two lateral tubular in disc florets
Corolla cruciform and reduced. basally adnate, twisted
wings, keel enclosing but ligulate in ray
valvate aestivation aestivation.
pistil and stamen), florets, aestivation valvate.
vexillary aestivaiton.
Stamens 5, absent in ray florets.
Numerous stamens Syngenesious (anther lobes are
Usually 3 but sometimes
Monadelphous fused laterally but the filaments are free)
Six stamens arranged in two Ten, diadelphous,(9)+1, 6 (as in Oryza), filament long,
epipetalous, epipetalous, anthers
Androecium whorls, 2+4, polyandrous anther dithecous, anthers versatile,
monothecous, extrorse dithecous fused to form a tube like
tetradynamous, dithecous. introrse. dithecous, dehiscence
anthers reniform, dehiscence structure around the style. Anthers
longitudingal.
transverse introse, dithecous, dehiscence
longitudinal
Monocarpellary (actually
tricarpellary but only one carpel is
Bicarpellary, syncarpous A compund pistil of functional),
monocarpellary, bicarpellary, syncarpous, unilocular,
superior ovary with two to many carpels, unilocular, ovary superior, style
Gynoecium unilocular with many superiour ovary. Style long, stigma bifid,
parietal placentation. syncarpous, axile long, stigma 2 and feathery (plants
ovules, single style, Ovary superior single ovule, basal placentation
Replum/false septum is present placentation. are always wind pollinated).
marginal placentation.
Placentation basal.
Usually cross pollination
piston mechanism Usually cross pollination
Usually cross pollination but self pollination in Favoured by protandry and Herkogamy Usually cross pollination
Usually cross pollination
Pollination Entomophily favoured by pisum and lathyrus Entomophily Anemophily
Entomophily
protandry and Herkogamy Entomophily In disc florets some times self pollination favoured by protandry
occurs by saftey mechanism
A single single seeded Caryopsis
Fruit Siliqua or silicula Capsule or schizocarp. Legume/Pod
seeded cypsela.
Characteristics BRASSICACEAE/ CRUCIFERAE MALVACEAE FABACEAE/PAPILIONOIDEAE ASTERACEAE/COMPOSITAE POACEAE /GRAMINAE
Seed with curved embryo and
Seed Small non-endospermic scanty One to many and non-endospermic dicotyledonous, non endospermic monocotyledonous, endospermic
endosperm.
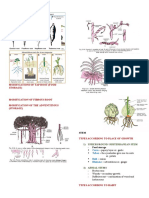
Floral formula
Floral diagram
i) The members of this i) These plants are used i) Members of this family are i) Oil Yielding plants : Helianthus annus i) Members of this family are mainly
family are sources of food, as food, e.g. mainly (sunflower oil), Carthamus (Safflower oil) used as food
e.g. Brassica campestris Abelmoschus esculentus used as food, i.e. pulses, e.g. gram, ii) Medicinal plants: Artemisia, Eclipta 1) Tritium aestivum
(mustard), (lady's finger). arhar, sem, moong, soybean, etc. alba used as hair tonic with (bread wheat) - a natural hexaploid
B. oleracea (cauliflower), Brassica Hibiscus cannabis (gongura) ii) Fodder, e.g. brahmi buti and commonly known as 2) Oryza sativa (Paddy)
rapa (turnip) and Raphanus sativus ii) Ornamentals, e.g. Trifolium, Sesbania, etc. Bringraj, -Chief cereal of India,
(radish). Althaea rosea (gulekhera), iii) Edible oil, e.g. soybean, ground Calendula officinalis bran oil obtained from husk
ii) Medicines, e.g. Iberis Hibiscus rosa-sinensis(China nut iii) Insecticide: Chrysanthemum 3) Zea mays (Maize) - food crop,
amara (gout and rheumatism), rose), iv) For fibres, e.g. sunhemp. cinerariifolium inflorescence unisexual, style
Lobularia (gonorrhoea), Lepidium iii) Medicines: roots and bark v) Ornamentation, e.g. lupin, sweet - Pyrethrum longest.
sativum (asthma and piles) of Urena lobata are used as a pea. iv) Food Yielding plants: Latuca sativa 4) Hordeum vulgare (Barley)
Economic iii) Ornamentals, e.g. Iberis cure for hydrophobia. VI) For the extraction of medicines, (Lettuce or Salad) -Oldest amongst cultivated plants.
