0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views3 pagesUnderstanding Rate, Base, and Percentage
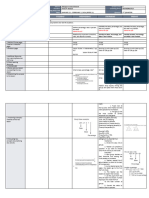
This lesson teaches students about rates, bases, and percentages. Students will work through word problems to identify and calculate each term. The teacher will begin with a bell-ringer problem, define the key terms, provide examples, and lead guided practice. Then students will independently work on a worksheet with similar problems before completing an exit ticket to assess understanding. Finally, the concepts will be reinforced through sorting activities and real-world applications.
Uploaded by
Glaiza SacpaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views3 pagesUnderstanding Rate, Base, and Percentage
This lesson teaches students about rates, bases, and percentages. Students will work through word problems to identify and calculate each term. The teacher will begin with a bell-ringer problem, define the key terms, provide examples, and lead guided practice. Then students will independently work on a worksheet with similar problems before completing an exit ticket to assess understanding. Finally, the concepts will be reinforced through sorting activities and real-world applications.
Uploaded by
Glaiza SacpaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd