Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laboratory 1 DMFD 2413 2019-2020
Uploaded by
Mohd Najib Ali MokhtarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory 1 DMFD 2413 2019-2020
Uploaded by
Mohd Najib Ali MokhtarCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory 1
FACULTY OF MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
FLUID POWER
DMFD 2413 SEMESTER 1 SESSION 2019/2020
1.0 Objective
At the end of the experiment, students should be able to:
a) To assemble basic pneumatic circuits that extend and retract for single as well as double
acting cylinder operation.
2.0 Learning Outcomes
Learning Outcomes (LO) Program Outcomes (PO)
LO2: Recognize the basic components and PO2: Identify and analyse well-defined
systems used in fluid power technologies in manufacturing engineering problems.
terms of its construction, symbol and
principle
3.0 Background
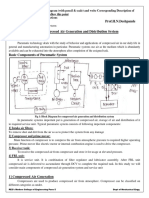
A pneumatic system is a system that uses compressed air to transmit and control energy.
Air is readily abundant & can be exhausted to the atmosphere after a task is completed.
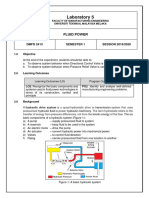
The six basic components of a pneumatics system (Figure 1):-
a) An air tank – store compressed air
b) A compressor – compress air from the atmosphere
c) An electric motor – drive the compressor
d) An actuator – convert air pressure into mechanical force
e) Valve – to control air direction
f) Piping – carries pressurized air from one location to another
Figure 1: A complete pneumatic system
4.0 Pneumatic Components
Identify the pneumatic components below which will be used in this exercise.
Table 1: List of components for Task 1
Part No. Pneumatic Component Quantity
1 Air Pressure supply 2
2 Start/Stop Push Button 1
3 3/2 Directional Control Valve 1
4 Flow Control Valve 1
5 Single Acting Cylinder 1
Table 2: List of components for Task 2
Part No. Pneumatic Component Quantity
1 Air Pressure supply 3
2 Start/Stop Push Button 2
3 5/2 Directional Control Valve 1
4 Flow Control Valve 2
5 Double Acting Cylinder 1
Table 3: List of components for Task 3
Part No. Pneumatic Component Quantity
1 Air Pressure supply 2
2 Start/Stop Push Button 2
3 OR Valve 1
4 Flow Control Valve 1
5 Single Acting Cylinder 1
Table 4: List of components for Task 4
Part No. Pneumatic Component Quantity
1 Air Pressure supply 2
2 Start/Stop Push Button 2
3 3/2 Directional Control Valve 1
4 Flow Control Valve 1
5 Single Acting Cylinder 1
5.0 Task
Task 1: Using the given components (Table 1) and layout (Figure 2):
a) Design a schematic circuit which will operate a single acting cylinder with speed control
for extension.
b) Connect components to match the schematic diagram.
c) Draw the pneumatic circuit diagram complete with appropriate symbols.
d) Answer questions regarding the circuit operation in U-learn.
Figure 2: Components layout for Task 1
Task 2: Using the given components (Table 2) and layout (Figure 3):
a) Design a schematic circuit which will operate a double acting cylinder with speed
control for extension and retraction stroke.
b) Connect components to match the schematic diagram.
c) Draw the pneumatic circuit diagram complete with appropriate symbols.
d) Answer questions regarding the circuit operation in U-learn.
Figure 3: Components layout for Task 2
Task 3: Using the given components (Table 3):
a) Design a schematic OR circuit which will operate a single acting cylinder with speed
control for extension.
b) Connect components to match the schematic diagram.
c) Draw the pneumatic circuit diagram complete with appropriate symbols.
d) Answer questions regarding the circuit operation in U-learn.
Task 4: Using the given components (Table 4):
a) Design a schematic AND circuit which will operate a double acting cylinder with speed
control for extension where 1 push button is use for the power supply and another
push button is to give signal to the Directional Control Valve.
b) Connect components to match the schematic diagram.
c) Draw the pneumatic circuit diagram complete with appropriate symbols.
d) Answer questions regarding the circuit operation in U-learn.
6.0 Conclusion
Conclude what you have learned from this experiment.