Importance amara (candytuft), iv) Fibres, e.g. e.g Cicborium intybus (chikori powder/Coffee 5) Pennisetum typhoidum
Cherianthus cheiri (wall Gossypium sp. (cotton), mulaithi. blend) (Pearl millet or Bajra) -A food
flower), etc. Bombax ceiba (silk cotton) VII) Dye-Indigofera (blue) v) Weeds: Parthenium hysterophorus crop, straw used as fodder.
vi) oil- seeds of Brassica v) Edible oil, e.g. cotton. commonly called ii) Fodder - Cynodon, Panicum,
carrot grass or congress grass. Cymbopogon iii)
vi) Dyes - Carthamus (red), Sugar - Saccharum
Tagetus (Yellow) iv) Building material - Bamboo
v) Paper making - Grasses,
Bamboo
You might also like
- Rosales and Brassicales Lab ReportDocument11 pagesRosales and Brassicales Lab ReportKoreen Bayani100% (1)
- Lab Work 6Document3 pagesLab Work 6Bella LopezNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants Mind MapDocument4 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants Mind MapAstha Agrawal89% (9)
- Table FinalDocument3 pagesTable Finallegendsac2000No ratings yet
- Plant Families NEETDocument2 pagesPlant Families NEETPratyush Raj SaranNo ratings yet
- KEY TO GENERA AND FAMILIES OF VIRGINIA PLANTSDocument30 pagesKEY TO GENERA AND FAMILIES OF VIRGINIA PLANTSAMALIA RIZQI ROSANINGDYAHNo ratings yet
- Families - Comparisions - Sundar Notes Final - 25.10.23Document20 pagesFamilies - Comparisions - Sundar Notes Final - 25.10.23priyamprakash0107No ratings yet
- Site planningAutoRecoveredDocument15 pagesSite planningAutoRecoveredRyuuichi KishimaNo ratings yet
- All FamilyDocument3 pagesAll FamilyRaunak KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPDocument10 pagesExperiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPMirahmad FadzlyNo ratings yet
- List of Endangered Philippine PlantsDocument7 pagesList of Endangered Philippine PlantsResearch AssistanceNo ratings yet
- Grass and Scientific NameDocument1 pageGrass and Scientific NameMJ Maravilla TaboboNo ratings yet
- Copy Biodiversity and Conservation wmDocument9 pagesCopy Biodiversity and Conservation wmleagueofkxx00No ratings yet
- AlismatalesDocument3 pagesAlismatalesSanchez MaroseNo ratings yet
- Family SystematicsDocument5 pagesFamily SystematicsJoshua Laurence PalconNo ratings yet
- Materia Medica of Western Herbs - (PG 393 - 394)Document2 pagesMateria Medica of Western Herbs - (PG 393 - 394)corallyNo ratings yet
- Activity 5: Roots - Understanding the Structure and Functions of RootsDocument9 pagesActivity 5: Roots - Understanding the Structure and Functions of RootsPenelopy DizonNo ratings yet
- MONOCOTSDocument1 pageMONOCOTSAunieyNo ratings yet
- FM1S1948004001064Document125 pagesFM1S1948004001064JewelNo ratings yet
- RM 01 Family ChartDocument2 pagesRM 01 Family Chartyogitachandwani19No ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants Mind MapsDocument4 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants Mind Mapsjai maa Durga aadi parashaktiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8 - Montibon - Estela MarieDocument11 pagesExercise 8 - Montibon - Estela MarieEstela Marie MontibonNo ratings yet
- Morphology Chart Eng 1Document1 pageMorphology Chart Eng 1angadgneware0% (1)
- FABACEAEDocument1 pageFABACEAEkegecaj152rc3sNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants: Structures, Modifications & FormulasDocument6 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants: Structures, Modifications & FormulasAMLAAN 10CNo ratings yet
- VND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Wordprocessingml Document&rendition 1Document2 pagesVND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Wordprocessingml Document&rendition 1Kishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity 2024Document47 pagesPlant Diversity 2024pieterhansconsultantNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsJigyansa DashNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - LAB2 - Weed GardenDocument10 pagesGroup 7 - LAB2 - Weed Gardendario albaNo ratings yet
