Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Infographic
Infographic
Uploaded by
kyle obozaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Infographic
Infographic
Uploaded by
kyle obozaCopyright:
Available Formats
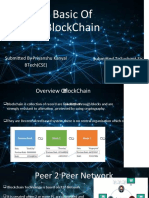
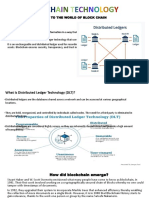
BLOCK CHAIN SYSTEM
“a distributed database that maintains a continuously growing
list of ordered records, called blocks.”
1. FACILITATING A TRANSACTION
A new transaction enters the blockchain network. All
the information that needs to be transmitted is doubly
encrypted using public and private keys.
2. VERIFICATION OF TRANSACTION
All the nodes on the network will check
for the validity of the transaction like if
a sufficient balance is available for
carrying out the transaction.
3. FORMATION OF 4. CONSENSUS
A NEW BLOCK ALGORITHM
In a typical blockchain The nodes that form a block
network there are many
will try to add the block to
nodes and many
transactions get verified at a the blockchain network to
time. Once the transaction is make it permanent. But if
verified and declared a every node is allowed to add
legitimate transaction, it will
blocks in this manner then it
be added to the mempool.
All the verified transactions will disrupt the working of
at a particular node form a the blockchain network.
mempool and such multiple
mempools form a block.
5. ADDITION OF THE NEW BLOCK TO
THE BLOCKCHAIN:
After the newly created block has got its hash value and is authenticated, now it
is ready to be added to the blockchain. In every block, there is a hash value of
the previous block and that is how the blocks are cryptographically linked to
each other to form a blockchain. A new block gets added to the open end of the
blockchain.
6. TRANSACTION COMPLETE
As soon as the block is added to the
blockchain the transaction is completed
and the details of this transaction are
permanently stored in the blockchain.
Anyone can fetch the details of the
transaction and confirm the
transaction.
You might also like
- Ustadznenen Satoshidisk BypassDocument3 pagesUstadznenen Satoshidisk BypassAdul DulaNo ratings yet
- 03 Dynamics 365 Marketing - Elevator PitchDocument3 pages03 Dynamics 365 Marketing - Elevator Pitchcursuri123712No ratings yet
- ABAP Q Bank - SR MGMT Review - WADocument194 pagesABAP Q Bank - SR MGMT Review - WANoufal Nazar0% (1)
- Project Management: For Implementation of Erp Software in IndustryDocument9 pagesProject Management: For Implementation of Erp Software in IndustryGaurav VermaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain SlidesDocument1 pageBlockchain Slideskhemj421No ratings yet
- Proof-Of-Stake Consensus Mechanisms For Future Blockchain Networks: Fundamentals, Applications and OpportunitiesDocument24 pagesProof-Of-Stake Consensus Mechanisms For Future Blockchain Networks: Fundamentals, Applications and OpportunitiesRaghu Nandan ReddyNo ratings yet
- What Is A Block Chain ?Document2 pagesWhat Is A Block Chain ?Anshul TembhareNo ratings yet
- Notes UNIT-3 and 5Document46 pagesNotes UNIT-3 and 5soman77kumarNo ratings yet
- Blockchain in E-BusinessDocument1 pageBlockchain in E-BusinessEthan MonkhouseNo ratings yet
- What Is BlockchainDocument8 pagesWhat Is BlockchainKansha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology in Online VotingDocument6 pagesBlockchain Technology in Online Votingbauer_mendoza3510No ratings yet
- Unit IDocument38 pagesUnit Isyednashita786No ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument11 pagesBlockchainJeffer MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Understanding BlockchainDocument19 pagesUnderstanding BlockchainDominick Dayton FinettiNo ratings yet
- Blockchain AnswerDocument35 pagesBlockchain AnswerGaurav ShankarNo ratings yet
- Cat 2 - Block Chain 15 Marks 1)Document6 pagesCat 2 - Block Chain 15 Marks 1)20CSR064 Natchattira T SNo ratings yet
