Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Extracted Pages From BIECh12 - 3
Uploaded by
Kareem TalaatOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Extracted Pages From BIECh12 - 3
Uploaded by
Kareem TalaatCopyright:
Available Formats
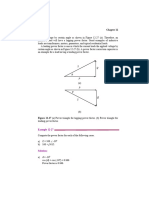
Fundamentals of Alternating Current 43
load is converting all the power consumed into real work. However, power factor
of 0.0 indicates that the load is not producing any real work. In general, the power
factor of a load will be between 0.0 and 1.0.
Because only the resistive portion of an AC circuit dissipates power, we are
interested in the resistive part of the impedance. The ratio of the circuit resistance
to the amplitude of the circuit impedance is called power factor. This is expressed
mathematically as
S
Q
θ
P
(a)
Z
X
θ
R
(b)
Figure 12-26 (a) Power triangle. (b) Impedance triangle.
R
Power factor = (12.43)
Z
According to Equation (12.28), the impedance of an AC circuit is resistive ( Z
= R). Therefore, the power factor is 1. When the impedance is reactive (Z = jX),
the power factor is zero. In general, the power factor is related to the phase angle
through the impedance diagram (Figure 12-26). This is expressed as
Power factor = cos (θ ) = R/ Z
12.9.3 Leading and Lagging Power Factor
A load in which the current lags the applied voltage is said to have a lagging
power factor. However, a load in which the current leads the applied voltage is
said to have a leading power factor. The current in an inductive load will lag the
You might also like
- Extracted Pages From BIECh12 - 4Document1 pageExtracted Pages From BIECh12 - 4Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From BIECh12 - 2Document1 pageExtracted Pages From BIECh12 - 2Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- EE301 Lesson 24 AC Power and PWR TriangleDocument23 pagesEE301 Lesson 24 AC Power and PWR TriangleJidi rectorNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis MCQ For Apgenco&aptranco PreparationDocument42 pagesNetwork Analysis MCQ For Apgenco&aptranco PreparationAkhil Gorla73% (22)
- GATE EE 2001 Actual Paper - 2Document18 pagesGATE EE 2001 Actual Paper - 2Hima SagarNo ratings yet
- Parallel AC Circuits SPLPDocument47 pagesParallel AC Circuits SPLPJoey TelinNo ratings yet
- EeDocument29 pagesEeravi16sb4531No ratings yet
- CH 11Document44 pagesCH 11toalomari0No ratings yet
- Week 1 2Document37 pagesWeek 1 2basit qureshiNo ratings yet
- AC Power AnalysisDocument19 pagesAC Power AnalysisMD EM MASUMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Steady State Single Phase AC Circuit Analysis Part 2 1Document19 pagesChapter 3 Steady State Single Phase AC Circuit Analysis Part 2 1temesgen adugnaNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 242 Experiment 3Document6 pages242 Experiment 3Jaymarkpperprn TimbalNo ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument11 pagesAlternating Currentjayaditya soniNo ratings yet
- Single Phase ParalelDocument17 pagesSingle Phase ParalelFaris RiyadiNo ratings yet
- Power TriangleDocument7 pagesPower TriangleKrishna MurariNo ratings yet
- Gate 2015 PDFDocument81 pagesGate 2015 PDFsameer meshramNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel Ac Networks RLCDocument19 pagesSeries and Parallel Ac Networks RLCSheikh RaselNo ratings yet
- Topic Refresher:: The Power TriangleDocument1 pageTopic Refresher:: The Power Triangleradhikadikshit9No ratings yet
- Chap 3 SinglePhase AC CctsDocument20 pagesChap 3 SinglePhase AC CctsbackuponecolosoNo ratings yet
- Passive Circuit ElementsDocument5 pagesPassive Circuit ElementsYumyoya KarmolchanokNo ratings yet
- AC BridgesDocument31 pagesAC BridgesSean100% (1)
- Exp - No.5 - Frequency Respoonse of RC An RLC CircuitDocument3 pagesExp - No.5 - Frequency Respoonse of RC An RLC Circuitforest lifeNo ratings yet
- 02 - Chap 2 - AC Power Analysis - 2021CDocument68 pages02 - Chap 2 - AC Power Analysis - 2021CZhong Kiat TehNo ratings yet
- Typical Questions & AnswersDocument170 pagesTypical Questions & AnswersvishwanathbrungiNo ratings yet
- ELE 201 - RC CircuitsDocument26 pagesELE 201 - RC CircuitsIB MasterNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument2 pagesCurrent ElectricityChesterNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint PresentationDocument21 pagesPowerPoint PresentationMrigankaiitkNo ratings yet
- Simple and Accurate Formula For Calculating The Conduction Angle of Single Phase RectifierDocument3 pagesSimple and Accurate Formula For Calculating The Conduction Angle of Single Phase RectifierMichele Oconnor0% (1)
- Network SolDocument189 pagesNetwork Solsandeep12911050% (2)
- Week 4 - Instructional Module - EE221 - EE222Document11 pagesWeek 4 - Instructional Module - EE221 - EE222AB CEDENo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Presentation - OrganizedDocument21 pagesPowerPoint Presentation - OrganizedMrigankaiitkNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 - AC Circuits - MG HusseinDocument20 pagesChapter-3 - AC Circuits - MG Husseinضياء بن احمد الكباريNo ratings yet
- 8 Alternating-Currentexericse PDFDocument51 pages8 Alternating-Currentexericse PDFpranjal singhNo ratings yet