- Lab Work 7Document4 pagesLab Work 7Bella LopezNo ratings yet
- Transport Water and SolutesDocument4 pagesTransport Water and SolutesAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- Adventitious Roots: 1) Underground/ Subterranean StemDocument2 pagesAdventitious Roots: 1) Underground/ Subterranean StemAprille CastroNo ratings yet
- Plant Systematics FinalsDocument5 pagesPlant Systematics FinalsJessaLagdameoBeatrizNo ratings yet
- Characters Rosaceae Solanaceae FabaceaeDocument1 pageCharacters Rosaceae Solanaceae FabaceaeMuhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Characteristics Comparison ChartDocument1 pagePlant Kingdom Characteristics Comparison ChartTanya SiyagNo ratings yet
- Comparing Characteristics of MonocotsDocument5 pagesComparing Characteristics of MonocotsAnna HarietNo ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW Nparks Gov Sgflorafaunawebflora313156Document1 pageHTTPSWWW Nparks Gov Sgflorafaunawebflora313156kohby2014No ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants: Mind MapsDocument4 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants: Mind MapsRiya Bhardwaj100% (1)
- Earthworm and Fire Ant CharacteristicsDocument20 pagesEarthworm and Fire Ant CharacteristicsMB LoterteNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument40 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantschdhrysudeepNo ratings yet
- Sheryn Common Name FinalDocument1 pageSheryn Common Name FinalMJ Maravilla TaboboNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument3 pagesReviewerVincent ArazaNo ratings yet
- Shiv AnjaniDocument4 pagesShiv AnjanisadafmajeedNo ratings yet
- UPV Tacloban College Leaf Morphology Lab ReportDocument5 pagesUPV Tacloban College Leaf Morphology Lab ReportAlyssa Pauline PalacioNo ratings yet
- Botany PPT 1Document60 pagesBotany PPT 1SidNo ratings yet
- Monocot vs. Dicot: Roots: Fibrous vs. TaprootDocument3 pagesMonocot vs. Dicot: Roots: Fibrous vs. TaprootExequiel ZoletaNo ratings yet
- 9 Plants Description 202Document6 pages9 Plants Description 202Ian GoNo ratings yet
- Plant TerminologyDocument29 pagesPlant TerminologyNguyễn An HạnhNo ratings yet
- The "Primitive" Flowering PlantsDocument36 pagesThe "Primitive" Flowering PlantsAkif waniNo ratings yet
- Plant Systematics and Angiosperm Phylogeny: AssignmentDocument15 pagesPlant Systematics and Angiosperm Phylogeny: AssignmentNikita JaiswalNo ratings yet
- PLT-CH2-Plant Description PrinciplesDocument62 pagesPLT-CH2-Plant Description PrinciplesArockia RajaNo ratings yet
- Mangrove Lab Report SummaryDocument34 pagesMangrove Lab Report SummaryEleonora IntanNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Kingdoms Classification GuideDocument17 pagesPlant and Animal Kingdoms Classification GuideAlisha JasaniNo ratings yet
- Ustet ReviewerDocument16 pagesUstet ReviewerVinzynt Isler Carmona100% (19)
- Lecture 10 - Leaves PDFDocument52 pagesLecture 10 - Leaves PDFChristine R. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Angiosperm FamiliesDocument11 pagesAngiosperm FamiliesGio Angelo IdosNo ratings yet
- Seed Plants History and ClassificationDocument25 pagesSeed Plants History and ClassificationCDB 1st Semester 2077100% (1)
- Journal No. 3 "Specialized Leaves"Document10 pagesJournal No. 3 "Specialized Leaves"Ej AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change: Beyond Coping. Women Smallholder Farmers in TajikistanDocument52 pagesClimate Change: Beyond Coping. Women Smallholder Farmers in TajikistanOxfamNo ratings yet
- Community Immersion ProposalDocument7 pagesCommunity Immersion ProposalAIKO MAGUINSAWANNo ratings yet
- Summative Science Test for 5th GradersDocument3 pagesSummative Science Test for 5th Graderscristina quiambaoNo ratings yet
