Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mse215 Materials Science I Mid Term 2020 2021
Uploaded by
yagmurdeniiizzzOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mse215 Materials Science I Mid Term 2020 2021
Uploaded by
yagmurdeniiizzzCopyright:
Available Formats
MSE-215 MATERIALS SCIENCE I
MID-TERM EXAM
Date: 10/12/2020 Time: 13:30-16:00 Duration: 150 mins
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6
Grade ….. / 20 ….. / 25 ….. / 10 ….. / 15 ….. / 15 ….. / 15
Name-Surname: Total Grade:
No:
Signature:
QUESTIONS
1. Define the following terms.
Coordination Number (CN) (Please also indicate what the CN is for SC, FCC, BCC, and
HCP)
Isotropy
Metallic Bonding
Crystalline Material
Polymorphism
Pauli exclusion principle
Materials Science and Engineering Good Luck
MSE-215 MATERIALS SCIENCE I
MID-TERM EXAM
Date: 10/12/2020 Time: 13:30-16:00 Duration: 150 mins
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6
Grade ….. / 20 ….. / 25 ….. / 10 ….. / 15 ….. / 15 ….. / 15
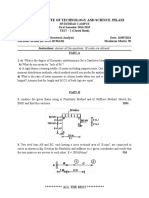
2. A) Within the following cubic unit cells (left and right), sketch the following directions (to left)
and planes (to right): [11 0], [014] , [111] and (210).
z z
y y
x x
B) Determine the Miller indices for the directions and planes shown in the following unit cells:
C) Derive linear density expression for BCC [110] in terms of the atomic radius R and compute
linear density value for this direction for tungsten. The atomic radius for tungsten is 0,137 nm.
Materials Science and Engineering Good Luck
MSE-215 MATERIALS SCIENCE I
MID-TERM EXAM
Date: 10/12/2020 Time: 13:30-16:00 Duration: 150 mins
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6
Grade ….. / 20 ….. / 25 ….. / 10 ….. / 15 ….. / 15 ….. / 15
3. Explain why the properties of polycrystalline materials are most often isotropic.
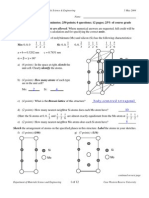
4. Figure 1 shows an x-ray diffraction pattern for α-iron (BCC) taken using a diffractometer and
monochromatic x-radiation having a wavelength of 0.1542 nm; each diffraction peak (first order)
on the pattern has been indexed. Compute the interplanar spacing for (110) set of planes
indexed; also determine the atomic radius of Fe for each of the peaks.
Figure 1: Diffraction pattern for α-iron
Materials Science and Engineering Good Luck
MSE-215 MATERIALS SCIENCE I
MID-TERM EXAM
Date: 10/12/2020 Time: 13:30-16:00 Duration: 150 mins
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6
Grade ….. / 20 ….. / 25 ….. / 10 ….. / 15 ….. / 15 ….. / 15
5. Below are listed the atomic weight, density, and atomic radius for three hypothetical elements.
For each determine whether its crystal structure is face-centered cubic (FCC), body-centered
cubic (BCC) or simple cubic (SC) and then justify your determination.
Elements Atomic Weight (g/mol) Density (g/cm3) Atomic Radius (nm)
A 107.6 13.42 0.133
B 77.4 8.22 0.125
C 50,9 5,96 0,132
Materials Science and Engineering Good Luck
MSE-215 MATERIALS SCIENCE I
MID-TERM EXAM
Date: 10/12/2020 Time: 13:30-16:00 Duration: 150 mins
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6
Grade ….. / 20 ….. / 25 ….. / 10 ….. / 15 ….. / 15 ….. / 15
6. A) Figure 2 represents the net potential energies and interatomic separation plots for two
(A and B) hypothetical materials. Compare these materials in terms of melting temperature (T m),
Elastic modulus (E), and coefficient of thermal expansion (α) by explaining the reasons.
Figure 2: The net potential energy versus interatomic separation plots for two hypothetical materials
B) Briefly cite the main properties of metals, ceramics and polymers (at least 4 items).
