Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electromagnetic Waves-1
Uploaded by
Gladwin SolomonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electromagnetic Waves-1
Uploaded by
Gladwin SolomonCopyright:
Available Formats
MICA PU COLLEGE, Mysuru Kiran Rao G
Electromagnetic waves
Ampere’s circuital law:
The integral value of the magnetic field around any closed conductor is equal to times the net current in
the conductor.
∮ ⃗ ⃗⃗⃗
Conduction current (IC):
The current carried by conductors due to flow of charges is called conduction current.
Mention the inconsistency of Ampere’s circuital law:
Ampere’s circuital law is used to determine the magnetic field produced by the conduction current. But fails
to determine magnetic field produced by displacement current which is due to time varying electric field.
This is inconsistency of Ampere’s circuital law.
Modification of Ampere’s circuital law made by Maxwell:
Maxwell added the displacement current to the conduction current in Ampere’s law, indicating that just as
changing magnetic fields give rise to electric fields, changing electric fields also give rise to magnetic fields.
What the generalization made by Maxwell?
The source of a magnetic field is not just the conduction current but it is also the rate of change of electric
field with time.
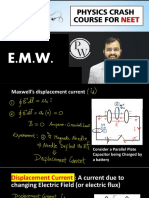
Displacement Current (Id):
The current which appears in the region in which the electric field is changing with time is called
displacement current.
Where is the permittivity of free space.
is the rate of change of electric flux
Mention the need of displacement current:
Kiran Rao G Electromagnetic Waves Page 1
MICA PU COLLEGE, Mysuru Kiran Rao G
Maxwell introduced the concept of displacement current to remove the inconsistency in Ampere’s circuital
law.
Properties of displacement current:
Displacement current exists whenever there is a change in electric field with time.
Displacement current is zero where the electric field is zero.
Displacement current acts as a source of magnetic field.
Mention the expression for Ampere’s – Maxwell law and explain the symbols
∮ ⃗ ⃗⃗⃗
∮ ⃗ ⃗⃗⃗
Where ⃗ is the magnetic field intensity.
⃗⃗⃗ is the infinitesimally small line element on the closed path,
IC is the conduction current
Id is the displacement current
Distinguish between conduction current and displacement current:
Conduction Current Displacement Current
It is due to the flow of charges It is due to the change in electric field
What is the displacement current between two plates of the capacitors if the capacitor is fully charged in
AC circuit?
Zero, because in a fully charged capacitor electric field between the plates is constant.
Electromagnetic waves:
Electromagnetic wave is the combination of time varying electric field and time varying magnetic field. These
two fields are perpendicular to each other and also perpendicular to the direction of propagation of wave.
Examples: Visible light, X – rays, UV rays etc.
Kiran Rao G Electromagnetic Waves Page 2
MICA PU COLLEGE, Mysuru Kiran Rao G
Who predicted the existence of the electromagnetic waves?
James Clerk Maxwell.
Who confirmed the existence of electromagnetic waves experimentally?
Heinrich Hertz.
Name the Indian Physicist who has worked in the field of production of electromagnetic wave.
Jagadish Chandra Bose. (J.C. Bose)
Sources of electromagnetic waves:
Oscillating charged particles is the sources of electromagnetic waves.
Nature of electromagnetic waves:
Transverse waves.
Characteristics of electromagnetic waves:
They travel along straight lines in homogeneous medium.
They travel with a velocity of 3 X 108 m/s in free space.
They are transverse waves.
They carry energy and momentum.
What is the angle between electric field vector and magnetic field vector of electromagnetic waves?
900
What is the angle between electric field vector / magnetic field vector with the direction of propagation in
an electromagnetic wave?
900
Kiran Rao G Electromagnetic Waves Page 3
MICA PU COLLEGE, Mysuru Kiran Rao G
Mention the expression for speed of light in terms of permittivity and permeability in free space.
Where is the permeability of free space
is the permittivity of free space
Mention the expression for speed of light in terms of permittivity and permeability in a material medium
Where is the permeability of the medium
is the permittivity of the medium
Relation between λ and f
What is the direction of magnetic field and electric field in a capacitor?
Magnetic field is parallel to the plates of the capacitor.
Electric field is perpendicular to the plates of the capacitor.
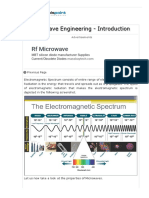
Electromagnetic spectrum:
It is an orderly arrangement of all the electromagnetic waves in a single chart according to their wavelengths
or frequencies.
