Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1611-Article Text-4421-1-10-20171222
Uploaded by
salsabila JacobOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1611-Article Text-4421-1-10-20171222
Uploaded by
salsabila JacobCopyright:
Available Formats
Dangi et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics.
2017; 7(7):131-133
Available online on 25.12.2017 at http://jddtonline.info
Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics
Open Access to Pharmaceutical and Medical Research
© 2011-17, publisher and licensee JDDT, This is an Open Access article which permits unrestricted non-
commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited
Open Access Research Article
DOCKING STUDY OF CHRYSIN DERIVATIVES ON DIFFERENT TARGETS
FOR ANTICANCER ACTIVITY
Suresh Chand Dangi, Sudha Vengurlekar
Sri Aurobindo Institute of Pharmacy, Indore, India
E-mail address: suresh91dangi@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
Some anticancer molecules using natural flavonoid chrysin were designed and docking studies were performed using Molegro
Virtual Docker (MVD) software. Of the available crystal structures of the non- mutated Homo sapiens, five were selected for the
final docking studies. The docking results with selected crystal structures shown that designed legends forms hydrogen bonds with at
least two out of three key active site residues (Asp, Val and Lys). It also form hydrogen bonds to other active site residues, in
particular Glu. The average MolDock score and the MolDock Re-rank score were obtained as -156.704 Kcal/mol and-125.649
Kcal/mol respectively. The docking results shown that some molecules fit well in the active site and interact with the residues in the
active site which are crucial for their biological activity.
Cite this article as: Dangi SC, Vengurlekar S, Docking study of chrysin derivatives on different targets for anticancer activity,
Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics. 2017; 7(7):131-133
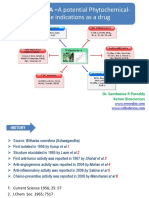
INTRODUCTION: MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Cancer is a group of diseases characterized by Designing of compounds
uncontrolled growth and multiplication of abnormal
New molecules were designed by combining chrysin
cells that invade and metastases to other parts of the
and cycloalkane derivatives. Four Molecules were
body1. Several techniques have been adopted for the
designed on the basis of literature of their biological
treatment and eradication of cancerous cells. These
response towards cancer cells (Figure 1)
techniques involved surgery, radiation, immunotherapy,
chemotherapy and chemoprevention. Ideal anticancer
drugs would eradicate cancer cells without harming
normal tissues. Chrysin, also known as 5, 7- Target Selection
dihydroxyflavone with an IUPAC name of 5, 7- Three targets (Table 1) were selected for performing
dihydroxy 2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one, belongs to the docking studies to check the binding affinity of designed
flavone sub-class of flavonoids. Its chemical structure is molecules with the target and to predict the potential
essentially based on a three ring nucleus with a phenyl molecules to be synthesized with the aim to have
ring attached to position 2 of the fused bicyclic and anticancer activity4.
rings. Flavonoids including flavones, flavonols, and
flavones possess various biological activities as Software
antioxidant, anticancer etc. chrysin as a flavonoids Ligand Preparation
shown activity for anticancer activity2.
The structures of Chrysin with cyclic compounds were
Binding of a small molecule (ligand) with a large converted into suitable chemical information using
molecule (protein) is called docking. Docking is the Chemdraw ultra v 10.0 (Cambridge software), copied to
process by which two molecules fit together in 3D Chem3D ultra v 10.0 to create a 3D model and, finally
space. Docking is a method which predicts the preferred subjected to energy minimization using molecular
orientation of one molecule to a second when bound to mechanics (MM2). The minimization was executed until
each other to form a stable complex3. the root mean square gradient value reached a value
smaller than 0.001kcal/mol5.
ISSN: 2250-1177 [131] CODEN (USA): JDDTAO
Dangi et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics. 2017; 7(7):131-133
O O
O O O
Cl
O
O
O Cl
O O
O O
HO O
O O O O O
OH O
Cl
O
O
O
Cl
O O
O O
Figure 1: Designed compounds
Protein Selection by X-ray diffraction, and resolution should be between
2.0-2.5Ao, it should contain a co-crystallized ligand; the
The selection of protein for docking studies is based
selected protein should not have any protein breaks in
upon several factors i.e. structure should be determined
their 3D structure.