Materials Science and Engineering Good Luck
You might also like
- Sabian Aspect OrbsDocument8 pagesSabian Aspect Orbsellaella13100% (2)
- Arudha PDFDocument17 pagesArudha PDFRakesh Singh100% (1)
- Cause Analysis For Spun Pile Crack and BrokenDocument11 pagesCause Analysis For Spun Pile Crack and BrokenRony LesbtNo ratings yet
- JUnit 5 User GuideDocument90 pagesJUnit 5 User GuideaawaakNo ratings yet
- Materials Data for Cyclic Loading: Aluminium and Titanium AlloysFrom EverandMaterials Data for Cyclic Loading: Aluminium and Titanium AlloysRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Blake Mouton Managerial GridDocument3 pagesBlake Mouton Managerial GridRashwanth Tc100% (1)
- Ceramic Raw Materials: Institute of Ceramics Textbook SeriesFrom EverandCeramic Raw Materials: Institute of Ceramics Textbook SeriesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Sprinkler Sizing en v1Document12 pagesSprinkler Sizing en v1CristianDumitru0% (1)
- Dec 2-7 Week 4 Physics DLLDocument3 pagesDec 2-7 Week 4 Physics DLLRicardo Acosta Subad100% (1)
- Saflex-Dg - 41 Data SheetDocument5 pagesSaflex-Dg - 41 Data SheetrasheedgotzNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting by Cabrera Solution Manual 2011 PDFDocument3 pagesManagement Accounting by Cabrera Solution Manual 2011 PDFClaudette Clemente100% (1)
- A Project Report ON Strategic Purchasing Procedure, Systems and Policies (Hospital Industry)Document20 pagesA Project Report ON Strategic Purchasing Procedure, Systems and Policies (Hospital Industry)amitwin1983No ratings yet
- Time Table: K.S.R. College of Engineering: Tiruchengode - 637 215Document6 pagesTime Table: K.S.R. College of Engineering: Tiruchengode - 637 215sabaaNo ratings yet
- Eg2010 2021 SP2Document8 pagesEg2010 2021 SP2Edwin JomonNo ratings yet
- Time Table Mbit 2020 CivilDocument4 pagesTime Table Mbit 2020 CivilKanhaiya BhagatNo ratings yet
- Mtech QP K.SDocument2 pagesMtech QP K.SmuthuNo ratings yet
- 221704171929Document2 pages221704171929Subhasish ShitNo ratings yet
- 2k19 6th Sem Final - WatermarkDocument14 pages2k19 6th Sem Final - WatermarkVishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Citing (2019) - Role of Material On The Performance of Multi-Stage Depressed CollectorsDocument4 pagesCiting (2019) - Role of Material On The Performance of Multi-Stage Depressed CollectorsEnginNo ratings yet
- Two Cycle Heat Treatment (Austempering + Tempering) of Low C Equivalent Ductile IronDocument58 pagesTwo Cycle Heat Treatment (Austempering + Tempering) of Low C Equivalent Ductile IronsaltbathNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document22 pagesLecture 1vishalkadavathNo ratings yet
- Final Exam + Solutions - Strength of Materials 201Document3 pagesFinal Exam + Solutions - Strength of Materials 201Bảo Phiên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 12 B.E Ee R2010Document138 pages12 B.E Ee R2010Giri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Institute of Space Technology: Department of Aeronautics & Astronautics Mechanics of Materials - Aero 17 (A&B)Document3 pagesInstitute of Space Technology: Department of Aeronautics & Astronautics Mechanics of Materials - Aero 17 (A&B)Muhammad Ubaid RazaNo ratings yet
- 2015 MT Mollecular NALLADocument45 pages2015 MT Mollecular NALLADeni haryadiNo ratings yet
- CCB211 - Engineering Materials Supplementary Test 1 of September 15, 2010Document2 pagesCCB211 - Engineering Materials Supplementary Test 1 of September 15, 2010Aobakwe SisilaNo ratings yet
- Use The Appendices Provided at The End of The Question Paper To Answer Some of - Scientific Calculator - Answer All The QuestionsDocument8 pagesUse The Appendices Provided at The End of The Question Paper To Answer Some of - Scientific Calculator - Answer All The QuestionsONNDWELA RAMALAMULANo ratings yet
- 4 5936176936635074808Document4 pages4 5936176936635074808Sirak SimonNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani: Instructions: Answer All The Questions. IS Codes Are AllowedDocument1 pageBirla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani: Instructions: Answer All The Questions. IS Codes Are Allowedaayushi doshiNo ratings yet
