Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laplace Transform of Derivatives and Integrals - ODEs
Uploaded by
rachel balaoroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laplace Transform of Derivatives and Integrals - ODEs
Uploaded by
rachel balaoroCopyright:
Available Formats
ME 221: Advanced Engineering Mathematics for ME
NOTES
Transforms of Derivatives & Integrals. ODEs
Laplace Transforms of Derivatives
L (𝑓 ′) = 𝑠L (𝑓 ) − 𝑓(0)
L (𝑓") = 𝑠 2 L (𝑓 ) − 𝑠𝑓 (0) − 𝑓′(0)
L (𝑓′′′) = 𝑠 3 L (𝑓 ) − 𝑠 2 𝑓 (0) − 𝑠𝑓 ′(0) − 𝑓"(0)
L (𝑓 𝐼𝑉 ) = 𝑠 4 L (𝑓 ) − 𝑠 3 𝑓 (0) − 𝑠 2 𝑓 ′(0) − 𝑠𝑓"(0) − 𝑓′′′(0)
L (𝒇𝒏 ) = 𝒔𝒏 L (𝒇) − 𝒔𝒏−𝟏 𝒇(𝟎) − 𝒔𝒏−𝟐 𝒇′ (𝟎) − ⋯ − 𝒇𝒏−𝟏 (𝟎)
Example:
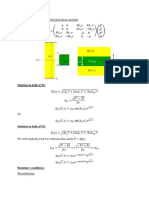
1) Find the L (𝑓 𝐼𝑉 ), if 𝑓(𝑡) = cos 4𝑡.
Steps Remarks
I 𝐼𝑉 ) 4 3 2 ′( Set-up the Transform.
L (𝑓 = 𝑠 L (𝑓 ) − 𝑠 𝑓 (0) − 𝑠 𝑓 0) − 𝑠𝑓"(0) − 𝑓′′′(0)
II
𝑓 (𝑡) = cos 4𝑡 𝑓 (0) = 1 Create a Table of Values
𝑠 𝑠 for the needed values in
L (𝑓 ) = 2 =
𝑠 + 42 𝑠 2 + 16 the Laplace Transform
′( ) 𝑓′(0) = 0 set-up as derived in Step
𝑓 𝑡 = −4 sin 4𝑡
𝑓 ′′ (𝑡) = −16 cos 4𝑡 𝑓 ′′ (0) = −16 I.
𝑓 ′′′ (𝑡) = 64 sin 4𝑡 𝑓′′′(0) = 0
𝑓 𝐼𝑉 (𝑡) = 256 cos 4𝑡
III 𝑠 Substitute the values
L (𝑓 𝐼𝑉 ) = 𝑠 4 ( 2 ) − 𝑠 3 (1) − 𝑠 2 (0) − 𝑠(−16) − (0)
𝑠 + 16 derived from the Table
in Step II to the
Transform set-up in Step
𝑠5 I. Then, simplify.
L (𝑓 𝐼𝑉 ) = − 𝑠 3 + 16𝑠
𝑠 2 + 16
256𝑠 𝑠
L (𝑓 𝐼𝑉 ) = = 256 ( 2 )
𝑠2+ 16 𝑠 + 16
IV L (𝑓 𝐼𝑉 ) = L (𝑓 𝐼𝑉 (𝑡)) = L (256 cos 4𝑡 ) Check your answer.
𝑠
L (256 cos 4𝑡 ) = 256L (cos 4𝑡 ) = 256 ( )
𝑠2 + 16
Test your understanding:
Find the L (𝑓 ′′′ ), if 𝑓(𝑡) = cos 𝜔𝑡
𝝎𝟒
Answer: L (𝝎𝟑 𝒔𝒊𝒏 𝝎𝒕) =
𝒔𝟐 +𝝎𝟐
Prepared by:
Engr. Reymart Jay G. Adaya
Faculty, College of Engineering
University of Southern Mindanao- Kidapawan City Campus
ME 221: Advanced Engineering Mathematics for ME
NOTES
Laplace Transform of the Integral of a Function
𝒕
𝟏
L {∫ 𝒇(𝝉)𝒅𝝉} = 𝑭(𝒔)
𝟎 𝒔
Thus,
𝒕
𝟏
∫ 𝒇(𝝉)𝒅𝝉 = L −𝟏 { 𝑭(𝒔)}
𝟎 𝒔
Example:
1
1) Find the inverse of .