Wavelength (λ) in m in increasing order
< 10 – 3nm 10 – 3nm 1nm to 400nm to 700nm to 1mm to >0.1m
to 1nm 400nm 700nm 1mm 0.1m
- rays X - rays UV – rays Visible rays I R – rays Micro Radio
Waves Waves
In this wide electromagnetic spectrum only a small portion between 4000 A0 and 7000 A0 is visible.
Kiran Rao G Electromagnetic Waves Page 4
MICA PU COLLEGE, Mysuru Kiran Rao G
Long wavelength Short wavelength
Low frequency High frequency
Low energy High energy
Gamma rays ( - rays):
These are high frequency electromagnetic radiation produced in nuclear reactions and also emitted by
radioactive nuclei.
These are the invisible electromagnetic radiations of wavelength range < 10-3nm.
Mention the use of gamma rays:
They are used in the treatment of cancer.
They are used in the treatment of skin diseases.
They are used to find the thickness of materials.
They are used to find the defects in buried petroleum pipes.
They are used in microscope.
X – Rays:
These are the invisible electromagnetic radiations of wavelength range 10-3nm to 1nm.
Kiran Rao G Electromagnetic Waves Page 5
MICA PU COLLEGE, Mysuru Kiran Rao G
X – rays are produced by bombarding a metal target by fast moving electronics.
Mention the use of X – rays:
They are used to detect fractures and dislocations of bones.
They are used in the treatment of brain tumor, skin diseases and cancer.
They are used to test the quality of welding in industry.
They are used in the crystal structure analysis.
Ultraviolet rays (UV - rays):
These are the invisible electromagnetic radiations of wavelength range 1nm to 400nm
Mention the use of UV – rays:
They are used in the treatment of skin diseases and bone diseases.
They are used in production of vitamin D.
They are used to distinguish between real and artificial gems.
They are used to activate rate of chemical reactions.
They are used in high resolving power microscopes.
Visible rays:
These are visible electromagnetic radiations of wavelength range 400nm to 700nm.
Mention the use of visible rays:
They are used to see the things around us.
They are used in photosynthesis
They are used in photocells.
Infrared rays (IR - rays):
Infrared rays are waves produced by all hot bodies.
These are the invisible electromagnetic radiations of wavelength range 700nm to 1mm
Mention the use of IR rays:
They are used in long distance photography.
They are used to treat muscular pains and skin diseases.
They are used to diagnose cure bone fractures.
They are used to protect food from decaying.
Kiran Rao G Electromagnetic Waves Page 6
MICA PU COLLEGE, Mysuru Kiran Rao G
Micro waves:
These are electromagnetic waves produced by electrical oscillations in LC circuit.
These are the invisible electromagnetic radiations of wavelength range 1mm to 0.1m
Mention the use of micro waves
Micro waves are used in micro ovens.
They are used in RADAR system.
They are used in long distance communication system via geostationary satellites.
Radio waves:
Radio waves are electromagnetic waves produced by the accelerated motion of charges in conducting wires.
These are the invisible electromagnetic radiations of very long wave length greater than 0.1m.
Mention the use of radio waves:
They are used in communication and broadcasting.
What is the wavelength range of electromagnetic spectrum?
10 – 14 m to 10 7 m
What is the frequency range of electromagnetic spectrum?
10 Hz to 1022 Hz.
Name the electromagnetic radiation having highest frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Gamma rays
Name the electromagnetic radiation having lowest frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Radio waves.
Name the electromagnetic radiation with highest wave length.
Radio waves.
Name the electromagnetic radiation with lowest wave length.
Gamma rays.
Arrange IR rays, Gamma rays, visible rays, X – rays in increasing order of wave length.
Gamma rays, X rays, visible rays and IR rays.
Kiran Rao G Electromagnetic Waves Page 7
MICA PU COLLEGE, Mysuru Kiran Rao G
Arrange micro waves, gamma rays, visible rays, X rays in increasing order of frequency.
Micro waves, visible rays, X rays and gamma rays.