Table 1: Selected anticancer drug targets with PDB ID
S. No. Name of anticancer target protein PDB ID 3D structure of target
Crystal structure of CphA N220G mutant with
1
inhibitor 18 3IOG
Crystal structure of a human cyclin-dependent
2 kinase 6 complex with a flavonol inhibitor,
1XO2
fisetin
Structure determinants of phosphoinositide 3-
3 1E8W
kinase inhibition
ISSN: 2250-1177 [132] CODEN (USA): JDDTAO
Dangi et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics. 2017; 7(7):131-133
Protein Preparation
All the X-ray crystal structures of the selected target
proteins were obtained from the RCSB Protein Data
Bank (http://www.rcsb.org/pdb). Subsequent to
screening for the above specific standards the resultant
protein targets.
Software Method Validation
Software method validation was performed in MVD
Molegro Virtual Docker 6.0 2013 and Marvin Sketch Figure 2: Biding affinity of Compound (a) with target
Product version 6.2.3 2013 were using Protein Data (where carbon is grey, oxygen is red, nitrogen is blue
Bank (PDB) protein 3IOG, 1XO2, 1E8W. and sulphur is yellow and hydrogen in white). Green
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION lines represent the hydrogen bonds in between the
ligand and the active site).
Dockings results reveals that compound no. 4 has shown
best affinity towards all the targets selected for the
study.
PDB code Ligand name MolDock Score Rerank Score HBond
3IOG Compound (a) -135.548(b) -106.292 -5.66085
Figure 3: Biding affinity of Compound (b) with target (where carbon is grey, oxygen is red, nitrogen is blue and sulphur is
yellow and hydrogen in white). Green lines represent the hydrogen bonds in between the ligand and the active site).
PDB code Ligand name MolDock Score Rerank Score HBond
1XO2 Compound (B) -155.357 -124.456 -3.68857
Figure 4: Biding affinity of Compound (b) with target (where carbon is grey, oxygen is red, nitrogen is blue and sulphur is
yellow and hydrogen in white). Green lines represent the hydrogen bonds in between the ligand and the active site).
PDB code Ligand name MolDock Score Rerank Score HBond
1E8W Compound (b) -126.682 -105.89 -4.50612
REFERENCES:
1. Ahmedin J, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun Molecules into a Protein Binding Site through Evolutionary
MJ, Cancer Statistics, CA, 2008, 58, 71–96. Programming, Proceedings of the Fourth International
2. Mohammed HA, Ba LA, Bhurkhloz T, Schumann E, Diesel Conference on Evolutionary Programming, 1995, 123-124.
B, Zapp J, Kiemer AK, Riesc, Hartmann RW, Hosny M, 4. Ramachandran GN, Sasisekharan V,) Conformation of
Jacob C, Facile synthesis of chrysin-derivatives with polypeptides and proteins, Adv Protein Chem, 1968, 23, 243-
promising activities as aromatase inhibitors, NPC, 2011, 6, 438.
31-34. 5. Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN,
3. Gehlhaar DK, Verkhivker G, Rejto PA, Fogel DB, Fogel LJ, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE, The Protein Data
Freer ST, Docking Conformationally Flexible Small Bank, Nucleic Acids Res, 2000, 24, 235-242.
ISSN: 2250-1177 [133] CODEN (USA): JDDTAO
You might also like
- Docking ManualDocument84 pagesDocking ManualGerman EsalasNo ratings yet
- BS1005 Computer Lab 1 - U1940636ADocument15 pagesBS1005 Computer Lab 1 - U1940636ADoug A. Hole100% (1)
- Introduction to Steroid Chemistry: The Commonwealth and International Library: a Course in Organic ChemistryFrom EverandIntroduction to Steroid Chemistry: The Commonwealth and International Library: a Course in Organic ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Practice 24 - PDB Cloning and Relocation Using DBCADocument11 pagesPractice 24 - PDB Cloning and Relocation Using DBCALogis M100% (1)
- Oracle 1Z0-083 - Simulado 1Document37 pagesOracle 1Z0-083 - Simulado 1ikki FenixNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry LettersDocument17 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry LettersAnonymous Rjh0ZA58No ratings yet
- Bioorganic Chemistry: SciencedirectDocument12 pagesBioorganic Chemistry: SciencedirectPooja NaikNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Presentation Ruturaj WarakeDocument22 pagesSynopsis Presentation Ruturaj WarakeRuturaj WarakeNo ratings yet