- 2k19 5th Sem Papers - Watermark-1Document15 pages2k19 5th Sem Papers - Watermark-1Vishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - : 180 Minutes 250 Points 6 Questions 12 Pages 25% of Course GradeDocument12 pagesFinal Exam - : 180 Minutes 250 Points 6 Questions 12 Pages 25% of Course GradeaychiluhimhailuNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus: Spring, 2020Document5 pagesCourse Syllabus: Spring, 2020Prosonjit Chandra DashNo ratings yet
- BS CeDocument3 pagesBS CeTalha.jNo ratings yet
- 28-Syllabus Strcture-MS-M.Tech. ThEDocument3 pages28-Syllabus Strcture-MS-M.Tech. ThEPriya Ranjan MallickNo ratings yet
- Class Test Notice For Odd Sem Session 2023-24Document4 pagesClass Test Notice For Odd Sem Session 2023-24Mohd YamanNo ratings yet
- Cse-2 Tentative Time TableDocument2 pagesCse-2 Tentative Time TableKalpana VenchiryalaNo ratings yet
- B.tech, MME, Metallurgical, 6th Sem, 2018-19 Batch 6th SemDocument20 pagesB.tech, MME, Metallurgical, 6th Sem, 2018-19 Batch 6th SemAnand Arya0% (1)
- 2018 Ques 5th SemDocument15 pages2018 Ques 5th SemVishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Schedule Phase Ii 20 - 2 - 2023 - 0Document10 pagesSchedule Phase Ii 20 - 2 - 2023 - 0Vishal singhNo ratings yet
- Revised - First Mid Examination-B.tech, BBA, BCA, MBA, MCA, BSC, BArch, Diploma ID (Except First Year) Odd Sem 2022-23Document12 pagesRevised - First Mid Examination-B.tech, BBA, BCA, MBA, MCA, BSC, BArch, Diploma ID (Except First Year) Odd Sem 2022-23Roʜʌŋ AŋʌŋɗNo ratings yet
- Production Syllabus 2017-18-1Document71 pagesProduction Syllabus 2017-18-1Akankshya MishraNo ratings yet
- Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila: Intramuros, ManilaDocument1 pagePamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila: Intramuros, ManilaErica JoannaNo ratings yet
- ME 2 391 SolutionDocument7 pagesME 2 391 SolutionAbdulrahman MohammedNo ratings yet
- Civil Engg Syllabus RGTU - 3rd To 6th SemDocument33 pagesCivil Engg Syllabus RGTU - 3rd To 6th Sembhustlero0o100% (1)
- Be Civil V & Vii Sem Offline TTDocument4 pagesBe Civil V & Vii Sem Offline TTVirender SehwagNo ratings yet
- 2nd MID Well LoggingDocument2 pages2nd MID Well LoggingA NI LNo ratings yet
- DMX3203 Tma01 2019 2020Document3 pagesDMX3203 Tma01 2019 2020Thushith WithanageNo ratings yet
- Project Report Phase1Document37 pagesProject Report Phase1Satyam vankayalaNo ratings yet
- November 2015 (v2) QP - Paper 2 CIE Chemistry A-LevelDocument12 pagesNovember 2015 (v2) QP - Paper 2 CIE Chemistry A-LevelFrengky WijayaNo ratings yet
- Optik: Original Research ArticleDocument8 pagesOptik: Original Research ArticlePramudio PakertiNo ratings yet
- ICRCET-2022 HadiResistivityDocument7 pagesICRCET-2022 HadiResistivityHarisIlmanFiqihNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Approved by BOS 16.06.09 Of: Electronics and Communication StreamDocument57 pagesSyllabus Approved by BOS 16.06.09 Of: Electronics and Communication Streamambar999No ratings yet
- (A.Y.2019-20) Engineering 4th Year (2014-Batch) End Semester Test Examinations Time Table For Regular Semester-2Document3 pages(A.Y.2019-20) Engineering 4th Year (2014-Batch) End Semester Test Examinations Time Table For Regular Semester-2Surya Prakash ManneNo ratings yet
- Aaes3202915 R1Document23 pagesAaes3202915 R1Dang MinhNo ratings yet
- Clpe-16 CT-2Document1 pageClpe-16 CT-2sachin mauryaNo ratings yet
- Sallybus 2020-24Document63 pagesSallybus 2020-24Aditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Be Civil III Sem Offline TTDocument2 pagesBe Civil III Sem Offline TTVirender SehwagNo ratings yet
- Cis Be Fall 2023Document7 pagesCis Be Fall 2023Amna YousufNo ratings yet
- Assignment 601Document7 pagesAssignment 601Nur Ain MunirahNo ratings yet
- THDC Institute of Hydropower Engineering and TechnologyDocument3 pagesTHDC Institute of Hydropower Engineering and TechnologyAnsh AroraNo ratings yet
- 27-Syllabus Strcture-MS-M.Tech. MSDDocument3 pages27-Syllabus Strcture-MS-M.Tech. MSDPriya Ranjan MallickNo ratings yet
