Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Dosage Calculations
Drug Dosage Calculations
Uploaded by
Nicholle VelosoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Dosage Calculations
Drug Dosage Calculations
Uploaded by
Nicholle VelosoCopyright:
Available Formats
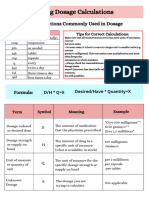
DRUG DOSAGE CALCULATIONS ✓ Formula,
✓ Proportion
Terms & Terminology
✓ Dimensional Analysis
FLOW RATE ➢ No one method is best for solving every type of problem.
Several good approaches are available, however, one of
is the volume per unit time usually expressed as ml/hr. can be the best in dimensional analysis
ml/min or ml/sec.
Rule #1 in drug calculations - STICK TO ONE METHOD!!!
DRIP RATE
Routes
is the number of drops per unit of time usually
IM– Intramuscular
expressed as drops/min(dpm).
IO– Intraosseous
DOSE
IV– Intravenous
amount of drug per unit time given to the patient expressed as
mg/min, g/hr, or IU/min. IVP– Intravenous Push
CONCENTRATION ID – Intradermal
amount of the drug in a given volume usually expressed as IN – Intranasal
mg/ml, g/l, or mIU/ml.
IP – Intraperitoneal
DROP FACTOR
IT – Intrathecal
is the number of drops per unit volume. Expressed as
IVPB – Intravenous piggyback
drops/ml.
p.o – By mouth
TITRATION
SC / SubQ – Subcutaneous
adjustment of the IV medication dosage within prescribed
parameters to achieve the desired effects. SL – Sublingual
Measurement Systems top. – Topical
Three main types: vag. – Vaginally
1. Apothecary Measurements
2. Household
3. Metric Kg – kilogram
gm – gram
mg – milligram
mcg – microgram
mEq - milliequivalent
L – liter
mL – milliliter
µg – microgram
gtt – drop
µgtt – micro drop
Calculation Methods tbsp – tablespoon
Various methods are used for solving medication calculation tsp – teaspoon
The most common methods are: mg/dL – milligrams per deciliter
Body Surface Area
Use either a normogram chart to fine the body surface area or
Recommended Volume for Administration Per Sites:
➢ Intradermal = 0.1 - 0.5 ml (allergy testing)
➢ Subcutaneous injection = 0.5 - 1.0 ml per site
➢ Intramuscular injection = 2.5 - 3.0 ml per site (1 ml in the
deltoid)
➢ IV injection (IV push) = 1 – 60 ml
Conversions
You might also like
- Drug CalculationDocument24 pagesDrug Calculationjinshajoseph05100% (7)
- Metric System Common Measure Conversion Factor Common UseDocument4 pagesMetric System Common Measure Conversion Factor Common UseMarielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Nursingbundleson - Compressed 4 15Document12 pagesNursingbundleson - Compressed 4 15ronique reidNo ratings yet
- Lab Units - AbbreviationsDocument2 pagesLab Units - Abbreviationsbilashdon100% (1)
- Dosage Calculation Tutorial 1-3-08Document5 pagesDosage Calculation Tutorial 1-3-08Jeremy TamisieaNo ratings yet
- A Nurse's Ultimate Guide To Accurate Drug Dosage Calculations - NurseBuffDocument19 pagesA Nurse's Ultimate Guide To Accurate Drug Dosage Calculations - NurseBuffalbin parajado100% (2)
- Self Compacting ConcreteDocument16 pagesSelf Compacting ConcreteAnubhab GhoshNo ratings yet
- Medication Dosage and CalculationsDocument32 pagesMedication Dosage and CalculationsGavinTLDNo ratings yet
- Drug Calculation Exercises Workbook - Student Copy (Campus Week 2)Document15 pagesDrug Calculation Exercises Workbook - Student Copy (Campus Week 2)shakyaNo ratings yet
- General Rules For Units: Infusion Rate CalculationsDocument3 pagesGeneral Rules For Units: Infusion Rate CalculationsVicky100% (2)
- Computation For Medication and Iv RegulationDocument14 pagesComputation For Medication and Iv RegulationKarlo BallonNo ratings yet
- IV Drip Rate CalculationsDocument3 pagesIV Drip Rate CalculationsMimi DenilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Dose CalculationsDocument6 pagesDrug Dose Calculationsmikrobyo_ng_wmsu100% (1)
- Health Calculations For NursesDocument7 pagesHealth Calculations For NurseskimberlyvalentineNo ratings yet
- Computation of Drugs and Solutions Edited Version 2014 MVIDocument27 pagesComputation of Drugs and Solutions Edited Version 2014 MVINoel V. ImmaculataNo ratings yet
- Drug Dose Calculation Using MeasurementsDocument17 pagesDrug Dose Calculation Using MeasurementsPEMAR ACOSTANo ratings yet
- Fluid RequiermentDocument14 pagesFluid RequiermentKrini TandelNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Recommendations: For IMRT Planning: ICRU 83Document22 pagesConcepts and Recommendations: For IMRT Planning: ICRU 83Bijay Kumar BarikNo ratings yet