- QSAR Study and Molecular Design of Open-Chain Enaminones As Anticonvulsant AgentsDocument15 pagesQSAR Study and Molecular Design of Open-Chain Enaminones As Anticonvulsant AgentsDevi Dwi AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Van-Meer nrm2330Document13 pagesVan-Meer nrm2330Oyindrila SamantaNo ratings yet
- Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters: Sciverse SciencedirectDocument6 pagesBioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters: Sciverse SciencedirectMegha ParwaniNo ratings yet
- Vanmeer2008 PDFDocument13 pagesVanmeer2008 PDFaaron quiroaNo ratings yet
- Design Synthesis and Enzyme Inhibition Evaluation of Some NovelDocument18 pagesDesign Synthesis and Enzyme Inhibition Evaluation of Some NovelSami ZiaNo ratings yet
- Mori Et 2023Document24 pagesMori Et 2023pampetraNo ratings yet
- DFT Calculations and Docking Study On SesquiterpenDocument5 pagesDFT Calculations and Docking Study On SesquiterpenNimra Naveed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Magpusao 2010Document5 pagesMagpusao 2010Gabriel FenteanyNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Average Molecular Weight of Hydroxyethyl Starches by Diffusionordered NMR SpectrosDocument2 pagesDetermination of The Average Molecular Weight of Hydroxyethyl Starches by Diffusionordered NMR SpectrosDian Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- Bioorganic Chemistry: SciencedirectDocument8 pagesBioorganic Chemistry: SciencedirectMehreen ZakaNo ratings yet
- Iii V: Internal Organization of The CellDocument32 pagesIii V: Internal Organization of The CellAdrian FlorezNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences: Sheng-Pu Li, Wei-Ling Xie, Huai-Hong Cai, Ji-Ye Cai, Pei-Hui YangDocument7 pagesEuropean Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences: Sheng-Pu Li, Wei-Ling Xie, Huai-Hong Cai, Ji-Ye Cai, Pei-Hui YangDan R. A. VieiraNo ratings yet
- Nguyen. 2016. Anti-Inflammatory Terpenylated Coumarins From The Leaves of Zanthoxylum Schinifolium With A-Glucosidase Inhibitory ActivityDocument6 pagesNguyen. 2016. Anti-Inflammatory Terpenylated Coumarins From The Leaves of Zanthoxylum Schinifolium With A-Glucosidase Inhibitory ActivityshaniNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter 1Document53 pages09 - Chapter 1M Irfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Molecular Docking of 1-Benzoyl-3-Methylthiourea As Anti Cancer Candidate and Its Absorption, Distribution, and Toxicity PredictionDocument6 pagesMolecular Docking of 1-Benzoyl-3-Methylthiourea As Anti Cancer Candidate and Its Absorption, Distribution, and Toxicity PredictionAhmadNo ratings yet
- Art Hab 2Document11 pagesArt Hab 2Sabrinna Karen Cardodo CostaNo ratings yet
- Preprints201904 0262 v1Document18 pagesPreprints201904 0262 v1Tuan DuyNo ratings yet
- Molekular Docking Dengan Metode Molegro Virtual Docker Turunan Kalkon Sebagai AntimikrobaDocument9 pagesMolekular Docking Dengan Metode Molegro Virtual Docker Turunan Kalkon Sebagai AntimikrobaWilliam SmithNo ratings yet
- Chirality in Drug Action PDFDocument40 pagesChirality in Drug Action PDFAllen SodaNo ratings yet
- A Ring Expansion Strategy Towards Diverse Azaheterocycles: ArticlesDocument12 pagesA Ring Expansion Strategy Towards Diverse Azaheterocycles: ArticlesRohanNo ratings yet
- Tetrahedron Letters: A New Set of Orthogonal Protecting Groups On A Monosaccharide ScaffoldDocument3 pagesTetrahedron Letters: A New Set of Orthogonal Protecting Groups On A Monosaccharide Scaffoldmisranasrof9No ratings yet
- On The Electrophilic Reactivities of Acarbonyl Heterocylces and ArenesDocument7 pagesOn The Electrophilic Reactivities of Acarbonyl Heterocylces and ArenesFinn NelsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 LipidsDocument16 pagesChapter 26 LipidsVenkat Sreenivas Rao ChNo ratings yet
- 2006-CHM6108 - L1L2 HandoutDocument11 pages2006-CHM6108 - L1L2 Handoutaidar.seralinNo ratings yet
- 7922Document17 pages7922Aleksandar DimkovskiNo ratings yet