- Major Tomato Pests and Diseases in Daloa, Côte d'IvoireDocument12 pagesMajor Tomato Pests and Diseases in Daloa, Côte d'IvoireKarl DiomoNo ratings yet
- Aquarium Fish Farm BudgetDocument3 pagesAquarium Fish Farm BudgetSarthak100% (1)
- (Destination) : 310.00 Boat BusDocument1 page(Destination) : 310.00 Boat BusKim MonteronaNo ratings yet
- Bukidnon Government Employees' CooperativeDocument8 pagesBukidnon Government Employees' CooperativeRey EdwardNo ratings yet
- Benue SoilSample FarmerlistDocument3,210 pagesBenue SoilSample FarmerlistlivityhotNo ratings yet
- Analytical ExpositionDocument6 pagesAnalytical ExpositionDaniel OktafiandiNo ratings yet
- National Boxed Beef Cutout Values Rise $2.71 For Choice, $0.69 For SelectDocument5 pagesNational Boxed Beef Cutout Values Rise $2.71 For Choice, $0.69 For SelectThiago PresaNo ratings yet
- AFRICAN History 1Document43 pagesAFRICAN History 1Sylvia NyakujawaNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Organic Fertilizer of Humus and Chemical Fertilizer Fructifol in The Effectiveness of Growth of The Fodder Maize (Zea Mayz)Document6 pagesImplementation of Organic Fertilizer of Humus and Chemical Fertilizer Fructifol in The Effectiveness of Growth of The Fodder Maize (Zea Mayz)Sergio RiveraNo ratings yet
- Horticulture IntroductionDocument42 pagesHorticulture IntroductionUsama ShahNo ratings yet
- How India's Millet Ambassador' Preserves Ancient Grains - and Helps Promote Food Security Global Development The GuardianDocument8 pagesHow India's Millet Ambassador' Preserves Ancient Grains - and Helps Promote Food Security Global Development The GuardiansanjayNo ratings yet
- Management Practices for Preventing Late Blight of PotatoDocument2 pagesManagement Practices for Preventing Late Blight of PotatoaiktiplarNo ratings yet
- Plant Breeding and Genetics:: Harvesting The Power of DNADocument40 pagesPlant Breeding and Genetics:: Harvesting The Power of DNAjkorentayer100% (1)
- L-2 Agronomy - TillageDocument16 pagesL-2 Agronomy - TillageashishNo ratings yet
- Algae Cultures To BiofuelsDocument15 pagesAlgae Cultures To BiofuelsSiva KondaveetiNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Utilization of Agricultural Extension Packages of Selected Arable CropsDocument8 pagesDeterminants of Utilization of Agricultural Extension Packages of Selected Arable CropsJubilant UmehNo ratings yet
- Growth and Yield of Sweet Corn Affected by Tillage and FertilizerDocument13 pagesGrowth and Yield of Sweet Corn Affected by Tillage and Fertilizermadel gracillaNo ratings yet
- Dragon Fruit Farming - PDF - Project ReportDocument6 pagesDragon Fruit Farming - PDF - Project ReportJinal PanchalNo ratings yet
- Hibiscus flower cultivation and export potentialsDocument7 pagesHibiscus flower cultivation and export potentialsAli Abdoulaye100% (1)
- World Food Production Food Production in The Philippines Socio-Cultural and Economic Status and Needs and AspirationDocument40 pagesWorld Food Production Food Production in The Philippines Socio-Cultural and Economic Status and Needs and AspirationJodie Mer DayamaNo ratings yet
- Mechanization of Horticulture - Icar-Iihr BengaluruDocument25 pagesMechanization of Horticulture - Icar-Iihr BengaluruSenthil KumaranNo ratings yet
- ECHO Technical Notes The Moringa Tree Dr. Martin PriceDocument19 pagesECHO Technical Notes The Moringa Tree Dr. Martin PriceManoj Thushara WimalarathneNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia: Attention Demanding Soil Pollution Repercussion: (Article Analysis)Document4 pagesEthiopia: Attention Demanding Soil Pollution Repercussion: (Article Analysis)IGP PilienNo ratings yet
- El Gallo PintoDocument19 pagesEl Gallo PintoVale Gómez MeyerNo ratings yet
- C. Content (TR)Document51 pagesC. Content (TR)Niño Embile DellomasNo ratings yet
- Azadirachta Indica (Neem) : Scientific ClassificationDocument7 pagesAzadirachta Indica (Neem) : Scientific ClassificationVishnu RamanNo ratings yet