Question bank
March 2014
1. Who predicted the existence of electromagnetic waves? Give the wavelength range of
electromagnetic spectrum. (2M)
.July 2014
1. Write any two uses of microwaves. (2M)
March 2015
1. Mention two applications of infrared radiation. (2M)
July 2015
1. What is displacement current? Write the expression for displacement current. (2M)
March 2016
1. Arrange micro waves, gamma rays, visible rays, X rays in increasing order of frequency. (2M)
July 2016
1. What are electromagnetic waves? Write the expression for the velocity of electromagnetic waves in
terms of permittivity and magnetic permeability of free space. (2M)
March 2017
1. What is displacement current? Write the expression for displacement current. (2M)
July 2017
1. Write Maxwell’s equation for the speed of electromagnetic waves and explain the terms. (2M)
March 2018
1. Give any two applications of X – rays. (2M)
July 2018
1. Give any two applications of ultraviolet radiation. (2M)
March 2019
1. Write the expression for speed of light in terms of μ0 and explain the terms. (2M)
July 2019
1. Write any two uses of ultra violet rays. (2M)
March 2020
1. What is displacement current? Write the expression for displacement current. (2M)
May 2022
1. Name the type of electromagnetic rays lying between ultraviolet and gamma rays. (1M)
2. Write the relation between the magnitude of the electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic
waves. (1M)
Ans:
Kiran Rao G Electromagnetic Waves Page 8
MICA PU COLLEGE, Mysuru Kiran Rao G
3. What is displacement current? Write the expression for displacement current. (2M)
March 2023
1. The ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum lies between (1M)
a) X – ray region and visible region b) Microwave region and radio – wave region
c) Gamma rays region and X – ray region d) Visible region and microwave region
2. What is displacement current? Write the expression for displacement current. (2M)
July 2023
1. Electromagnetic waves are produced by (1M)
a) Accelerated charges b) Stationary charges
c) Charges in uniform motion d) A conductor carrying steady current
2. What is displacement current and conduction current? (2M)
Kiran Rao G Electromagnetic Waves Page 9
You might also like
- An Introduction to the Theory of Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Theory of Microwave CircuitsK. KurokawaNo ratings yet
- Ansh KDocument14 pagesAnsh KAnsh KumarNo ratings yet
- LVL 4 Lec 1Document44 pagesLVL 4 Lec 1aloqab778030No ratings yet
- Group 5 SlideDocument30 pagesGroup 5 SlideCuong LaidangNo ratings yet
- 101science WavelengthDocument53 pages101science Wavelengthnm9536766No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves: y Z y ZDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: y Z y Zmaruthi cyber19No ratings yet
- Pengantar ANSPEKDocument56 pagesPengantar ANSPEKFlorencia AngellicaNo ratings yet
- Radio and Microwaves ExplainedDocument10 pagesRadio and Microwaves ExplainedShelly Ryn SaligumbaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves (EM Waves)Document17 pagesElectromagnetic Waves (EM Waves)Joshdave cuambotNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves ExplainedDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Waves ExplainedMohitha Reddy CNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy Unit 1Document19 pagesSpectroscopy Unit 1veluselvamaniNo ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations and the Discovery of Electromagnetic WavesDocument8 pagesMaxwell's Equations and the Discovery of Electromagnetic WavesRobin BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Q2Document33 pagesLesson 1 Q2odnimernNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument50 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumMisty Vito100% (1)
- Chapter 8 (Assignment)Document6 pagesChapter 8 (Assignment)asmaaysha121No ratings yet
- EM Waves Study GuideDocument7 pagesEM Waves Study GuidePreethiNo ratings yet
- EM Waves and Its ApplicationDocument30 pagesEM Waves and Its ApplicationShakthi GaneshNo ratings yet
- G1o U2l1 - Electromagnetic Wave 10 - 1819 - 22Document73 pagesG1o U2l1 - Electromagnetic Wave 10 - 1819 - 22Erika Mae CorderoNo ratings yet
- Microwave Communication GuideDocument18 pagesMicrowave Communication GuideAkhil RajuNo ratings yet
- EM Waves - UPHDocument20 pagesEM Waves - UPHSHIVA THAVANI100% (1)