- Caregiving: Department of Education - Republic of The PhilippinesDocument17 pagesCaregiving: Department of Education - Republic of The PhilippinesRina Vianney De Leon83% (6)
- Pharma Lesson 4Document2 pagesPharma Lesson 4BabyJane GRomeroNo ratings yet
- Acceptable Prescribing Terms and Abbreviations PosterDocument1 pageAcceptable Prescribing Terms and Abbreviations PosterAdelNo ratings yet
- Lanyard AbbreviationsDocument2 pagesLanyard AbbreviationsShreya AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Definition of DrugsDocument9 pagesDefinition of DrugsSanhati Ghosh BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Drug Calculations For Nurses A Step-by-Step Approa... - (Chapter 8 Infusion Rate Calculations)Document22 pagesDrug Calculations For Nurses A Step-by-Step Approa... - (Chapter 8 Infusion Rate Calculations)HarjotBrarNo ratings yet
- WK3 Dosage and ComputationDocument3 pagesWK3 Dosage and Computationcaitie miracleNo ratings yet
- Household MeasurementDocument4 pagesHousehold MeasurementYna EstabilloNo ratings yet
- PN Study Guide Nu4008Document40 pagesPN Study Guide Nu4008Alison Gifford100% (1)
- SOP TEC 15 Calculating Drug Doses v1.1Document2 pagesSOP TEC 15 Calculating Drug Doses v1.1rajenderizeNo ratings yet
- Dosing Protocol RPeducationDocument28 pagesDosing Protocol RPeducationbala muruganNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage Calculation ReviewerDocument3 pagesDrug Dosage Calculation ReviewerLeah Abdul KabibNo ratings yet
- (Pha6113 Lec) 1ST Shifting ReviewerDocument28 pages(Pha6113 Lec) 1ST Shifting ReviewerAndrei RoqueNo ratings yet
- 107.11.1 GlycopeptidePK - 20181101 - GIOCP - Case - Part2Document4 pages107.11.1 GlycopeptidePK - 20181101 - GIOCP - Case - Part2ft84nzzc92No ratings yet
- Microcontroller Based Anesthesia InjectorDocument9 pagesMicrocontroller Based Anesthesia InjectorMohita Mohi100% (1)
- 3M Med Math Chapters 7 8 Special Types of IV Calculations Dosage Problems For Infants and ChildrenDocument33 pages3M Med Math Chapters 7 8 Special Types of IV Calculations Dosage Problems For Infants and Childrenvjson13No ratings yet
- Dosage CalculationsDocument6 pagesDosage CalculationspdfsellssNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Based Anesthesia Injector: Embedded SystemsDocument9 pagesMicrocontroller Based Anesthesia Injector: Embedded Systemslucky jNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Dosage Calculation 2020Document25 pagesLesson 4 - Dosage Calculation 2020Ford SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Computation of Drugs and Solutions Edited Version 2014 MVIDocument27 pagesComputation of Drugs and Solutions Edited Version 2014 MVIOpaque ITNo ratings yet
- 10 Pharmaceutical Calculations inDocument27 pages10 Pharmaceutical Calculations inTilaye GebruNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Agilia SP TIVA ID: Pt. Fresenius Kabi IndonesiaDocument1 pageSpesifikasi Agilia SP TIVA ID: Pt. Fresenius Kabi IndonesiaSajar BudiNo ratings yet
- Dosage Handouts 2020 2021Document16 pagesDosage Handouts 2020 2021chrystan maconNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Dosage Calculation GuideDocument20 pagesPharmacology - Dosage Calculation GuideKyla Avila TorrevillasNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapies Nitrates Comparison ChartDocument7 pagesCardiovascular Drugs and Therapies Nitrates Comparison ChartArvi J-idNo ratings yet
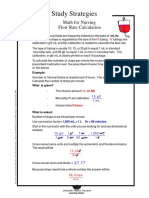
- Math Study Strategies: Math For Nursing Flow Rate CalculationDocument1 pageMath Study Strategies: Math For Nursing Flow Rate CalculationVette Angelikka Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- The Metric System and Drug Dosage Calculations: ObjectivesDocument16 pagesThe Metric System and Drug Dosage Calculations: ObjectivesMacMacNo ratings yet
- Injectomat AgiliaDocument2 pagesInjectomat Agiliasergio ribeiroNo ratings yet
- Brown and Mulhollands Drug Calculations Ratio and Proportion Problems For Clinical Practice 12Th Edition Ann B Tritak Elmiger Full ChapterDocument60 pagesBrown and Mulhollands Drug Calculations Ratio and Proportion Problems For Clinical Practice 12Th Edition Ann B Tritak Elmiger Full Chapterstephanie.stewart777100% (4)
- Ia IjapDocument4 pagesIa IjapPharmacy On FingerTipsNo ratings yet
