Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Entity Sets
Entity Sets
Uploaded by
ANUBHAV CHATAUT0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesAn entity can be a physical or conceptual object, and an entity set is the collection of all entities of a particular entity type. There are two types of entities: strong entities, which have a primary key to uniquely identify them, and weak entities, which cannot be uniquely identified without a strong identifying entity they depend on. Weak entities are represented by double rectangles and have a total participation in an identifying relationship with their strong entity, shown as a double diamond.
Original Description:
Entity sets
Original Title
Entity sets
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn entity can be a physical or conceptual object, and an entity set is the collection of all entities of a particular entity type. There are two types of entities: strong entities, which have a primary key to uniquely identify them, and weak entities, which cannot be uniquely identified without a strong identifying entity they depend on. Weak entities are represented by double rectangles and have a total participation in an identifying relationship with their strong entity, shown as a double diamond.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesEntity Sets
Entity Sets
Uploaded by
ANUBHAV CHATAUTAn entity can be a physical or conceptual object, and an entity set is the collection of all entities of a particular entity type. There are two types of entities: strong entities, which have a primary key to uniquely identify them, and weak entities, which cannot be uniquely identified without a strong identifying entity they depend on. Weak entities are represented by double rectangles and have a total participation in an identifying relationship with their strong entity, shown as a double diamond.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
2.
1 Introduction to Entity
An Entity may be an object with a physical existence – a particular person, car,
house, or employee – or it may be an object with a conceptual existence – a
company, a job, or a university course.
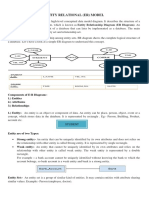
Entity Set:
An Entity is an object of Entity Type and a set of all entities is called an entity
set. For Example, E1 is an entity having Entity Type Student and the set of all
students is called Entity Set. In the ER diagram, Entity Type is represented as:
1.Strong Entity
A Strong Entity is a type of entity that has a key Attribute. Strong Entity does not
depend on other Entity in the Schema. It has a primary key, that helps in
identifying it uniquely, and it is represented by a rectangle. These are called
Strong Entity Types.
2. Weak Entity
An Entity type has a key attribute that uniquely identifies each entity in the entity
set. However, some entity type exists for which key attributes can’t be defined.
These are called Weak Entity types.
For Example, A company may store the information of dependents (Parents,
Children, Spouse) of an Employee. But the dependents wouldn’t have existed
without the employee. So Dependent will be a Weak Entity Type and
Employee will be Identifying Entity type for Dependent, which means it
is Strong Entity Type.
A weak entity type is represented by a Double Rectangle. The participation of
weak entity types is always total. The relationship between the weak entity type
and its identifying strong entity type is called the identifying relationship and it is
represented by a double diamond.
You might also like
- Entity Relationship Model PDFDocument37 pagesEntity Relationship Model PDFDivansh Sood100% (2)
- Entities and AttributesDocument1 pageEntities and Attributesnupur786No ratings yet
- EntityDocument3 pagesEntityIsmail ZebNo ratings yet
- InfoMan-Week 7-Entity Types-Entity Sets2021Document21 pagesInfoMan-Week 7-Entity Types-Entity Sets2021Sherwin LimboNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship ModelDocument8 pagesEntity Relationship ModeltanujaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Lab 3 ER DIagramDocument5 pagesDBMS Lab 3 ER DIagramSYED MUHAMMAD WAQASNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit 2Document54 pagesDBMS Unit 2Nishita PandeyNo ratings yet
- Dbms Unit2Document11 pagesDbms Unit2Shubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Entity, Entity Type, Entity Set - : Components of The E-R ModelDocument8 pagesEntity, Entity Type, Entity Set - : Components of The E-R Modelshivank tiwariNo ratings yet
- Intro - To-Database - Chapter No 2Document49 pagesIntro - To-Database - Chapter No 2KhanNo ratings yet
- E-R ModelDocument14 pagesE-R Modelkiller HackingNo ratings yet
- DBMS-lecture 4 ER-Model IntroductionDocument14 pagesDBMS-lecture 4 ER-Model IntroductionMonica TimberNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship Diagram - ER DiagramDocument10 pagesEntity Relationship Diagram - ER DiagramSwati HansNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Part-2)Document15 pagesUnit-1 (Part-2)Avinash ReddyNo ratings yet
