Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 19
Chapter 19
Uploaded by
Jessie Marie DuhaylungsodOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 19
Chapter 19
Uploaded by
Jessie Marie DuhaylungsodCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 19: NITRIC OXIDE
Source of Nitric oxide: Nitroglycerin
MOA: Nitric oxide donor
Enzymes:
1. Neuronal NOS (nitric oxide synthase)
Calcium dependent
2. Endothelial NOS
3. Inducible NOS/ macrophage- not calcium dependent
3 Target of Nitric Oxide:
1. Metalloproteins
-initial reaction of NO
2. Thiols (all compounds that contain Sulfur)
-S nitrosylation (reaction/ process with regards to NO & S containing
compounds)
Product: GSH
3. Tyrosine
-Tyrosine Nitration: formation of superoxide (powerful oxidants)
Product: Superoxide
GSH (glutathione): Major intracellular sulfur containing compound
- scavenger of superoxides
Aldehyde reductase
Nitroglycerin Nitric Oxide
Heme of guanylyl cyclase
Activation of guanylyl cyclase
GTP
cGMP
Vasodilators
PKG
Thus, NO does not directly cause
vasodilation
NO: increase cGMP & PKG
Effects of NO:
A. Vasodilation- used in hypertension
B. Antioxidant- ex. Glutathione (s-nitrosylation)
Nitrosoglutathione= NO + Glutathione
-stable form of nitric oxide
-antioxidant
C. Decreases platelet aggregation
NO: prevent formation of foam cells in arterialwall/ cholesterol plaque
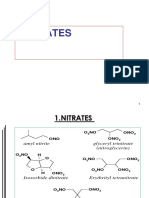
1.ORGANIC NITRATES
ISOSORBIDE DINITRATE
BN: Isordil
-metabolized to NO
-with continous use; effectivity will decrease (Nitrate Tolerance)
2.ORGANIC NITRITES
ISOAMYL NITRITE
3.SODIUM NITROPRUSSIDE (Emergency use only)
-rapid reduction of BP
-used for hypertensive emergencies
4. NO GAS INHALATION
5. SILDENAFIL (not a NO donor) Action of Phosphodiesterase inhibitor:
BN: Viagra Prolongs effect cGMP
MOA: 5 Phohphodiesterase inhibitor More vasodilation
Does not cause direct increase of cGMP
NITRIC OXIDE IN DISEASE
Septicemia- iNOS will be triggered (induced by the infection)
=dilation of blood vessel
=low BP; normal blood volume
How to reverse hypotension in Sepsis?
-prevent action of NO by scavenging of NO by hemoglobin
Hemoglobin: scavenger of NO
Inhalation type of NO: reduced pulmonary hypertension
You might also like
- Introduction To Everyday Science MCQs (For Competitive Exams) PDFDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Everyday Science MCQs (For Competitive Exams) PDFSadia manzoorNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT NO. 2 Guide (The Silver Group)Document6 pagesEXPERIMENT NO. 2 Guide (The Silver Group)Kaye OmoNo ratings yet
- NITRATESDocument21 pagesNITRATESFrancisNo ratings yet
- Preview Farmako Katzung 4Document35 pagesPreview Farmako Katzung 4gunubgpeNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Kwento Ni RosarioDocument17 pagesCase Analysis Kwento Ni RosarioMeg YunsonNo ratings yet
- Münzel Et Al 2005 Explaining The Phenomenon of Nitrate ToleranceDocument11 pagesMünzel Et Al 2005 Explaining The Phenomenon of Nitrate ToleranceButyl KamonphunNo ratings yet
- Erythrityl Tetranitrate: IndicationDocument3 pagesErythrityl Tetranitrate: IndicationAbeerNo ratings yet
- Hypotensive AgentsDocument48 pagesHypotensive AgentsFaizan Ahmad AliNo ratings yet
- Anti Anginal DrugsDocument60 pagesAnti Anginal DrugsPranish SawantNo ratings yet
- Drugs For IHDDocument36 pagesDrugs For IHDASHUTOSH KHADANGANo ratings yet
- NitratesDocument2 pagesNitratessujyotsharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Antianginal DrugsDocument28 pagesLecture 7 Antianginal DrugsjawadNo ratings yet
- Antianginal DrugsDocument38 pagesAntianginal Drugslemmademe204No ratings yet
- 11cardiac Glycosides, Antianginals, and AntidysrhythmicsDocument114 pages11cardiac Glycosides, Antianginals, and AntidysrhythmicsaryahsmaeNo ratings yet
- Nsaid (: Non Steroid Anti Inflammation Drugs) & Gout TherapyDocument46 pagesNsaid (: Non Steroid Anti Inflammation Drugs) & Gout TherapyTutde SedanaNo ratings yet
- 12 Digoxin 2Document2 pages12 Digoxin 2Aymen BekirNo ratings yet
- 6 AntianginalDocument38 pages6 AntianginalAyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs: by Dr. Md. Ruhul KuddusDocument56 pagesCardiovascular Drugs: by Dr. Md. Ruhul Kuddus53-Deepankar SutradharNo ratings yet
- Vasoactive PeptidesDocument35 pagesVasoactive PeptidesKetan patilNo ratings yet
- Vasodilators and Drugs Used in The Treatment of Angina PectorisDocument52 pagesVasodilators and Drugs Used in The Treatment of Angina PectorisAbdiweli AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Lecture #13Document2 pagesLecture #13yeeticusfinchlmaoNo ratings yet