- Use of Block Chain Technology For Subsidy Payments!Document32 pagesUse of Block Chain Technology For Subsidy Payments!Suraj Bhati'sNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument9 pagesBlock Chainkopi fompyNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology in BitcoinDocument2 pagesBlockchain Technology in BitcoinMUHAMMAD YAZIBNo ratings yet
- Unlock The Power of Blockchain - DigitalOceanDocument14 pagesUnlock The Power of Blockchain - DigitalOceanMihai TiberiuNo ratings yet
- Blockchain ImportantDocument10 pagesBlockchain Importantshuklaanshul312No ratings yet
- 3) Unit - 1 - P1 - Block Chain TechnologyDocument26 pages3) Unit - 1 - P1 - Block Chain TechnologyKeshav RaoNo ratings yet
- Block Chain GlossaryDocument16 pagesBlock Chain GlossaryJaya RoadlinesNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)Document6 pagesBlockchain: Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)Amen AbatemameNo ratings yet
- Anti-Malware With Blockchain - CSE105Document2 pagesAnti-Malware With Blockchain - CSE105Jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Current Issue - Blockchain TechnologyDocument20 pagesCurrent Issue - Blockchain TechnologyMikayla HaninaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. Blockchain TechnologyDocument18 pagesUnit 3. Blockchain Technologylaxmimane245No ratings yet
- The Truth About BlockchainDocument9 pagesThe Truth About BlockchainRavikanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit - IDocument45 pagesUnit - ISivaNo ratings yet
- Basic Blockchan 7aDocument14 pagesBasic Blockchan 7arama tejaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologiesDocument45 pagesBlockchain Technologiesmeghanavalli2003No ratings yet
- Module 5 CsitDocument12 pagesModule 5 CsitPulkit JainNo ratings yet
- Blockchain - Curs 2Document36 pagesBlockchain - Curs 2Farmacie Baia de AramaNo ratings yet
- Event Management Ticket Booking Using BlockChainDocument5 pagesEvent Management Ticket Booking Using BlockChainRitesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Virtualcoin PDF.d2a8e9461e1bd156e33fDocument30 pagesVirtualcoin PDF.d2a8e9461e1bd156e33f251789036No ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument10 pagesBlock ChainVu Trung QuanNo ratings yet
- Cryptolearnwhat Is BlockchainDocument16 pagesCryptolearnwhat Is Blockchainlewgraves33No ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument28 pagesBlockchainPhương NgNo ratings yet
- Training Workshop - Blockchain BasicsDocument3 pagesTraining Workshop - Blockchain Basicsvuthihoangngan220905No ratings yet
- UNIT I OVERVIEW OF BLOCKCHAIN - Blockchain NotesDocument22 pagesUNIT I OVERVIEW OF BLOCKCHAIN - Blockchain NotesSavithri SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Chapter IiDocument16 pagesChapter IigenelyndelatorredelfinNo ratings yet
- Priyanshu BlockChain 1Document13 pagesPriyanshu BlockChain 1Priyanshu TechNo ratings yet
- (IJCST-V7I2P1) :azhar UshmaniDocument3 pages(IJCST-V7I2P1) :azhar UshmaniEighthSenseGroupNo ratings yet
- Block Chain Technology InformationDocument24 pagesBlock Chain Technology InformationDeepa ChuriNo ratings yet
- Management ConsultingDocument25 pagesManagement Consultingsangeeta jinNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument7 pagesBlockchain Technologymahmoodtareq0000No ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology NewDocument23 pagesBlockchain Technology NewKshitij NayakNo ratings yet
- How Blockchain Is Transforming Capital Market PDFDocument18 pagesHow Blockchain Is Transforming Capital Market PDFYuva RanuNo ratings yet
- Use of Blockchain Technology: By-Kunal Khandelwal Vikas Saini Arshdeep Rajnish KumarDocument8 pagesUse of Blockchain Technology: By-Kunal Khandelwal Vikas Saini Arshdeep Rajnish KumarRaj NishNo ratings yet
- Bitcoin: What Is A Blockchain?Document10 pagesBitcoin: What Is A Blockchain?Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- CSC200 ProjectDocument16 pagesCSC200 ProjectolatunjiemioluwaNo ratings yet
- Present BlockchainDocument28 pagesPresent BlockchainPhương NgNo ratings yet
- BLOCKCHAINDocument3 pagesBLOCKCHAINKshama PathakNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument2 pagesBlockchainSeun OgunlaNo ratings yet