- Drug AdministrationDocument87 pagesDrug AdministrationMikylla MelecioNo ratings yet
- Ma M-L/T F/A M-L/T - L or M/L-T Dynes/cm G/cm-S M/L F/L M-L/T - L or M/T Fs M-L /TDocument2 pagesMa M-L/T F/A M-L/T - L or M/L-T Dynes/cm G/cm-S M/L F/L M-L/T - L or M/T Fs M-L /TGNCDWNo ratings yet
- Common Conversions: Methods of CalculationDocument13 pagesCommon Conversions: Methods of CalculationNormala Macabuntal SaripadaNo ratings yet
- Pharm Cal Dom 1 CeeDocument9 pagesPharm Cal Dom 1 CeeJoanna MalizaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Calculations 2Document9 pagesClinical Calculations 2evacawleyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Calculations 1Document8 pagesClinical Calculations 1evacawleyNo ratings yet
- ZUG MMP12 DetailedSpecsBrochureDocument9 pagesZUG MMP12 DetailedSpecsBrochureasokanenNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic Models MultiDocument79 pagesPharmacokinetic Models Multiuday sainiNo ratings yet
- 2 Defining OperationallyDocument15 pages2 Defining OperationallyssskguNo ratings yet
- PHCL Midterms - Lesson 1 (Calculation of Doses General Consideration)Document4 pagesPHCL Midterms - Lesson 1 (Calculation of Doses General Consideration)Lazaro, Javen Andrie A.No ratings yet
- Chromosomalabnormalities 150413160537 Conversion Gate01Document25 pagesChromosomalabnormalities 150413160537 Conversion Gate01John MccartneyNo ratings yet
- Rhetorical AnalysisDocument7 pagesRhetorical Analysisapi-402052001No ratings yet
- Itf TCCDocument29 pagesItf TCCRalf TholenNo ratings yet
- Types of Heart DiseasesDocument4 pagesTypes of Heart DiseaseslalalallaNo ratings yet
- Msds o Xylene PDFDocument6 pagesMsds o Xylene PDFPriska Dewi AnjarsariNo ratings yet
- Cox - 1975 - Overhead-Line PracticeDocument9 pagesCox - 1975 - Overhead-Line PracticePoleomanNo ratings yet
- 0996 en 0209Document8 pages0996 en 0209fagnermacedosaNo ratings yet
- Bercham 7Document14 pagesBercham 7Kent WaiNo ratings yet
- FMT - Chap 9 - SolutionsDocument6 pagesFMT - Chap 9 - SolutionsVũ Hương ChiNo ratings yet
- SONEX Do Wing - Tip - Install Fiberglass Wing TipsDocument1 pageSONEX Do Wing - Tip - Install Fiberglass Wing TipsNZHHNo ratings yet
- PpeDocument7 pagesPpeylaala8010No ratings yet
- Gardacid X: Safety Data SheetDocument6 pagesGardacid X: Safety Data Sheetbabu541No ratings yet
- R XPT PDFDocument11 pagesR XPT PDFIvan GrkajacNo ratings yet
- REport STP P.S PadiDocument9 pagesREport STP P.S PadiESAKKI RAJANNo ratings yet
- Medication Information For Parents and Teachers: Carbamazepine-Tegretol, Carbatrol, Epitol, Equetro, Tegretol XRDocument8 pagesMedication Information For Parents and Teachers: Carbamazepine-Tegretol, Carbatrol, Epitol, Equetro, Tegretol XRMonique WrightNo ratings yet
- Pump Suction Pipe Design ConsiderationsDocument7 pagesPump Suction Pipe Design ConsiderationsAbdulrahman Al HuribyNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Harzards at HomeDocument8 pagesDifferent Types of Harzards at HomeApril Jean Latosa PiscosNo ratings yet
- Normas InternacionalesDocument3 pagesNormas Internacionalesmalota2108No ratings yet
- Npi Format For Rle 1Document9 pagesNpi Format For Rle 1Patricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Fire Insurance Policy: ImportantDocument13 pagesFire Insurance Policy: ImportantNilesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Jaro Leyte - The Municipality of JARO Is A 3 Class Municipality in LEYTE, PHILIPPINES and Has 46 Barangays.Document4 pagesJaro Leyte - The Municipality of JARO Is A 3 Class Municipality in LEYTE, PHILIPPINES and Has 46 Barangays.Jezreel Retalo ColladoNo ratings yet
- Habitat Influences On Urban Avian AssemblagesDocument21 pagesHabitat Influences On Urban Avian AssemblagesMolina ThirumalNo ratings yet
- Using Drone: Ils / Vor / PapiDocument28 pagesUsing Drone: Ils / Vor / Papifika puteraNo ratings yet
- Kalwall BrochureDocument12 pagesKalwall BrochureMike VetzalNo ratings yet
- SRP DraftDocument6 pagesSRP Draftapi-280391204No ratings yet
- Colonic Polyps and Polyposis SyndromesDocument30 pagesColonic Polyps and Polyposis SyndromesIndhumathiNo ratings yet
- Boilers Classifications PDFDocument50 pagesBoilers Classifications PDFSYED FADZIL SYED MOHAMEDNo ratings yet
- Muscle - Re EducationDocument20 pagesMuscle - Re EducationRam RamNo ratings yet
- The Spice House Beverage MenuDocument7 pagesThe Spice House Beverage MenuTan MaiNo ratings yet