7.0 References
a) Anthony Esposito, Fluid Power with Applications, 7th Edition, Prentice Hall, 2009
b) Pneumatic Systems, HKEdCity, retrieved from www.resources.hkedcity.net
You might also like
- Laboratory 2 DMFD 2413 2019-2020Document4 pagesLaboratory 2 DMFD 2413 2019-2020Mohd Najib Ali MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 5 DMFD 2413 2019-2020Document3 pagesLaboratory 5 DMFD 2413 2019-2020Mohd Najib Ali MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Mechatronic Lab ManualDocument23 pagesMechatronic Lab ManualTeaching ClubNo ratings yet
- Basic Pure Pneumatic Circuit Design: Experiment: 1 Title: Duration: 2 Hours: 1 0F 3Document3 pagesBasic Pure Pneumatic Circuit Design: Experiment: 1 Title: Duration: 2 Hours: 1 0F 3shirleyna saraNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Pneumatic SystemDocument13 pagesLab 1 - Pneumatic SystemSiti SarahNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Report Mem 665 1Document13 pagesPneumatic Report Mem 665 1Nazif NazriNo ratings yet
- Lab No 2 - Logic Functions - AND ORDocument5 pagesLab No 2 - Logic Functions - AND ORMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- Technical Report 1Document19 pagesTechnical Report 1jaigemuk0% (1)
- Midterm Project - Design and LayoutDocument8 pagesMidterm Project - Design and Layoutneil palmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Pneumatics: Module 5: Double Acting CylinderDocument14 pagesBasic Pneumatics: Module 5: Double Acting Cylinderاحمد السيدNo ratings yet
- Lab No 4 - Speed Control of Double Acting CylindersDocument6 pagesLab No 4 - Speed Control of Double Acting CylindersMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- Lab No 4 - Speed Control of Double Acting Cylinders-1Document6 pagesLab No 4 - Speed Control of Double Acting Cylinders-1HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Design of Simple Pneumatics SystemsDocument5 pagesDesign of Simple Pneumatics SystemsRiya JadhavNo ratings yet
- Ast Act No.06 (Rivera)Document3 pagesAst Act No.06 (Rivera)MARY GRACE CAGBABANUANo ratings yet
- JKM Pneumatic CIRCUIT SystemDocument50 pagesJKM Pneumatic CIRCUIT SystembeselamuNo ratings yet
- ME 3242 1 Pneumatic Sequential Circuits: Location: (E2 01 02)Document7 pagesME 3242 1 Pneumatic Sequential Circuits: Location: (E2 01 02)Genna NgNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Module2 Student VersionDocument13 pagesHydraulics Module2 Student VersionvozoscribdNo ratings yet
- CD180053 Bda18301 ReportDocument62 pagesCD180053 Bda18301 ReportAhmad FaidhiNo ratings yet
- Mee2025 Fps ManualDocument27 pagesMee2025 Fps ManualHarrish dhakshinamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Circuit Design AnalysisDocument7 pagesPneumatic Circuit Design AnalysismebrahtuNo ratings yet
- Fluid Automation Example of Exam 5Document1 pageFluid Automation Example of Exam 5Daniel Andres Montoya EspinosaNo ratings yet
- 2.1.1 The Basic of Pneumatic SystemDocument4 pages2.1.1 The Basic of Pneumatic SystemmorolosusNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document3 pagesActivity 2ron Joshua QuirapNo ratings yet
- V2 EXP2 Logic Valve and Sequence Control For Multiple Cylinder OperationDocument12 pagesV2 EXP2 Logic Valve and Sequence Control For Multiple Cylinder OperationGeetha Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Excercise 16Document8 pagesLaboratory Excercise 16Fernando Magallanes Jr.No ratings yet
- Pneumatic Schematics: Using Graphic Symbols To Illustrate Basic Circuit DesignsDocument45 pagesPneumatic Schematics: Using Graphic Symbols To Illustrate Basic Circuit DesignsAhmed AhmedNo ratings yet
- JJ512 Pneumatic PH 4 Lab SheetDocument4 pagesJJ512 Pneumatic PH 4 Lab SheetIjal HaizalNo ratings yet
