0% found this document useful (0 votes)
341 views3 pagesReduction Formulas for Integral Calculus
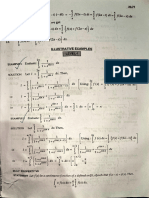
The document provides 25 fundamental formulae for integrals involving basic functions like polynomials, trigonometric functions, exponential functions, and their inverses. It also provides 8 formulae for hyperbolic functions and 8 reduction formulae for integrals of trigonometric functions with variable upper limits. The document concludes with 6 practice problems evaluating definite integrals using the reduction formulae.
Uploaded by
megazordallianxeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
341 views3 pagesReduction Formulas for Integral Calculus
The document provides 25 fundamental formulae for integrals involving basic functions like polynomials, trigonometric functions, exponential functions, and their inverses. It also provides 8 formulae for hyperbolic functions and 8 reduction formulae for integrals of trigonometric functions with variable upper limits. The document concludes with 6 practice problems evaluating definite integrals using the reduction formulae.
Uploaded by
megazordallianxeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd