Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enzymes - Notes
Uploaded by
hiba.alkubaisyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Enzymes - Notes
Uploaded by
hiba.alkubaisyCopyright:
Available Formats
ENZYMES - GRADE – 9 NOTES
Catalyst: is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction and is not
changed by the reaction.
Enzyme: is a protein that functions as a biological catalyst.
Enzymes, like catalysts, can be used over and over again because they are not used
up during the reaction and only a small amount is needed to speed the reaction up.
The enzymes and substrate molecules have complementary shapes (like
adjacent pieces of a jigsaw) so they fit together.
Substrate: the substance on which the enzyme acts.
Products: the molecules produced.
Anabolic reaction: reactions in which large molecules are built up from smaller
molecules.
Catabolic reaction: reactions that splits large molecules into smaller ones.
Enzyme-substrate complex: is formed temporarily when the enzyme combines with
the substrate.
Enzymes are specific, this means simply that an enzyme which normally acts on one
substance will not act on a different one.
Q. Explain why the shape of an enzyme is important.3
correct ref to active site ;
enzyme must be complementary shape to, substrate / alcohol ;
to make enzyme – substrate complex / to allow substrate to bind to
enzyme ;
ref to only fits one substrate / specific to one substrate ;
The enzyme has a shape called the active site, which exactly fits the substances on
which it acts. The shape of the active site of the enzyme molecule and the substrate
molecules are complementary.
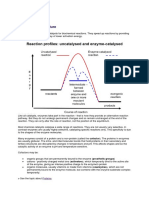
Effect of temperature:
The rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction increases as the temperature increases.
However, at high temperatures the rate decreases again because the enzyme
becomes denatured and can no longer function as a biological catalyst.
As the temperature is increased, the molecules gain more kinetic energy, so they
move faster and there is a greater chance of collisions happening. Therefore the rate
of reaction increases.
Above the optimum temperature the reaction slows down. This is because enzyme
molecules are proteins. Proteins molecules start to lose their shape at higher
temperatures, so the active site becomes deformed.
Substrate molecules cannot fit together with the enzyme, stopping the reaction.
(Denaturation)
Q. Explain why an increase in temperature causes an increase in
enzyme activity.3
increased kinetic energy ;
molecules move faster ;
increased frequency of collisions ;
increased number of successful collisions ;
Effects of pH:
Changes in pH alter the shape of an enzyme’s active site. Different enzymes work
best at different pH values.
The optimum pH for an enzyme depends on where it normally works. For example,
intestinal enzymes have an optimum pH of about 7.5, but stomach enzymes have
an optimum pH of about 2.
Each enzyme has an optimum pH, if this pH changes, the shape of the active site of
the enzyme is changed (Denature), thus the substrate will not be able to fit in it, and
the enzyme becomes useless
You might also like
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- EnzymesDocument4 pagesEnzymesii15021No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument22 pagesEnzymesRohan PaneruNo ratings yet
- Gibbs Free Energy and Metabolism RegulationDocument29 pagesGibbs Free Energy and Metabolism RegulationMaya AwadNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Structure, Function and Factors Affecting ActivityDocument5 pagesEnzymes: Structure, Function and Factors Affecting Activitytiyf mojaleedNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument7 pagesEnzymesMahin TayyabNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ChemistryDocument9 pagesEnzyme ChemistryVictor OmoloNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Function, Structure, and Factors Affecting ActivityDocument5 pagesEnzymes: Function, Structure, and Factors Affecting ActivitySameer ButtNo ratings yet
- General Biology: Peralta III Edwin C. STEM-GalileoDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology: Peralta III Edwin C. STEM-GalileoSavage CabbageNo ratings yet
- AP BIO Febraury Break With AnswersDocument12 pagesAP BIO Febraury Break With AnswersMehak BectorNo ratings yet
- STPM BIOLOGY Control in CellsDocument35 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY Control in Cellswkwhui100% (1)
- Biological Catalysts: Enzymes and MetabolismDocument2 pagesBiological Catalysts: Enzymes and MetabolismAlimm12No ratings yet