𝑠(𝑠 2 +𝜔2 )
Solution:
−1 1 −1 1 1
L { }=L { • 2 }
𝑠(𝑠2 + 𝜔2 ) 𝑠 𝑠 + 𝜔2
Following the format of the Laplace Transform of the Integral of a Function, in
this case,
1
𝐹(𝑠) =
𝑠2 + 𝜔2
Thus,
𝜔
1 1 𝜔 1
{ 2 𝜔 2} = L
−1 −1 −1
𝑓(𝜏) = L { 2 }=L { 2 } = sin 𝜔𝑡
𝑠 + 𝜔2 𝑠 +𝜔 𝜔 𝑠 +𝜔 2 𝜔
In this sense,
𝑡 𝑡
−1 {
1 −1 1 1 1
L 𝐹 (𝑠)} = L { • } = ∫ 𝑓 (𝜏)𝑑𝜏 = ∫ sin 𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝜏
𝑠 𝑠 𝑠2 + 𝜔 2
0 0 𝜔
𝑡
1
= ∫ sin 𝜔𝑡 𝑑𝜏
𝜔 0
𝑡
1
= (− cos 𝜔𝑡)|
𝜔2
0
1
=− (cos 𝜔𝑡 − cos 0)
𝜔2
𝟏
= (𝟏 − 𝐜𝐨𝐬 𝝎𝒕)
𝝎𝟐
Test your understanding:
1
Given the information in Prob. 1, find the inverse of .
𝑠 2 (𝑠 2 +𝜔2 )
𝒕 𝒔𝒊𝒏 𝝎𝒕
Answer: −
𝝎𝟐 𝝎𝟑
Prepared by:
Engr. Reymart Jay G. Adaya
Faculty, College of Engineering
University of Southern Mindanao- Kidapawan City Campus
ME 221: Advanced Engineering Mathematics for ME
NOTES
Solving ODEs using Laplace Transforms
Example:
Find 𝑦(𝑡) for the initial value problem,
𝑦" − 𝑦 = 𝑡 , 𝑦(0) = 1 , 𝑦′(0) = 1
Steps Remarks
L (𝑦") = 𝑠 2 L (𝑦) − 𝑠𝑦(0) − 𝑦′(0) Set-up the Laplace
L (𝑦 ) Transforms of the parameters
I
1 in the ODE.
L (𝑡) = 2
𝑠
𝑦" − 𝑦 = 𝑡 Substitute the derived
L (𝑦") − L (𝑦) = L (𝑡) transforms in Step I to the
II 1 ODE.
𝑠 2 L (𝑦) − 𝑠𝑦(0) − 𝑦′(0) − L (𝑦) =
𝑠2
1
𝑠 2 L (𝑦) − 𝑠𝑦(0) − 𝑦′(0) − L (𝑦) =
𝑠2
1 Set 𝒀 = L (𝑦) to form the
𝑠 2 𝒀 − 𝑠𝑦(0) − 𝑦 ′(0) − 𝒀 = 2 subsidiary equation. Then,
𝑠
2
1 substitute the values given as
III
𝑠 𝒀 − 𝑠(1) − 1 − 𝒀 = 2 initial conditions, and further
𝑠
simplify the equation so that
1 all the 𝒀 − 𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚𝑠 are on one
𝑠 2𝒀 − 𝒀 = 𝑠 + 1 +
𝑠2 side, and the other non- 𝒀 −
𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚𝑠 on the other side.
1
(𝑠 2 − 1)𝒀 = 𝑠 + 1 +
𝑠2
From Step III, simplify
1 further by obtaining the
𝑠+1+ 2
𝒀= 𝑠 value of 𝒀.
𝑠2 − 1
Note: Formally, this method is
1 also called multiplying both
𝑠+1 𝑠 2
𝒀= 2 + 2 sides of the equation by the
𝑠 −1 𝑠 −1 transfer function. The transfer
1 function is basically the
𝑠+1
𝑠 2 reciprocal of the function
𝒀= 2 + 2 alongside 𝒀.
𝑠 −1 𝑠 −1
IV
𝑠+1 1 After, the function of 𝒀
𝒀= 2 + 2 2 obtained must be intuitively
𝑠 − 1 𝑠 (𝑠 − 1)
strategic enough, following
1 1 any of the format of the
𝒀= + elementary transforms
𝑠−1 𝑠 2 (𝑠 2
− 1)
introduced earlier in this
1 1 1 chapter.