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (Nsaids) : Analgesic, Anti-Pyretic and Anti-Inflammatory AgentsDocument45 pagesNon-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (Nsaids) : Analgesic, Anti-Pyretic and Anti-Inflammatory AgentsArvi KhanNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument24 pagesAngina PectorisAyu PurbaNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument24 pagesAngina PectorisAshwin Raghav SankarNo ratings yet
- Antianginal ClassDocument32 pagesAntianginal ClassAnonymous whcvnPBeQNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 - Polypeptides - 16 Oct 2006Document63 pagesLecture 15 - Polypeptides - 16 Oct 2006api-3703352No ratings yet
- Nsaid PDFDocument38 pagesNsaid PDFسامر الرفاعيNo ratings yet
- Antianginal Drugs Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesAntianginal Drugs Lecture NotesPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Final Year B. Pharm.: 3.3 DiureticsDocument58 pagesFinal Year B. Pharm.: 3.3 DiureticsSHEFALI CHAUDHARINo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Eicosanoids and SignalingDocument10 pagesSynthesis of Eicosanoids and SignalingCLEMENTNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Benefi Ts of SGLT2Document10 pagesCardiovascular Benefi Ts of SGLT2GVRNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Assignment 3Document31 pagesPharmacology Assignment 3Tujiyye kooNo ratings yet
- Pcol AnginaDocument3 pagesPcol AnginaRAMOS, Khristine JoesellNo ratings yet
- Nitric Oxide SynthaseDocument58 pagesNitric Oxide Synthasenidhiya sara sabuNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 (Prep - of Na2S2O3.5H2O) & 4 (Excercise)Document12 pagesExp 3 (Prep - of Na2S2O3.5H2O) & 4 (Excercise)photocopy photocopyNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument12 pagesDiureticsteranrobleswaltergabrielNo ratings yet
- Nitric Oxide: Dr. Abrar M Babateen Clinical Nutrition Department Faculty of Applied Medical SciencesDocument25 pagesNitric Oxide: Dr. Abrar M Babateen Clinical Nutrition Department Faculty of Applied Medical SciencesTasneem KutbiNo ratings yet
- Antianginal Drugs Are Used Primarily To Restore The Balance Between The Oxygen SupplyDocument8 pagesAntianginal Drugs Are Used Primarily To Restore The Balance Between The Oxygen SupplyUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- Nitric OxideDocument11 pagesNitric OxideDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Nitrate Tolerance ARSDocument45 pagesNitrate Tolerance ARSButyl KamonphunNo ratings yet
- Essential Oils: Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA)Document1 pageEssential Oils: Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA)Oscar A. LuévanoNo ratings yet
- Kono 1978Document7 pagesKono 1978Musfeera KhanNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy For Angina Pectoris - Pak WilarDocument3 pagesDrug Therapy For Angina Pectoris - Pak WilarVikneswaran VîçkýNo ratings yet
- Backyard Chemistry - Nitric ..Document5 pagesBackyard Chemistry - Nitric ..Ricardo Fontanari de CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- P-Drug FK Umm 2009Document504 pagesP-Drug FK Umm 2009MulYaniNo ratings yet
- Antidote LectureDocument78 pagesAntidote LectureAliyan KhosoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 (Week 2)Document3 pagesChapter 19 (Week 2)Supipi GamageNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive DrugsDocument62 pagesAntihypertensive DrugsYeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- Nitrates in The Management of Chronic Coronary Syndrome - UpToDateDocument18 pagesNitrates in The Management of Chronic Coronary Syndrome - UpToDateijmp7No ratings yet
- 05 Cell Respiration Fermentation Anaerobic and MoreDocument21 pages05 Cell Respiration Fermentation Anaerobic and MoreneelNo ratings yet
- Sodium GlucoseDocument20 pagesSodium GlucoseYati Nurul HashfiNo ratings yet
- NsaidsDocument16 pagesNsaidsraffia mahakNo ratings yet
- Antianginal DrugsDocument36 pagesAntianginal DrugscreativejoburgNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Antianginal Drugs: Tri Widyawati M. IchwanDocument43 pagesPharmacology of Antianginal Drugs: Tri Widyawati M. IchwanYohanna SinuhajiNo ratings yet
- Blood Thinners: Maher Khdour Clinical Pharmacy, BSC, MSC, PHDDocument68 pagesBlood Thinners: Maher Khdour Clinical Pharmacy, BSC, MSC, PHDYousef JafarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology RevisedDocument59 pagesPharmacology Revisedjohnstockton12100% (1)