- Enzymes: Biology Lecture Prepared By: Waleed Zahoor Team Roshni Step-Up PakistanDocument11 pagesEnzymes: Biology Lecture Prepared By: Waleed Zahoor Team Roshni Step-Up PakistanRabia KhalilNo ratings yet
- LMRN Molecules of LifeDocument2 pagesLMRN Molecules of LifeVic AuNo ratings yet
- Bio Sem 1Document123 pagesBio Sem 1HALFAH BT HASSANNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument23 pagesEnzymessamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Enzymes PDFDocument5 pagesModule 1 - Enzymes PDFJenny GoNo ratings yet
- What Are Enzymes?: E E E EDocument15 pagesWhat Are Enzymes?: E E E EFarhana MuradNo ratings yet
- Effect of Temperature on Enzyme ActivityDocument5 pagesEffect of Temperature on Enzyme ActivityKIARA B SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Test Reaction Biochem Report Group 12Document7 pagesEnzymatic Test Reaction Biochem Report Group 12almira garciaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Reading in ScienceDocument3 pagesEnzymes Reading in SciencecinsssNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Biological Catalysts Speed Up Chemical ReactionsDocument2 pagesEnzymes: Biological Catalysts Speed Up Chemical ReactionsKirusaanth SathiyathasanNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument43 pagesEnzymesMaryam SabirNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 EnzymesDocument4 pagesCh-5 EnzymesMahamudul HassanNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Structure: OxidoreductasesDocument7 pagesEnzyme Structure: OxidoreductasesSamuel MutungaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Mode of Action and Factors Affecting RateDocument6 pagesEnzymes: Mode of Action and Factors Affecting RateNamra MazherNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument31 pagesEnzymemiriam harriottNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument40 pagesEnzymesVeronica HanyNo ratings yet
- Enzymes.Document9 pagesEnzymes.42h47n5zvrNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument1 pageEnzymesKarim El NefeidiNo ratings yet
- Enzyme and Its Substrate and The Formation of A ProductDocument4 pagesEnzyme and Its Substrate and The Formation of A ProductMehul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Biological Catalysts that Speed Up ReactionsDocument6 pagesEnzymes: Biological Catalysts that Speed Up ReactionsSarah Farhah2000100% (1)
- Chapter 3: Enzymes: SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 3: Enzymes: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter EnzymesDocument2 pagesChapter EnzymesJaved SohawonNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Bio IgcseDocument7 pagesChap 5 Bio Igcseananya.arumugarajanNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Lab: Investigating Factors that Impact Reaction RateDocument15 pagesEnzyme Lab: Investigating Factors that Impact Reaction RateAshalee JonesNo ratings yet
- How Do Enzymes Speed Up Chemical Reactions?: Active SiteDocument2 pagesHow Do Enzymes Speed Up Chemical Reactions?: Active SitepbNo ratings yet
- How Enzymes Catalyze ReactionsDocument296 pagesHow Enzymes Catalyze ReactionsSureshkumaryadavNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Enzyme LabDocument25 pagesGrade 12 Enzyme LabKrystalLovejoyNo ratings yet
- Dr. Kumari's Online Class on Enzyme MechanismsDocument13 pagesDr. Kumari's Online Class on Enzyme MechanismsPoonam ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Catalysis: Salahaddin-University-Erbil College of Education Chemistry DepartmentDocument11 pagesEnzyme Catalysis: Salahaddin-University-Erbil College of Education Chemistry DepartmentZana EdrisNo ratings yet
- Enzymes PPT BioDocument22 pagesEnzymes PPT Biovoyav37617No ratings yet
- Enzymes: Mechanism of Enzymatic ActionDocument5 pagesEnzymes: Mechanism of Enzymatic ActionMoon PhạmNo ratings yet
- Enzyme StructureDocument17 pagesEnzyme Structureام احمدNo ratings yet
- St. Mary's College of Tagum Enzyme ActivityDocument6 pagesSt. Mary's College of Tagum Enzyme ActivityHarvey Q. JontongNo ratings yet
- S.5 EnzymesDocument16 pagesS.5 Enzymesmusokelukia6No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument3 pagesEnzymesChampika NiranjaniNo ratings yet
- Module 5. EnzymesDocument15 pagesModule 5. EnzymesThe GreatNo ratings yet
- Chidrawi M1 C PDFDocument33 pagesChidrawi M1 C PDFZA AustraliaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesUsman AhmadNo ratings yet
- L8_EnzymesDocument26 pagesL8_Enzymesayaanali.voraNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument20 pagesEnzymesRICHARD NESTORNo ratings yet
- Module 11: EnzymesDocument3 pagesModule 11: EnzymesMariam EskandariNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument10 pagesEnzymesSanchit Dhyani100% (1)