𝒀= +( − )
𝑠−1 𝑠2 −1 𝑠2
Note: This fraction was
expanded through partial
Prepared by:
Engr. Reymart Jay G. Adaya
Faculty, College of Engineering
University of Southern Mindanao- Kidapawan City Campus
ME 221: Advanced Engineering Mathematics for ME
NOTES
1 1 1 fraction reduction—therefore,
𝒀= + − the expression in the next step.
𝑠−1 𝑠2 −1 𝑠2
−1 −1 1 1 1 Finally, obtain the required
𝑦(𝑡) = L (𝒀) = L ( + − )
𝑠−1 𝑠2 −1 𝑠2 ODE solution by getting the
inverse of the transform of 𝒀
−1
−1 1 −1 1 −1 1 or L (𝒀).
=L ( )+L ( )−L ( 2)
𝑠−1 𝑠2 −1 𝑠
𝒚(𝒕) = 𝒆𝒕 + 𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐡 𝒕 − 𝒕
Strengthen your knowledge:
Find 𝑦(𝑡) for the initial value problem,
𝑦 ′ + 5.2𝑦 = 19.4 sin 2𝑡 , 𝑦(0) = 0
Prepared by:
Engr. Reymart Jay G. Adaya
Faculty, College of Engineering
University of Southern Mindanao- Kidapawan City Campus
You might also like
- Laplace Transforms. Linearity. First Shifting TheoremDocument5 pagesLaplace Transforms. Linearity. First Shifting Theoremrachel balaoroNo ratings yet
- VCT Imp QuestionsDocument6 pagesVCT Imp QuestionscringeNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Notes for Mathematics IIDocument28 pagesLaplace Transform Notes for Mathematics IIaliNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Unit 2Document61 pagesLinear Algebra Unit 2Scout opNo ratings yet
- Topic-3-3.1-3.9 Laplace-TransformsDocument18 pagesTopic-3-3.1-3.9 Laplace-Transformsgeorge obongenNo ratings yet
- Laplace transform problems and solutionsDocument2 pagesLaplace transform problems and solutionsRishitaNo ratings yet
- LaplaceDocument42 pagesLaplaceAseel OtoumNo ratings yet
- AEMN04E_Topic 3 (3.1-3.9)_Laplace TransformsDocument18 pagesAEMN04E_Topic 3 (3.1-3.9)_Laplace TransformsRafael ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Laplace Transform and The IVP (Sect. 6.2)Document12 pagesThe Laplace Transform and The IVP (Sect. 6.2)Anonymous Jy6ASdQ45JNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Achieved by ALI Shamkhi: Pierre-Simon de LaplaceDocument29 pagesLaplace Transform Achieved by ALI Shamkhi: Pierre-Simon de LaplaceMOHAMMAD PRINCENo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document4 pagesExercise 1Vienice AllanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 38Document16 pagesLecture # 38Mazoon ButtNo ratings yet
- Laplace Nao HomogeneoDocument12 pagesLaplace Nao HomogeneoaldmarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1 PDFDocument1 pageTutorial Sheet 1 PDFNavjot WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Mathematical ModellingDocument19 pagesChapter 2 - Mathematical ModellingANDREW LEONG CHUN TATT STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 1 2Document13 pagesChapter 7 1 2Muhd RzwanNo ratings yet
- Module 3.1 Lapalce Transform of Periodic FunctionsPartial Differential EquationsDocument15 pagesModule 3.1 Lapalce Transform of Periodic FunctionsPartial Differential EquationsrupinsgmNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform NotesDocument135 pagesLaplace Transform NotesAmit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Laplace TransformationDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Laplace Transformationप्रियांशु मिश्राNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transforms For PBL - P2027Document4 pagesLaplace Transforms For PBL - P2027Jean Orveil PAMBOUNo ratings yet
- 1 - WWW - Mindvis.inDocument2 pages1 - WWW - Mindvis.inPrashantKumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20Document7 pagesLecture 20pankaj sharmaNo ratings yet
- Laplace and Z-TransformsDocument23 pagesLaplace and Z-TransformsHussam AliraqiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics 1 Transform Functions: QuestionsDocument20 pagesEngineering Mathematics 1 Transform Functions: QuestionsSyahrul SulaimanNo ratings yet
- 2. Transfer FunctionDocument4 pages2. Transfer FunctionhillaryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Laplace TransformDocument77 pagesChapter 3 Laplace TransformafiqNo ratings yet