- EntityDocument9 pagesEntitytemp16112000No ratings yet
- Unit-02 Notes - DBMSDocument24 pagesUnit-02 Notes - DBMSsudhanshuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 ER Diagram in DBMSDocument35 pagesLecture 5 ER Diagram in DBMSEichhorst AutomobilesNo ratings yet
- DE Module2 ERModel PPTDocument59 pagesDE Module2 ERModel PPTwowafer745No ratings yet
- Entity Relationship ModelDocument9 pagesEntity Relationship ModelMalik Umair AlamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document27 pagesLecture 7Ahmad Hussain Shafi SE-3rdNo ratings yet
- Entity-Relationship (E-R) Data ModelDocument4 pagesEntity-Relationship (E-R) Data ModelTheodore ReyesNo ratings yet
- VND - Openxmlformats Officedocument - Presentationml.presentation&rendition 1 2Document42 pagesVND - Openxmlformats Officedocument - Presentationml.presentation&rendition 1 2fashion20trendsNo ratings yet
- ER Model - Basic ConceptsDocument12 pagesER Model - Basic ConceptsGwelambertNo ratings yet
- A346739964 - 17673 - 9 - 2017 - Er ModelDocument52 pagesA346739964 - 17673 - 9 - 2017 - Er ModelChetan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship Model (Poster)Document10 pagesEntity Relationship Model (Poster)Vishwajeet Deepak GudadheNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 The Entity Relationship Data ModelDocument17 pagesChapter 8 The Entity Relationship Data ModelpabithasNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iv: Entity Relationship Models: Basic Concepts Like Entity SetDocument47 pagesUnit - Iv: Entity Relationship Models: Basic Concepts Like Entity SetArnav ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- ER Model InfoDocument34 pagesER Model Infokiran_qaNo ratings yet
- GP - DBMS - Creating ERDocument6 pagesGP - DBMS - Creating ERVishal ReddyNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 & 4 Entity Relationship Modelling: Er. Pradip KharbujaDocument68 pagesTopic 3 & 4 Entity Relationship Modelling: Er. Pradip Kharbujaniravthegreate999No ratings yet
- Group ActivityW7Document2 pagesGroup ActivityW7Pierce ValdezNo ratings yet
- ER Diagram - KameshwariDocument12 pagesER Diagram - KameshwariKameshwari PurusothmanNo ratings yet
- The Entity-Relationship ModelDocument15 pagesThe Entity-Relationship ModelCherry PepitoNo ratings yet
- ER ModelDocument12 pagesER Modelwaleed.khaldNo ratings yet
- Lab Assessment - 4: Entity Set and Relationship SetDocument4 pagesLab Assessment - 4: Entity Set and Relationship SetAnchit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- ERModellingDocument125 pagesERModellingBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Entity-Relationship ModelDocument86 pagesUnit 1: Entity-Relationship ModelJua IgnNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 DBMS NotesDocument51 pagesUnit-2 DBMS NotesAmrith MadhiraNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship Model: Objectives Time RequiredDocument4 pagesEntity Relationship Model: Objectives Time RequiredComputer Science & Engg, PusadNo ratings yet
- ER ModelDocument49 pagesER ModelNalini.R c1405No ratings yet
- UNIT-2: Entanty InstanceDocument23 pagesUNIT-2: Entanty InstanceSreeram RaoNo ratings yet
- SQL - Day 3: Structured Query LanguageDocument12 pagesSQL - Day 3: Structured Query LanguageNight KingNo ratings yet
- ER ModelDocument8 pagesER ModelAhmad FakharNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document25 pagesUnit 2ananyamarysebastian05No ratings yet
- DBMS GFGDocument21 pagesDBMS GFGRaghavendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- DBMS IntroDocument53 pagesDBMS IntroramNo ratings yet
- Unit-II DBMSDocument20 pagesUnit-II DBMSMsr. B. Jeyalakshmi Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- ER ModelDocument13 pagesER ModelManit MittalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PDFDocument32 pagesUnit 2 PDFyuvrajNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Part 2 ER Models PDFDocument32 pagesUnit-I Part 2 ER Models PDFAman MugutNo ratings yet
- 7-Module-2 (Relational Model and ER Mapping) - 08!05!2023Document6 pages7-Module-2 (Relational Model and ER Mapping) - 08!05!2023Vaishnavi JagtapNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document33 pagesUnit 2yuvrajNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship Diagram - ER DiagramDocument6 pagesEntity Relationship Diagram - ER DiagramMayank GoswamiNo ratings yet
- 19bce2279 VL2020210504460 Ast04Document4 pages19bce2279 VL2020210504460 Ast04Anchit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Differentitate Strong and Weak Entity SetDocument2 pagesDifferentitate Strong and Weak Entity Settiyixe1817No ratings yet
- Data Modeling ER Model Concept: Component of ER DiagramDocument21 pagesData Modeling ER Model Concept: Component of ER DiagramAnick KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2Document33 pagesUnit - 2yuvrajNo ratings yet
- What Is ErdDocument16 pagesWhat Is ErdArifullah StanikzaiNo ratings yet
- Entity RelationalDocument8 pagesEntity RelationalRoyal Green AchrolNo ratings yet