- 1.2 EnzymesDocument4 pages1.2 EnzymesMohammed RagabNo ratings yet
- Notes #5 - EnzymesKey CleanDocument10 pagesNotes #5 - EnzymesKey CleanLanz MoenNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument10 pagesEnzymeszaydharoon419No ratings yet
- Enzymes 1Document6 pagesEnzymes 1zarszNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 3.1 Movement of Subtances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument3 pagesWORKSHEET 3.1 Movement of Subtances Across The Plasma MembraneFadhliana UzalliNo ratings yet
- Deepmind's Ai Predicts Structures For A Vast Trove of ProteinsDocument1 pageDeepmind's Ai Predicts Structures For A Vast Trove of ProteinsLuis RomeroNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument41 pagesNucleic Acid MetabolismPavani AkkalaNo ratings yet
- Sarcopenia, Frailty and Their Prevention by ExerciseDocument22 pagesSarcopenia, Frailty and Their Prevention by ExerciseJoe PolancoNo ratings yet
- G9 STE Q3 Biotechnology ReviewerDocument9 pagesG9 STE Q3 Biotechnology ReviewerJoyz Etneilas ArguillesNo ratings yet
- General PharmacologyDocument76 pagesGeneral PharmacologyMiyuru HasarangaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument1 pageAmino Acids and ProteinsQuang OngNo ratings yet
- PROTEASYLDocument4 pagesPROTEASYLAlberto Espinosa HernándezNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0022202 X 17332761Document9 pagesPi Is 0022202 X 17332761Riefka Ananda ZulfaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of The RH Antigens: Use Only. For PersonalDocument14 pagesMolecular Biology of The RH Antigens: Use Only. For PersonaldeviNo ratings yet
- Initiation 3 Defined Step of Transcription Initiation 1st StepDocument1 pageInitiation 3 Defined Step of Transcription Initiation 1st StepSivatharsini ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Signs of Inflammation and the Cellular MembraneDocument2 pagesSigns of Inflammation and the Cellular MembraneKathleen NocheNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4 Part 1 Last Minute Revision ReallyacademicsDocument67 pagesBiology Unit 4 Part 1 Last Minute Revision ReallyacademicsWill AndyNo ratings yet
- Transverse Urea-Gradient Gel Electrophoresis UNIT 7.4 BASIC PROTOCOLDocument13 pagesTransverse Urea-Gradient Gel Electrophoresis UNIT 7.4 BASIC PROTOCOLNancy Marianna Muñoz ValeraNo ratings yet
- Protoplasm MCQDocument41 pagesProtoplasm MCQBiozeneca classesNo ratings yet
- Vaksin Influenza OverviewDocument27 pagesVaksin Influenza OverviewMaria Astika DewiNo ratings yet
- Poster Nicole AltomareDocument1 pagePoster Nicole Altomaresagun maharjanNo ratings yet
- The main functions and structure of centrioles in cell divisionDocument2 pagesThe main functions and structure of centrioles in cell divisiontherese lamelaNo ratings yet
- Monogastric Digestive SystemDocument25 pagesMonogastric Digestive SystemMae Sntg OraNo ratings yet
- Cells Organelles W KSTDocument3 pagesCells Organelles W KSTJay-r Valdez100% (1)
- Gene Silencing Gene Silencing: Niranjana.S.Karandikar Msc-I Roll No.12Document21 pagesGene Silencing Gene Silencing: Niranjana.S.Karandikar Msc-I Roll No.12Niranjana KarandikarNo ratings yet
- Prelim Oral ExamDocument3 pagesPrelim Oral ExamJP2001No ratings yet
- MCQ PDF 10 AgbDocument2 pagesMCQ PDF 10 Agbtarun chourhaNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 7 Respiration, Muscles and The Internal Environment - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelDocument11 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 7 Respiration, Muscles and The Internal Environment - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelYashodya WimalagunasekaraNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular BlockersDocument15 pagesNeuromuscular BlockersBharane DharranNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatic Tools and Guideline For PCR Primer DesignDocument5 pagesBioinformatic Tools and Guideline For PCR Primer DesignDeepak Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument20 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelY. PurwandariNo ratings yet
- Uncovering The Mechanisms of Ranunculus Ternatus Against Breast Cancer Based On Network Pharmacology and Molecular DockingDocument13 pagesUncovering The Mechanisms of Ranunculus Ternatus Against Breast Cancer Based On Network Pharmacology and Molecular DockingHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet
- Assay Development Final RevisedDocument38 pagesAssay Development Final RevisedvershaparchaNo ratings yet
- Introductory Activities: Case StudiesDocument16 pagesIntroductory Activities: Case StudiesormattNo ratings yet