- Study Material of Class 12 Physics 2023-24-65-99Document35 pagesStudy Material of Class 12 Physics 2023-24-65-99budgies2005No ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document42 pagesLesson 2Essah Vlogs03No ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Electronic Spectros PDFDocument38 pagesChapter 3. Electronic Spectros PDFPoorvansh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Class 12 TH PDF 2nd Term For Share FileDocument108 pagesClass 12 TH PDF 2nd Term For Share FileDeepak singh SengarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.1 - EM WavesDocument8 pagesLecture 2.1 - EM WavesAPPLE CAGUNGUN-BELGICANo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 8: History of EMWDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Waves Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 8: History of EMWShaku JoshiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Wave TheoryDocument75 pagesElectromagnetic Wave TheoryLen Cardona Bagunas100% (1)
- Chapter Eight Chapter Eight: Physics Group PR OjectDocument24 pagesChapter Eight Chapter Eight: Physics Group PR OjectSyeda haniNo ratings yet
- Q2-M1 Electromagnetic WavesDocument58 pagesQ2-M1 Electromagnetic WavesJaycob Sedrick TaboNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument74 pagesElectromagnetic WavesJohnNo ratings yet
- Wireless Power Transfer and Health EffectsDocument20 pagesWireless Power Transfer and Health EffectsDevarajanRaghavan0% (1)
- E M WavesDocument11 pagesE M WavesEleena GuptaNo ratings yet
- Elec - Nav L07a EmgwavesDocument87 pagesElec - Nav L07a EmgwavesEreNNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (B - MARCH 2022Document40 pagesUnit-1 (B - MARCH 2022Vibin SimonNo ratings yet
- 2023-11-10 11 - 13 - 50.563 - 1Document2 pages2023-11-10 11 - 13 - 50.563 - 1pranitjadhav0407No ratings yet
- 1.unit - 1 - Interference PPT - NewDocument60 pages1.unit - 1 - Interference PPT - Newprithviraj gavhaneNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves CH8Document13 pagesElectromagnetic Waves CH8Rishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 EM WaveDocument5 pagesUnit 2 EM Wavevenkata karthikNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 - Arellano University - Prepared by Sir - Andro RomanoDocument31 pagesGeneral Physics 2 - Arellano University - Prepared by Sir - Andro RomanoKesia AlmodalNo ratings yet
- Bardsley EngDocument12 pagesBardsley EngAkshat TripathiNo ratings yet
- Iipucphysics-Electromagneticwave 52249Document3 pagesIipucphysics-Electromagneticwave 52249ashiya.jendiNo ratings yet
- Displacement CurrentDocument10 pagesDisplacement Currentojhamunesh388No ratings yet
- Everything about electromagnetic wavesDocument10 pagesEverything about electromagnetic wavesSahil NaikwadiNo ratings yet
- Mechanecal Wave and Electromagnetic Wave: Prepered By: Sir LeviDocument16 pagesMechanecal Wave and Electromagnetic Wave: Prepered By: Sir Levilevi loretoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves ExplainedDocument44 pagesElectromagnetic Waves Explainedvenom eNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics Assignment 1Document9 pagesApplied Physics Assignment 1areejNo ratings yet
- Assign. Physics (Autosaved)Document17 pagesAssign. Physics (Autosaved)zakir4532rtewNo ratings yet
- MicrowaveDocument82 pagesMicrowavemr mrNo ratings yet
- C12-Electromagnetic WavesDocument74 pagesC12-Electromagnetic WavesGerald S. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering NotesDocument2 pagesMicrowave Engineering NotesJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument7 pagesPHYSICSSurya A S100% (1)
- Radio Wave PropagationDocument81 pagesRadio Wave PropagationJoseph JeremyNo ratings yet
- Radio Waves and MicrowavesDocument25 pagesRadio Waves and Microwavesporshathegreat156No ratings yet
- Batch Basic MathsDocument75 pagesBatch Basic Mathssoumava palitNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer q2Document6 pagesScience Reviewer q2Samuel IdoNo ratings yet
- What Can We Learn From The Electromagnetic Spectrum?: A Wjoshi and Alok KumarDocument18 pagesWhat Can We Learn From The Electromagnetic Spectrum?: A Wjoshi and Alok KumarAndrei Cojanu100% (1)
- PhysicsDocument22 pagesPhysicsNurul JamalNo ratings yet
- Wireless Transmission of Electricity PDFDocument13 pagesWireless Transmission of Electricity PDFcrazymangeshNo ratings yet