- Peptides As Molecular Imaging ProbesDocument3 pagesPeptides As Molecular Imaging Probesbiosynthesis12No ratings yet
- Bioorganic & Medicinal ChemistryDocument13 pagesBioorganic & Medicinal ChemistryTiến Dũng TrầnNo ratings yet
- Withaferyn ADocument41 pagesWithaferyn AAlexNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Fall 2020 Midterm Exam SolutionsDocument44 pagesBiochemistry Fall 2020 Midterm Exam SolutionsEren KayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Answers An Introduction To Medicinal Chemistry Patrick 4e Questions in The Book AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 6 Answers An Introduction To Medicinal Chemistry Patrick 4e Questions in The Book Answersnishi kNo ratings yet
- Acsmedchemlett 9b00642Document8 pagesAcsmedchemlett 9b00642Kasta GurningNo ratings yet
- Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry LettersDocument4 pagesBioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry LetterslucasgirioNo ratings yet
- Research Article Selaginella DoederleiniiDocument10 pagesResearch Article Selaginella DoederleiniiNimra Naveed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 1-Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Benzene-Ethanol Bearing 124-Triazole Derivatives As Potential Antimicrobial AgentsDocument8 pages1-Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Benzene-Ethanol Bearing 124-Triazole Derivatives As Potential Antimicrobial AgentsDiana VargasNo ratings yet
- 8 Electrozi Ion SelectiviDocument8 pages8 Electrozi Ion SelectiviOana Nicoleta LeoveanuNo ratings yet
- Docking AnalysisDocument7 pagesDocking AnalysisDIPANGKAR DUWARAHNo ratings yet
- MetabonomicsDocument8 pagesMetabonomicsapi-19793040No ratings yet
- Scipharm 86 00031Document21 pagesScipharm 86 00031aruna aNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences: Meng Li, Yunjing Li, Weiwei Liu, Rongli Li, Cuiying Qin, Nan Liu, Jing HanDocument9 pagesEuropean Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences: Meng Li, Yunjing Li, Weiwei Liu, Rongli Li, Cuiying Qin, Nan Liu, Jing Hanaulia nova kusumaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Metabolism/ BiotransformationDocument69 pagesMetabolism/ Biotransformationshuklasanskar2003No ratings yet
- 1.4 CarbohydratesDocument2 pages1.4 CarbohydrateslaranbazziiNo ratings yet
- Section 1 General Properties-1Document850 pagesSection 1 General Properties-1anaNo ratings yet
- Study of Prodrugs in Problem Related To Bioavailability and Elegance of FormulationDocument23 pagesStudy of Prodrugs in Problem Related To Bioavailability and Elegance of Formulationamit vermaNo ratings yet
- Macrolide Antibiotics: Binding Site, Mechanism of Action, ResistanceDocument15 pagesMacrolide Antibiotics: Binding Site, Mechanism of Action, ResistancevitulNo ratings yet
- Development of Potent and Selective PfCLK3 Inhibitors Based On GSK-TCMDC151 As A New Class of Antimalarials v1Document18 pagesDevelopment of Potent and Selective PfCLK3 Inhibitors Based On GSK-TCMDC151 As A New Class of Antimalarials v1Shashank SharanNo ratings yet
- Molecules: Characterization of Flavonoid Subgroups and Hydroxy Substitution by HPLC-MS/MSDocument14 pagesMolecules: Characterization of Flavonoid Subgroups and Hydroxy Substitution by HPLC-MS/MSturani janosNo ratings yet
- Physicochemical Properties Part 1Document34 pagesPhysicochemical Properties Part 1arigbede atinukeNo ratings yet
- Bioorganic Chemistry: SciencedirectDocument11 pagesBioorganic Chemistry: SciencedirectWalid Ebid ElgammalNo ratings yet
- Glyc o QuizzdsadsadsadsaDocument15 pagesGlyc o QuizzdsadsadsadsaEmilio MelvyNo ratings yet
- Articulo PDFDocument7 pagesArticulo PDFJulii TrochezNo ratings yet
- Engineering CAR-T Cells To Activate Small-MoleculeDocument24 pagesEngineering CAR-T Cells To Activate Small-MoleculeKudelko MatNo ratings yet
- Polymorphism in CocrystalsDocument15 pagesPolymorphism in CocrystalsBenjamín Marc Ridgway de SassouNo ratings yet
- 23-04-2021-1619175914-8-Ijans-5. Ijans - Synthesis, Anticancer, and Antioxidant Activities of New Azomethine Dye and Its Co - III - ComplexDocument10 pages23-04-2021-1619175914-8-Ijans-5. Ijans - Synthesis, Anticancer, and Antioxidant Activities of New Azomethine Dye and Its Co - III - Complexiaset123No ratings yet