- Syllabus and Course Structure BDocument98 pagesSyllabus and Course Structure B19BEC036 EkanshNo ratings yet
- Hi-Tech College of Engineering & Technology Gandipet-Himayathnagar, CB Post, Hyderabad-75 Dept of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument6 pagesHi-Tech College of Engineering & Technology Gandipet-Himayathnagar, CB Post, Hyderabad-75 Dept of Electronics and Communication Engineeringapi-3704956No ratings yet
- Sheet 1: Materials Science Academic Year (2016-2017) (Spring) Tutorial Problems Dr. Mohamed Abdallah BhlolDocument2 pagesSheet 1: Materials Science Academic Year (2016-2017) (Spring) Tutorial Problems Dr. Mohamed Abdallah BhlolBahgat HafezNo ratings yet
- 04 Scheme Syllabus B Tech EE 3rd 4th1Document49 pages04 Scheme Syllabus B Tech EE 3rd 4th1B06Shifa FatimaNo ratings yet
- 52.1 Radioactivity Cie - Igcse - Physics - Ext Theory QPDocument10 pages52.1 Radioactivity Cie - Igcse - Physics - Ext Theory QPÅBanDonNo ratings yet
- Atm-Quiz 2-TEK (Odd)Document2 pagesAtm-Quiz 2-TEK (Odd)Aslıhan KayaNo ratings yet
- For The Candidates Admitted From The Academic Year 2018-2019 OnwardsDocument2 pagesFor The Candidates Admitted From The Academic Year 2018-2019 OnwardsPriyanka GandhiNo ratings yet
- Department of Metallurgical Engineering and Materials Science Time Table Spring Semester (Jan. - June) 2012Document2 pagesDepartment of Metallurgical Engineering and Materials Science Time Table Spring Semester (Jan. - June) 2012mohommedaamirNo ratings yet
- Copper Zinc Tin Sulfide-Based Thin-Film Solar CellsFrom EverandCopper Zinc Tin Sulfide-Based Thin-Film Solar CellsKentaro ItoNo ratings yet
- 2.0. Design, Protection and Sizing of Low Voltage Electrical Installations (Wiring) To IEE Wiring Regulations BS 7671 MS IEC (IEC) 60364 - 16&17.12.15Document2 pages2.0. Design, Protection and Sizing of Low Voltage Electrical Installations (Wiring) To IEE Wiring Regulations BS 7671 MS IEC (IEC) 60364 - 16&17.12.15Edison LimNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Compressive Strength of Research PaperDocument9 pagesPrediction of Compressive Strength of Research PaperTaufik SheikhNo ratings yet
- Internal Resistance To Corrosion in SHS - To Go On WebsiteDocument48 pagesInternal Resistance To Corrosion in SHS - To Go On WebsitetheodorebayuNo ratings yet
- My BaboogDocument1 pageMy BaboogMaral Habeshian VieiraNo ratings yet
- MSDS Buffer Solution PH 4.0Document5 pagesMSDS Buffer Solution PH 4.0Ardhy LazuardyNo ratings yet
- End-Of-Chapter Answers Chapter 7 PDFDocument12 pagesEnd-Of-Chapter Answers Chapter 7 PDFSiphoNo ratings yet
- WWW Ranker Com List Best-Isekai-Manga-Recommendations Ranker-AnimeDocument8 pagesWWW Ranker Com List Best-Isekai-Manga-Recommendations Ranker-AnimeDestiny EasonNo ratings yet
- CycleMax IntroDocument13 pagesCycleMax IntroIslam AtefNo ratings yet
- Core CompetenciesDocument3 pagesCore Competenciesapi-521620733No ratings yet
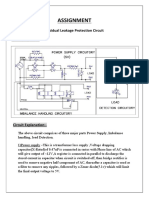
- Assignment: Residual Leakage Protection Circuit Circuit DiagramDocument2 pagesAssignment: Residual Leakage Protection Circuit Circuit DiagramShivam ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Accessoryd-2020-07-31-185359.ips 2Document20 pagesAccessoryd-2020-07-31-185359.ips 2Richard GarciaNo ratings yet
- Agma MachineDocument6 pagesAgma Machinemurali036No ratings yet
- Object Oriented ParadigmDocument2 pagesObject Oriented ParadigmDickson JohnNo ratings yet
- 123Document3 pages123Phoebe AradoNo ratings yet
- FS-1040 FS-1060DN: Parts ListDocument23 pagesFS-1040 FS-1060DN: Parts List1980cvvrNo ratings yet
- White Paper: 1 Definitive Guide To Data QualityDocument18 pagesWhite Paper: 1 Definitive Guide To Data QualityGonçalo MartinsNo ratings yet
- Table of Reinforcement Anchorage Length & Lap Length - Eurocode 2Document7 pagesTable of Reinforcement Anchorage Length & Lap Length - Eurocode 2NgJackyNo ratings yet
- CIPD L5 EML LOL Wk3 v1.1Document19 pagesCIPD L5 EML LOL Wk3 v1.1JulianNo ratings yet
- Chakir Sara 2019Document25 pagesChakir Sara 2019hiba toubaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Short-Term SchedulingDocument49 pagesChapter 2 Short-Term SchedulingBOUAZIZ LINANo ratings yet