- 9 Drugs Affecting Angina PectorisDocument3 pages9 Drugs Affecting Angina PectoristiaraNo ratings yet
- Dr. Binu Babu PH.D., M.Sc. (N), MBA Mrs. Jincy Ealias M.Sc. (N)Document75 pagesDr. Binu Babu PH.D., M.Sc. (N), MBA Mrs. Jincy Ealias M.Sc. (N)Prachi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Nitrates andDocument61 pagesNitrates andMrunalini DandamudiNo ratings yet
- 12 - G6PD and Hemolytic AnemiaDocument26 pages12 - G6PD and Hemolytic AnemiaLíria SouzaNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Chemical Glycosylation: Advances in Stereoselectivity and Therapeutic RelevanceFrom EverandHandbook of Chemical Glycosylation: Advances in Stereoselectivity and Therapeutic RelevanceAlexei V. DemchenkoNo ratings yet
- CHM 213-Exp 6Document7 pagesCHM 213-Exp 6hafiqah100% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S1050464820305544 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S1050464820305544 MainDiana Steffany Gutierrez ZorroNo ratings yet
- USP-NF Cefotaxime InjectionDocument3 pagesUSP-NF Cefotaxime InjectionCongluanNo ratings yet
- Present Status of Feedstock Management & Technology Developments in Ethanol SectorDocument22 pagesPresent Status of Feedstock Management & Technology Developments in Ethanol Sectorsong LiNo ratings yet
- مواد الأيض الثانويDocument22 pagesمواد الأيض الثانويMarwa BelaNo ratings yet
- Impression Materials New EraDocument116 pagesImpression Materials New EraKumar A Mds100% (1)
- Contoh Soal BingDocument3 pagesContoh Soal Bingaristi dewantiNo ratings yet
- BIOC201 - Acetylation of Sugars (Prepared by Nothando Gasa)Document10 pagesBIOC201 - Acetylation of Sugars (Prepared by Nothando Gasa)Sydney McDonaldNo ratings yet
- A GRADE 8 ACP Q1M5 Teacher Copy TLE Final LayoutDocument32 pagesA GRADE 8 ACP Q1M5 Teacher Copy TLE Final LayoutMerjulyn AsilumNo ratings yet
- Prohibited and Restricted Substances: Suppliers GuideDocument7 pagesProhibited and Restricted Substances: Suppliers GuideAlprecoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering Laboratory SeriesDocument38 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Laboratory SeriesHaqeem HNo ratings yet
- Schedule: Issue Date: 29 September 2017 Valid Until: 8 December 2020Document16 pagesSchedule: Issue Date: 29 September 2017 Valid Until: 8 December 2020ediasianagriNo ratings yet
- Artigo Macauba PCADocument14 pagesArtigo Macauba PCAjuventude JuventudePIBFNo ratings yet
- Clean, Sanitize and Store Kitchen Tools andDocument20 pagesClean, Sanitize and Store Kitchen Tools andReyna Marke Buhawe100% (2)
- Lurgi Sulfur ManagementDocument8 pagesLurgi Sulfur ManagementRamon IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Midland STANDARDDocument63 pagesMidland STANDARDmhaioocNo ratings yet
- Austin's School District Initial Evaluation About Coal Tar Sealers at SchoolsDocument10 pagesAustin's School District Initial Evaluation About Coal Tar Sealers at SchoolsTom EnnisNo ratings yet
- Insect-Resistant Packaging: Michael A. Mullen Jade M. Vardeman Jim BagwellDocument8 pagesInsect-Resistant Packaging: Michael A. Mullen Jade M. Vardeman Jim BagwellYuki CabilingNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry HL IA (MAY 2021)Document13 pagesIB Chemistry HL IA (MAY 2021)Insiyah Huzefa BasraiNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab Reviewer Midterm 1st SemDocument26 pagesAnaphy Lab Reviewer Midterm 1st SemSeaniah Faith ApolonaNo ratings yet
- Fabrication and Electrical Measurements of Mis Based Memory DevicesDocument5 pagesFabrication and Electrical Measurements of Mis Based Memory DevicesErick OpiyoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of Mentha SpeciesDocument36 pagesChemical Composition and Biological Activities of Mentha SpeciesMARIA ANGGIE CANTIKA DEWANINo ratings yet
- EN71part 9 - 2005Document1 pageEN71part 9 - 2005sudhirkumarmbaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Written Examination 2Document17 pagesChemistry: Written Examination 2luctonNo ratings yet
- ERT CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science ChemistryDocument8 pagesERT CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science ChemistryshanthaNo ratings yet
- VM 032 - VM 068 - VM 100 - VM 150 - AuDocument9 pagesVM 032 - VM 068 - VM 100 - VM 150 - AuMariana CardosoNo ratings yet
- Materials Used in Making DocumentsDocument23 pagesMaterials Used in Making Documentslovelytrazona7No ratings yet
- Form Four Holiday Package-1Document25 pagesForm Four Holiday Package-1Angelista ErasmiNo ratings yet