- Essential Molecular BiologyDocument19 pagesEssential Molecular BiologySandra JelynNo ratings yet
- Oxetane PresentationDocument60 pagesOxetane PresentationEena BarmanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics & Acidity: Objectives GoalDocument21 pagesThermodynamics & Acidity: Objectives GoalNahokoSatomiNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Pirido 5Document39 pagesJurnal Pirido 5salsabila JacobNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Acuan 3Document33 pagesJurnal Acuan 3salsabila JacobNo ratings yet
- Fraksinasi IsolasiDocument40 pagesFraksinasi Isolasisalsabila JacobNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Levels Furosemide Stocks and Tablet Generic Name Trade in Spectrophotometry UltravioletDocument8 pagesComparison of Levels Furosemide Stocks and Tablet Generic Name Trade in Spectrophotometry Ultravioletsalsabila JacobNo ratings yet
- 151 ArticleText 545 1 10 20220314Document12 pages151 ArticleText 545 1 10 20220314salsabila JacobNo ratings yet
- Sympo 4 - Prof. WinDocument23 pagesSympo 4 - Prof. Winsalsabila JacobNo ratings yet
- Espript/Endscript: Extracting and Rendering Sequence and 3D Information From Atomic Structures of ProteinsDocument4 pagesEspript/Endscript: Extracting and Rendering Sequence and 3D Information From Atomic Structures of ProteinsRigers ZalliNo ratings yet
- Kaid Seloua-PdbDocument9 pagesKaid Seloua-Pdbseloua kaidNo ratings yet
- Multitenant MAADocument74 pagesMultitenant MAADida UserNo ratings yet
- SeLnIkRaj - Ligand ScoutDocument26 pagesSeLnIkRaj - Ligand ScoutselnikrajNo ratings yet
- Reverse PharmacognosyDocument15 pagesReverse PharmacognosyJesús GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User GuideDocument700 pagesOracle Database Backup and Recovery User GuideMichael J GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Modeller I IntroductionDocument12 pagesModeller I IntroductionjesusNo ratings yet
- Spartan Student OverviewDocument136 pagesSpartan Student OverviewBianca AlinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Protein Data Bank FormatDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Protein Data Bank Formatmapix iNo ratings yet
- Biopython Org DIST Docs Tutorial Tutorial HTMLDocument267 pagesBiopython Org DIST Docs Tutorial Tutorial HTMLAdriano Marini Flmkr ScrwtrNo ratings yet
- Oracle Examquestions 1z0-083 v2020-04-14 by William 46qDocument27 pagesOracle Examquestions 1z0-083 v2020-04-14 by William 46qtusharnemadeNo ratings yet
- Dali TutorialDocument19 pagesDali TutorialADITI KONARNo ratings yet
- How To Use The PDB: 1) What Is Protein Data Bank (PDB) ?Document4 pagesHow To Use The PDB: 1) What Is Protein Data Bank (PDB) ?Sumit HalderNo ratings yet
- MD Simulation Tutorial in GromacsDocument9 pagesMD Simulation Tutorial in GromacsSimanta PaulNo ratings yet
- Protein Data BankDocument5 pagesProtein Data Bankwilliam919No ratings yet
- 5.plug & UnPlug DatabaseDocument16 pages5.plug & UnPlug DatabaseAns SembiringNo ratings yet
- PDBepisaDocument15 pagesPDBepisaProject Wyzon BioticsNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument365 pagesTutorialToxicNo ratings yet
- Ramachandran ScoreDocument13 pagesRamachandran Scorebianca.lujan.pereiraNo ratings yet
- Siridevi Et Al., 2019 Starter MicrobiomaDocument8 pagesSiridevi Et Al., 2019 Starter MicrobiomaYon SadisticNo ratings yet
- Flex EM TutorialDocument4 pagesFlex EM Tutorialha_saoxetNo ratings yet
- Spec Tra: The Use of Computers and The Internet in Chemistry ResearchDocument12 pagesSpec Tra: The Use of Computers and The Internet in Chemistry ResearchGrishma Dixit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Discovery Studio VisualizerDocument31 pagesDiscovery Studio VisualizerbitMorph3rNo ratings yet
- Oracle 23c 04Document55 pagesOracle 23c 04cpcNo ratings yet
- H3-Rules - Identification of CDR-H3 Structures in AntibodiesDocument10 pagesH3-Rules - Identification of CDR-H3 Structures in Antibodiesricky_connollyNo ratings yet
- PyMol ReferenceDocument2 pagesPyMol Referenceshu_panNo ratings yet