- 8 Alternating-Currentexericse PDFDocument51 pages8 Alternating-Currentexericse PDFIndranilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - AC ELECTRICITY PDFDocument140 pagesChapter 5 - AC ELECTRICITY PDFleogarybonNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument18 pagesProblem SetDWARAM VENKATA SUBBA REDDY 1816No ratings yet
- Worksheet (02) - Electrostatic Potential (KP)Document10 pagesWorksheet (02) - Electrostatic Potential (KP)Harish ChinthalNo ratings yet
- Calculating Loadability Limits of Distance RelaysDocument14 pagesCalculating Loadability Limits of Distance RelaysYrene De Jesus Alvarez VasquezNo ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument5 pagesAlternating CurrentShivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Exp 9Document6 pagesExp 93a2dNo ratings yet
- Ac QuantitiesDocument7 pagesAc Quantitiessrinivas100% (1)
- Impedance and Admittance and PowerDocument35 pagesImpedance and Admittance and PowerSubhadeep BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Network and Transmission Lines 100 MCQDocument21 pagesNetwork and Transmission Lines 100 MCQNandakumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Power in Ac Circuits: Resistive LoadDocument8 pagesPower in Ac Circuits: Resistive LoadMunyaradzi zonkeNo ratings yet
- 6.013 Electromagnetics and Applications: R + + V (T) Z 100 - V (T) Au (T) Z DDocument3 pages6.013 Electromagnetics and Applications: R + + V (T) Z 100 - V (T) Au (T) Z DMichael Medina FloresNo ratings yet
- RL Circuit Transient Analysis RC & RLC Transient AnalysisDocument22 pagesRL Circuit Transient Analysis RC & RLC Transient AnalysisSarvesh AhujaNo ratings yet
- Q. 1 - Q. 25 Carry One Mark Each.: GATE 2015 Set1 Electrical - EeDocument14 pagesQ. 1 - Q. 25 Carry One Mark Each.: GATE 2015 Set1 Electrical - EeVidhyaNo ratings yet
- 2 TransientsDocument22 pages2 Transientsabhijeet rastogiNo ratings yet
- RL Circuit Transient Analysis RC & RLC Transient AnalysisDocument22 pagesRL Circuit Transient Analysis RC & RLC Transient AnalysisSarvesh AhujaNo ratings yet
- Power Formula SheetDocument3 pagesPower Formula SheetyeeeNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical by FarhanaDocument28 pagesBasic Electrical by FarhanaEr Rouf UlAlam BhatNo ratings yet
- Impedance Measurement Instruments: 26.1. Introduction To Impedance MeasurementsDocument26 pagesImpedance Measurement Instruments: 26.1. Introduction To Impedance MeasurementsHeiner Farid Castillo AvellaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering (PDFDrive) (099-100)Document2 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering (PDFDrive) (099-100)Wail IrwanNo ratings yet
- Qualifier 2018Document12 pagesQualifier 2018Karishtain NewtonNo ratings yet
- AC Quiz KeyDocument5 pagesAC Quiz KeyAgrima PrasadNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument53 pagesRectifierYogi Bekti P100% (1)
- 12th Physics MCQs (CH 7) NCRTDocument7 pages12th Physics MCQs (CH 7) NCRTRock StudiesNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Ac Power - 1Document1 pageAc Power - 1Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Operation:-: ObservationDocument1 pageOperation:-: ObservationKareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- F= d p dt, p is the momentum of a particle acted upon by force F - The momentum p is proportional to the velocity υ of a particle through the relationship p = m υ ,Document1 pageF= d p dt, p is the momentum of a particle acted upon by force F - The momentum p is proportional to the velocity υ of a particle through the relationship p = m υ ,Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Ac Power - 5Document1 pageAc Power - 5Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Educational Requirements: X Medical Physics: A Specialty and ProfessionDocument1 pageEducational Requirements: X Medical Physics: A Specialty and ProfessionKareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Examination System 1. Database Design and Implementation For General ChemistryDocument1 pageMultiple Choice Examination System 1. Database Design and Implementation For General ChemistryKareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Examination System 1. Database Design and Implementation For General ChemistryDocument1 pageMultiple Choice Examination System 1. Database Design and Implementation For General ChemistryKareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Database Design: Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 5, July-December 2004 P. 18-33Document1 pageDatabase Design: Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 5, July-December 2004 P. 18-33Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 5, July-December 2004 P. 18-33Document1 pageLeonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 5, July-December 2004 P. 18-33Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Examination System 1. Database Design and Implementation For General ChemistryDocument1 pageMultiple Choice Examination System 1. Database Design and Implementation For General ChemistryKareem TalaatNo ratings yet