- Exp3 - Air Pressure ControlDocument8 pagesExp3 - Air Pressure ControlDon LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Pneumatic FullDocument22 pagesLab 1 Pneumatic Fullbella100% (12)
- Lab No 1 - Direct and Indirect Control of CylindersDocument5 pagesLab No 1 - Direct and Indirect Control of CylindersMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document4 pagesActivity 3ron Joshua QuirapNo ratings yet
- Lab No 3 - Pressure Dependent Control and Time-Delay ValveDocument5 pagesLab No 3 - Pressure Dependent Control and Time-Delay ValveHuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Abu Dhabi Polytechnic Hydraulics Oct (Emex 286)Document9 pagesAbu Dhabi Polytechnic Hydraulics Oct (Emex 286)مريم التميميNo ratings yet
- Lab No 3 - Pressure Dependent Control and Time-Delay ValveDocument5 pagesLab No 3 - Pressure Dependent Control and Time-Delay ValveMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- V2 EXP2 Logic Valve and Sequence Control For Multiple Cylinder OperationDocument12 pagesV2 EXP2 Logic Valve and Sequence Control For Multiple Cylinder OperationJane Ruby GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Module 2 (LAB)Document5 pagesModule 2 (LAB)alli latifNo ratings yet
- Appendix C - CommsDocument12 pagesAppendix C - CommsBryan NadimpallyNo ratings yet
- Exp No2Document2 pagesExp No2PATAN ASIF KHAN STUDENT - MECHNo ratings yet
- Pneumatics ManualDocument19 pagesPneumatics ManualAditya PratapNo ratings yet
- 4 Principles of Pneumatic ControlDocument13 pages4 Principles of Pneumatic ControlAfatih As-SalimNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Control System-EDocument15 pagesPneumatic Control System-EmohamedNo ratings yet
- EE052 Pneumatic PR InstDocument75 pagesEE052 Pneumatic PR InstSameera KodikaraNo ratings yet
- Operator's Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and TroubleshootingFrom EverandOperator's Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Labsheet MifzalarifDocument11 pagesLabsheet MifzalarifMeefzal ArifNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Schematics: Using Graphic Symbols To Illustrate Basic Circuit DesignsDocument45 pagesPneumatic Schematics: Using Graphic Symbols To Illustrate Basic Circuit DesignsayaNo ratings yet
- Cooking ManualDocument12 pagesCooking ManualathreyanjaneyaNo ratings yet
- 5-EM-A2.1-M-BAJU-001-D Governor System Commissioning ManualDocument33 pages5-EM-A2.1-M-BAJU-001-D Governor System Commissioning Manualayisheshimgetinet05No ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 3 (June 2019)Document5 pagesWORKSHEET 3 (June 2019)imranNo ratings yet
- Lab 02 The Application of Pressure Relief Valve and Flow Control Valve v1Document17 pagesLab 02 The Application of Pressure Relief Valve and Flow Control Valve v1afiqcivil980No ratings yet
- Lab Manual PneumaticsDocument19 pagesLab Manual PneumaticsGautam Anikirala50% (2)
- Me6i IHP Microproject (F)Document20 pagesMe6i IHP Microproject (F)Krishnakant DhakaneNo ratings yet
- Module - Time Delay ValveDocument9 pagesModule - Time Delay ValvescribdNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam - HydraulicDocument4 pagesMidterm Exam - HydraulicIVÁN ARAYA100% (2)
- ET 4850 Fluid Power Lab 5Document3 pagesET 4850 Fluid Power Lab 5Federico ComaschiNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Actuators 1: Needs, Reliability and Hydraulic Power SolutionsFrom EverandAerospace Actuators 1: Needs, Reliability and Hydraulic Power SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in Mechanical Engineering: Decision Making, Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics and Heat TransferFrom EverandCase Studies in Mechanical Engineering: Decision Making, Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics and Heat TransferRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Introduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15From EverandIntroduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15No ratings yet