- How Can Blockchain Power Industrial Manufacturing?Document10 pagesHow Can Blockchain Power Industrial Manufacturing?ABHINAV SAURAVNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: The Chain in BlockchainDocument2 pagesBlockchain: The Chain in BlockchainShashin SinghNo ratings yet
- BLockchainDocument24 pagesBLockchainQADEER AHMADNo ratings yet
- Shri S.V. Patel College of C.S & B.M. Affiliated To V.N.S.G.U. Blockchain TechnologyDocument13 pagesShri S.V. Patel College of C.S & B.M. Affiliated To V.N.S.G.U. Blockchain Technology069 Bhumi DudhatNo ratings yet
- Bahirdar University: DistributedDocument7 pagesBahirdar University: DistributedAmen AbatemameNo ratings yet
- Blockchain PresentationDocument18 pagesBlockchain Presentationanum.tariqNo ratings yet
- Finxter Bitcoin Whitepaper CheatSheet High ResDocument1 pageFinxter Bitcoin Whitepaper CheatSheet High ResHaseem AjazNo ratings yet
- Blog On Blockchain by Ashwin NagarDocument2 pagesBlog On Blockchain by Ashwin NagarAshwin NagarNo ratings yet
- VIR - Reform in TelecommunicationsDocument10 pagesVIR - Reform in TelecommunicationsNgu HoangNo ratings yet
- Why Redundancy and Replication?Document5 pagesWhy Redundancy and Replication?avcNo ratings yet
- SAP Security Overview For BT: July 13, 2007 Ravi KoppakulaDocument15 pagesSAP Security Overview For BT: July 13, 2007 Ravi Koppakulayogeeswar5b9No ratings yet
- Self Study Report: Submitted For Accreditation ToDocument491 pagesSelf Study Report: Submitted For Accreditation Tocetogix353No ratings yet
- Microsoft Office 365 Key Words List: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Office 365 Key Words List: ObjectiveZelNo ratings yet
- Module 39 Siebel Task UIDocument21 pagesModule 39 Siebel Task UIRealVasyaPupkinNo ratings yet
- Message 6Document17 pagesMessage 6hoangphuoctm3No ratings yet
- Sophos Threat Report 2023Document36 pagesSophos Threat Report 2023josbjsNo ratings yet
- Patient Information SystemDocument38 pagesPatient Information SystemNavlesh Agarwal40% (5)
- 4 - Predict Visitor Purchases With A Classification Model in BQMLDocument25 pages4 - Predict Visitor Purchases With A Classification Model in BQMLsubodhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To DbmsDocument27 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Dbmssathya priyaNo ratings yet
- Common Services Platform Collector Quick Start Guide2.5Document18 pagesCommon Services Platform Collector Quick Start Guide2.5imtiyazshaukatNo ratings yet
- Designing Data Intensive Applications: Part 1: Storage and RetrievalDocument85 pagesDesigning Data Intensive Applications: Part 1: Storage and RetrievalRavi LochanNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions On Oracle DBADocument3 pagesInterview Questions On Oracle DBAapi-3728238No ratings yet
- Project Report FinalDocument40 pagesProject Report FinalNITIN FAUJDARNo ratings yet
- Feasibility StudyDocument8 pagesFeasibility StudyTynan SokNo ratings yet
- NihongiDocument895 pagesNihongiKauê Metzger OtávioNo ratings yet
- Seeburger Integration SuitDocument9 pagesSeeburger Integration SuitrahullNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Report-TemplateDocument12 pagesMini Project Report-TemplatepranavNo ratings yet
- SAP BW Testing Episode 1 - Introduction: 1 PrerequistsDocument6 pagesSAP BW Testing Episode 1 - Introduction: 1 PrerequistsAnilNo ratings yet
- Pranav - Galatagi - Resume - 09 06 2023 20 58 12Document2 pagesPranav - Galatagi - Resume - 09 06 2023 20 58 12Pranav GalatagiNo ratings yet
- Wa0003Document163 pagesWa0003savan anvekarNo ratings yet
- ProfileDocument2 pagesProfileJaviier Arellano BravoNo ratings yet
- CHARTERDocument29 pagesCHARTERashagrieNo ratings yet
- (Certification Guide) Omar Santos, Joseph Muniz, Stefano de Crescenzo - CCNA Cyber Ops SECFND #210-250 Official Cert Guide-Cisco Press (2017)Document7 pages(Certification Guide) Omar Santos, Joseph Muniz, Stefano de Crescenzo - CCNA Cyber Ops SECFND #210-250 Official Cert Guide-Cisco Press (2017)Sanjin ZuhricNo ratings yet