- eBook+Introduction+to+Spectroscopy Pavis 32 121Document7 pageseBook+Introduction+to+Spectroscopy Pavis 32 121devi dwi rustaminingrumNo ratings yet
- Guideunit 5Document5 pagesGuideunit 5Kavi SanjaiNo ratings yet
- Bayer Snap Fit Joints For PlasticsDocument26 pagesBayer Snap Fit Joints For PlasticsEllen NicDiarmadaNo ratings yet
- Falcon 9 Users Guide Rev 2.0Document41 pagesFalcon 9 Users Guide Rev 2.0jarzola11No ratings yet
- Numerical Modeling of Flow Over A Rectangular Broa PDFDocument12 pagesNumerical Modeling of Flow Over A Rectangular Broa PDFSawab MadeneNo ratings yet
- (Energy Science, Engineering and Technology) Mykhaylo v. Zagirnyak, Zhanna IV. Romashykhina, Andrii P. Kalinov - The Diagnostics of Induction Motor Broken Rotor Bars On The Basis of The ElectromotiveDocument205 pages(Energy Science, Engineering and Technology) Mykhaylo v. Zagirnyak, Zhanna IV. Romashykhina, Andrii P. Kalinov - The Diagnostics of Induction Motor Broken Rotor Bars On The Basis of The ElectromotiveKAVINNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Design Criteria For Subways - KueselDocument10 pagesEarthquake Design Criteria For Subways - KueselAA_BB_HHNo ratings yet
- IndustrialCatalog ArmorX PDFDocument28 pagesIndustrialCatalog ArmorX PDFjuan pablo castro gallegoNo ratings yet
- TTT DiagramDocument17 pagesTTT DiagramGAURAV SINGHNo ratings yet
- The Design of Vibro Replacement (Stone Column)Document17 pagesThe Design of Vibro Replacement (Stone Column)sirtiendungNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Stresses and Strains Near The End of A Crack Traversing A PlateDocument2 pagesAnalysis of Stresses and Strains Near The End of A Crack Traversing A Platearash125No ratings yet
- Padeye PATIDocument43 pagesPadeye PATIbayu_23RNo ratings yet
- Tribological Behavior of Nitrided Stainless Steel Against Cast Iron Under Severe Test Condition Marcia M. Maru Deniol K. Tanaka Amilton SinatoraDocument8 pagesTribological Behavior of Nitrided Stainless Steel Against Cast Iron Under Severe Test Condition Marcia M. Maru Deniol K. Tanaka Amilton Sinatoravsraju2No ratings yet
- An Investigation Into The Distinctive Properties of LiAuS A - 2023 - Results inDocument7 pagesAn Investigation Into The Distinctive Properties of LiAuS A - 2023 - Results inronaldquezada038No ratings yet
- CE-UG-2018 Spring FEB-JUN 2020Document42 pagesCE-UG-2018 Spring FEB-JUN 2020SalmanNo ratings yet
- HardnessDocument21 pagesHardnessJerry Man UtdNo ratings yet
- Level Gages PenberthyDocument34 pagesLevel Gages PenberthySrta IncognitaNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument3 pagesStrength of Materialsvp0209198825% (4)
- Credit-2 Electronics FundamentalsDocument113 pagesCredit-2 Electronics FundamentalsRamNo ratings yet
- 11th Batch Question PaperDocument55 pages11th Batch Question PaperArul Gnana JohnNo ratings yet
- Underbalanced Drilling in ShaleDocument19 pagesUnderbalanced Drilling in ShaleKarwan IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 in Modphy MempinDocument12 pagesExam 3 in Modphy MempinCrizaldo MempinNo ratings yet
- A 3D Method To Evaluate Moisture Losses in A Low Pressure SteamDocument11 pagesA 3D Method To Evaluate Moisture Losses in A Low Pressure SteamMuhammad Junaid DarNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Surface Texture and Coating Thickness of Nickel Coated ABS-3D PartsDocument8 pagesOptimizing Surface Texture and Coating Thickness of Nickel Coated ABS-3D PartsAnand NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Born Solvation - From CherieDocument7 pagesBorn Solvation - From CherieNandika Kasaru JackNo ratings yet
- Imec M01A: Science of Engineering MaterialsDocument23 pagesImec M01A: Science of Engineering MaterialsJimmyNo ratings yet
- Theories of FailureDocument23 pagesTheories of FailureDheerajGunwant25% (4)
- Fracture Mechanics: Stress Concentration and Fracture ToughnessDocument22 pagesFracture Mechanics: Stress Concentration and Fracture Toughnessaap1No ratings yet
- Dental Materials: Investment MaterialDocument4 pagesDental Materials: Investment MaterialErwin GunawanNo ratings yet
- Student Lab 1 Intro Semiconductor LabvoltDocument5 pagesStudent Lab 1 Intro Semiconductor LabvoltbishoyNo ratings yet
- CH128P Syllabus-E01Document8 pagesCH128P Syllabus-E01Christian LeeNo ratings yet
- 3.basics of Strain GaugeDocument20 pages3.basics of Strain GaugeRaunaq SinghNo ratings yet