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGFrom EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNo ratings yet
- Suzuki Jimny 4WD SystemDocument29 pagesSuzuki Jimny 4WD SystemRuben Michel67% (9)
- Jd-800e (#122-, Yh70) ManualDocument166 pagesJd-800e (#122-, Yh70) ManualOrhan HasanogluNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Installation PDFDocument45 pagesCylinder Installation PDFMahdi Khanfir HachenniNo ratings yet
- Metrology and Quality Assurance Lab: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument7 pagesMetrology and Quality Assurance Lab: Department of Mechanical EngineeringAliNo ratings yet
- EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (2AZ FE) CamryDocument30 pagesEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (2AZ FE) CamryRahmat HidayatNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Inspection ChecklistDocument5 pagesSaudi Aramco Inspection Checklistnisha_khanNo ratings yet
- N XL2200 Gradall Parts 4-17Document360 pagesN XL2200 Gradall Parts 4-17PhilNo ratings yet
- Tablas de Equipos USF-22-A2Document2 pagesTablas de Equipos USF-22-A2Carlos RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of 3ph IMDocument4 pagesSpeed Control of 3ph IMKrushna PisalNo ratings yet
- Tata Motors PCBUDocument42 pagesTata Motors PCBUGirish Sp100% (1)
- Gearbox Phoenix 2 Upgrade Sundyne 40-20-26 Field Engineering BulletinDocument4 pagesGearbox Phoenix 2 Upgrade Sundyne 40-20-26 Field Engineering Bulletinjamil ahmedNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts Inventory MEADocument161 pagesSpare Parts Inventory MEAGrupo ValoracionNo ratings yet
- Motor Cat 3176-3196Document17 pagesMotor Cat 3176-3196Fabiano Oliveira67% (3)
- 544B Loader IntroductionDocument7 pages544B Loader IntroductionDenis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Wesco-Trans Part2Document2 pagesWesco-Trans Part2escoleinNo ratings yet
- Carro Bicapa (484.1100.1.15.DT#PARTSMANUAL FFD) PDFDocument32 pagesCarro Bicapa (484.1100.1.15.DT#PARTSMANUAL FFD) PDFkelly ArmasNo ratings yet
- Cummins Onan X1.7 and X2 Service Repair ManualDocument6 pagesCummins Onan X1.7 and X2 Service Repair ManualDean RimbaudNo ratings yet
- Msi30 204559,547308PDDocument382 pagesMsi30 204559,547308PDJose PereiraNo ratings yet
- Sl1, SLV: 1.1 - 11 KW, 50 HZDocument40 pagesSl1, SLV: 1.1 - 11 KW, 50 HZDasun NirmalaNo ratings yet
- Nordex N60: Long-Term Experience All Over The WorldDocument8 pagesNordex N60: Long-Term Experience All Over The WorldHung NGUYENNo ratings yet
- Cat 4100 UkDocument899 pagesCat 4100 UkAl borjaNo ratings yet
- LW0798 1Document284 pagesLW0798 1ferpimentel0590No ratings yet
- Ford Workshop Manuals - Transit 2006.5 (04.2006-) - Mechanical Repairs - 3 Powertrain - 303 Engine - 303-01B Engine - 2Document2 pagesFord Workshop Manuals - Transit 2006.5 (04.2006-) - Mechanical Repairs - 3 Powertrain - 303 Engine - 303-01B Engine - 2torrencial0% (1)
- System Operation Testing and Adjusting 3304 Vehicular EngineDocument103 pagesSystem Operation Testing and Adjusting 3304 Vehicular EngineAbdelbagi100% (2)
- Terex Ta30 Articulated Truck Parts BookDocument20 pagesTerex Ta30 Articulated Truck Parts Bookrhonda100% (54)
- Part Catalog Es22d5 Es28d5 X3engineDocument96 pagesPart Catalog Es22d5 Es28d5 X3engineSugeng Ariyadi100% (1)
- A - TH360B - CAT - Elect Schem PDFDocument4 pagesA - TH360B - CAT - Elect Schem PDFBart JohnNo ratings yet
- Catálogo Guías Bronce Aleado Aplicación-MotorDocument3 pagesCatálogo Guías Bronce Aleado Aplicación-Motorfernando yanezNo ratings yet
- Yamaha Mio Compression PressureDocument1 pageYamaha Mio Compression Pressuremotley crewzNo ratings yet
- 2021 Nissan Armada Brochure enDocument8 pages2021 Nissan Armada Brochure enYudyChenNo ratings yet