- Using Laplace Transform-Solving RLC Electric Circuits (15.10.2020)Document6 pagesUsing Laplace Transform-Solving RLC Electric Circuits (15.10.2020)phoe aung100% (1)
- 11 Solving Linear IVPs by Laplace TransformsDocument14 pages11 Solving Linear IVPs by Laplace TransformsKeisha LastimadoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Laplace and Z-Transforms: Ali Sinan Sert OzDocument34 pagesLecture Notes On Laplace and Z-Transforms: Ali Sinan Sert Ozjohn sybeloNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Laplace and Z-Transforms: Ali Sinan Sert OzDocument34 pagesLecture Notes On Laplace and Z-Transforms: Ali Sinan Sert OzMarcelo LimaNo ratings yet
- Laplace TutorialDocument3 pagesLaplace TutorialYusuf GoriawalaNo ratings yet
- Derivatives, Integrals, Multiplication and Division by T Laplce Transforms by Michael PantonillaDocument21 pagesDerivatives, Integrals, Multiplication and Division by T Laplce Transforms by Michael PantonillaMichael PantonillaNo ratings yet
- Inverse LaplaceDocument33 pagesInverse LaplacePrajapati NareshNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Control SystemsDocument113 pagesIntroduction to Control SystemsWondatir GoshimNo ratings yet
- CE50P Lecture 1Document19 pagesCE50P Lecture 1John Alex BlancaflorNo ratings yet
- L V C I: John Rio M. Abejo February 6, 2019 2011-8755 EE 131-FDocument4 pagesL V C I: John Rio M. Abejo February 6, 2019 2011-8755 EE 131-FRio Mateo AbejoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Laplace Transform: 1 Learning OutcomesDocument22 pagesChapter 1 The Laplace Transform: 1 Learning OutcomesMorsaleen ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- TD Chimie Théorique S5 Série 1Document2 pagesTD Chimie Théorique S5 Série 1Youssef OubahasNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus Laplace Transforms HandoutDocument35 pagesVector Calculus Laplace Transforms HandoutAakanksha KartikNo ratings yet
- Cvde Unit i Qtn BankDocument3 pagesCvde Unit i Qtn BankgandurikNo ratings yet
- ILT (1) Lecture 5Document13 pagesILT (1) Lecture 5Hasibur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Exponential & Logarithmic Functions Logarithmic Functions Logarithms Were Invented by John Napier Because of His Interest in Reducing ComplexDocument8 pagesExponential & Logarithmic Functions Logarithmic Functions Logarithms Were Invented by John Napier Because of His Interest in Reducing ComplexCaren Pelayo JonelasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - IIDocument12 pagesLecture 2 - IIgks5kc8bhdNo ratings yet
- Tables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39From EverandTables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39No ratings yet
- Mce371 6Document16 pagesMce371 6Abul HasnatNo ratings yet
- Lec 25 Laplace DerivativesDocument29 pagesLec 25 Laplace DerivativesTalha Chaudhary100% (1)
- Lecture Notes On Laplace and Z-Transforms: Ali Sinan Sert Oz Sertoz@fen - Bilkent.edu - TR 11 April 2003Document34 pagesLecture Notes On Laplace and Z-Transforms: Ali Sinan Sert Oz Sertoz@fen - Bilkent.edu - TR 11 April 2003SuptryNo ratings yet
- Course 10 - Laplace 2Document32 pagesCourse 10 - Laplace 2ali fulanNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Video 2 - Analytical Sol Via TFDocument6 pagesWeek 3 Video 2 - Analytical Sol Via TFJovi LeoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Laplace Transform PDFDocument34 pagesChapter 2 - Laplace Transform PDFSritaran BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mohammed Gulam AhamadDocument37 pagesDr. Mohammed Gulam AhamadMohammad Gulam AhamadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part 1 (Laplace Transform)Document60 pagesChapter 3 Part 1 (Laplace Transform)TJ HereNo ratings yet
- Mod 3 Laplace Transfrom - NotesDocument49 pagesMod 3 Laplace Transfrom - NotesAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- 2-Laplace TransformDocument11 pages2-Laplace TransformMüge ERDOĞANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Laplace TransformDocument57 pagesChapter 3 - Laplace TransformBukhari ManshoorNo ratings yet
- J. Math. Comput. Sci. 11 (2021), No. 5, 5729-5741 ISSN: 1927-5307Document13 pagesJ. Math. Comput. Sci. 11 (2021), No. 5, 5729-5741 ISSN: 1927-5307vedaNo ratings yet
- Review Notes: Advanced Eng'g Math Part 2Document3 pagesReview Notes: Advanced Eng'g Math Part 2JefrilAmboyNo ratings yet
- MATH024C Activity 4 Laplace Transform.Document12 pagesMATH024C Activity 4 Laplace Transform.Mark Glenn SiapcoNo ratings yet
- Geodesic Completeness of The Left-Invariant Metrics On RHNDocument8 pagesGeodesic Completeness of The Left-Invariant Metrics On RHNSrdjan VukmirovicNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Finite GeometryDocument10 pagesFinite GeometryAey Eks QuaredNo ratings yet
- Product and Quotient RuleDocument41 pagesProduct and Quotient RuleMary JoyceNo ratings yet
- Final Exam of Calculus 1 and The Answer KeyDocument12 pagesFinal Exam of Calculus 1 and The Answer Keyes20btech11023No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Stiffness (Displacement) MethodDocument12 pagesIntroduction To The Stiffness (Displacement) MethodZaher MoftyNo ratings yet
- Analysis and algebra+NT - Victor Wang - XDocument14 pagesAnalysis and algebra+NT - Victor Wang - XCris DeVid GamerNo ratings yet
- Real Analysis Royden 3rd EditionDocument684 pagesReal Analysis Royden 3rd EditionleoastorsNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions of Discrete MathematicsDocument120 pagesObjective Questions of Discrete MathematicsJagdish Kapadnis68% (28)
- La PlaceDocument7 pagesLa Placenani233100% (1)
- Putnam Exam Calculus ProblemsDocument9 pagesPutnam Exam Calculus ProblemstadkarNo ratings yet
- 7.6 Rational Zero TheoremDocument18 pages7.6 Rational Zero Theoremkyle jesterNo ratings yet
- Maths. TaibaDocument11 pagesMaths. TaibaGânőőķ WäřņäNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TOnLINEAR PROGRAMMINGDocument9 pagesINTRODUCTION TOnLINEAR PROGRAMMINGPrincess Amber0% (2)
- The 0-1 Knapsack Problem: An Introductory SurveyDocument13 pagesThe 0-1 Knapsack Problem: An Introductory SurveyRahma JabriNo ratings yet
- Y Sec 2t Sec 2t: What Is The Value of The Derivative of The Function Below For T 1? The Given Angle Is in RadiansDocument24 pagesY Sec 2t Sec 2t: What Is The Value of The Derivative of The Function Below For T 1? The Given Angle Is in RadiansRhian LlerinNo ratings yet
- CS 135 Discrete Structures Syllabus: Text BooksDocument1 pageCS 135 Discrete Structures Syllabus: Text BooksRowelyn BlancoNo ratings yet
- BMAT 102L CAT-II Review Meeting MinutesDocument3 pagesBMAT 102L CAT-II Review Meeting Minutesdhanraj singhNo ratings yet
- LinearAlgebra MatlabDocument12 pagesLinearAlgebra MatlabAndres Felipe CisfNo ratings yet
- Ordinal NumbersDocument19 pagesOrdinal NumbersDenditric CellNo ratings yet
- Slide 2 LinearEquationSystemDocument25 pagesSlide 2 LinearEquationSystemtetsu 1945No ratings yet
- Answers To Chapter 23Document2 pagesAnswers To Chapter 23Mahan ZwixNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus BC Exam: SECTION I: Multiple ChoiceDocument103 pagesAP Calculus BC Exam: SECTION I: Multiple ChoiceDrastic Pranksters Inc.40% (5)
- Math Grade 9 ExamDocument3 pagesMath Grade 9 ExamCristie MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Activity 3Document1 pageThis Study Resource Was: Activity 3Sheah DeratasNo ratings yet
- 2020 DJ 1Document4 pages2020 DJ 1Sachdev KingNo ratings yet
- Mathematics TermsDocument11 pagesMathematics TermsTangkas PangestuNo ratings yet
- 12 Maths NcertSolutions Chapter 6 3Document26 pages12 Maths NcertSolutions Chapter 6 3Supreme Pubg TournamentsNo ratings yet
- Prime Numbers of The Kind n2 1Document4 pagesPrime Numbers of The Kind n2 1humejiasNo ratings yet
- 1 Fourier AnalysisDocument60 pages1 Fourier AnalysisdowntolabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-3 The Simplex MethodDocument19 pagesChapter 2-3 The Simplex MethodHACHALU FAYENo ratings yet
- 6 - Mathematics - of - Graphs - PPTX Filename - UTF-8''6 Mathematics of GraphsDocument46 pages6 - Mathematics - of - Graphs - PPTX Filename - UTF-8''6 Mathematics of GraphsLia Alegre0% (2)