Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Third Space Learning Parallel and Perpendicular Lines GCSE Worksheet
Uploaded by
Ayana KhudaiberganovaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Third Space Learning Parallel and Perpendicular Lines GCSE Worksheet
Uploaded by
Ayana KhudaiberganovaCopyright:
Available Formats
GCSE Maths Revision | Algebra
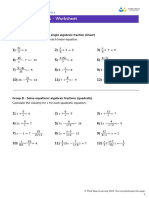
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines - Worksheet
Skill
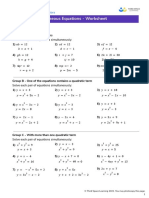
Group A - Parallel Lines
State the equation of a line that is parallel to the given equation.
1) 𝑦 = 2𝑥 2) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 + 5 3) 𝑦 = 7𝑥 − 3
1
4) 𝑦 = 2
𝑥+4 5) 𝑦 =− 𝑥 + 3 6) 𝑦 =− 5𝑥 − 3
𝑥
7) 𝑦 = 6 − 𝑥 8) 𝑦 = 3 − 2𝑥 9) 𝑦 = 5
+7
10) 2𝑦 − 9 = 𝑥 11) 3𝑦 + 4𝑥 = 10 12) 2(𝑥 − 𝑦) = 15
Group B - Perpendicular Lines
State the gradient that is perpendicular to the given equation.
1) 𝑦 = 𝑥 2) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 3) 𝑦 = 6𝑥 + 1
1
4) 𝑦 = 2
𝑥 5) 𝑦 =− 3𝑥 6) 𝑦 =− 2𝑥 + 7
1 2
7) 𝑦 =− 5
𝑥 8) 𝑦 = 5
𝑥 9) 𝑦 = 0. 6𝑥 + 0. 25
1 3
10) 𝑦 = 1 2
𝑥+3 11) 𝑦 =− 2 4
𝑥 12) 𝑦 =− 3. 6𝑥 + 5
Group C - Parallel or Perpendicular
Show that the two straight line equations are parallel, perpendicular or neither.
1) 𝑦 = 2𝑥 + 4 2) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 + 3 3) 𝑦 =− 2𝑥
1
𝑦 = 2𝑥 + 9 𝑦 =− 𝑥 + 3 𝑦= 2
𝑥
4) 𝑦 = 3𝑥 + 5 5) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 + 6 6) 𝑦=4−𝑥
𝑦 = 3 + 5𝑥 2𝑦 = 8𝑥 + 18 𝑦=𝑥−4
2
7) 𝑦= 3
𝑥+2 8) 3𝑦 = 4𝑥 + 1 9) 𝑥+𝑦=1
3 1
𝑦=6− 𝑥 𝑦 =− 12
𝑥+8 𝑥−𝑦=1
2
𝑥
10) 3𝑦 = 6 − 2
11) 𝑦 − 0. 6𝑥 = 17 12) 5𝑦 =− 2𝑥 + 6
𝑥 3
5𝑦 = 10 − 𝑦= 5
𝑥 + 14 𝑦 = 2. 5𝑥 + 7
2
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 1
GCSE Maths Revision | Algebra
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines - Worksheet
Applied
1) a) Given that the two lines A and B are parallel and the equation of line A is
𝑦 = 3 + 𝑥, state the equation of line B.
b) Show that line C is perpendicular to lines A and B.
2) a) Use the lines 𝑦 = 𝑥 and 𝑦 =
1
4
𝑥 to state the value of 𝑚 for the line 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥.
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 2
b) Draw the line that is perpendicular to the line 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 at the origin using your
answer to part a) to help you.
3) a) Line A is parallel to the 𝑥 axis. State the equation of line A.
b) Line B is perpendicular to line A at the point (4,5). State the equation of line B.
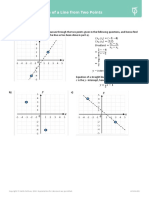
4) a) Construct the perpendicular to the line 𝑦 =
1
3
𝑥 + 1 on the set of axes below
going through the coordinate (9,4).
b) Hence calculate the gradient of the perpendicular.
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 3
GCSE Maths Revision | Algebra
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines - Exam Questions
1) (a) The line A is the tangent to the circle of centre 𝑂. The tangent
meets the circle at the coordinate (4,4). Calculate the gradient of
the tangent.
….……………
(2)
(b) Line B is parallel to the 𝑥 axis going through the point (4,4).
State the coordinate P.
….……………
(1)
(3 marks)
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 4
2) (a) The equation of a line A is 2y+4x=11. Another line B is parallel
to line A. What is the gradient of line B? Circle the correct
answer.
….……………
(1)
(b) Line C is perpendicular to line A. What is the gradient of line C?
Circle the correct answer.
….……………
(1)
(2 marks)
3) Two lines A and B are perpendicular. They intersect at the point
P. Calculate the coordinate P.
….……………
(8)
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 5
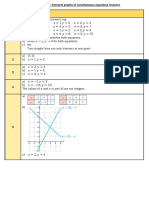
4) Show that the shape ABCD is a square using parallel and
perpendicular lines.
….……………
(8)
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 6
GCSE Maths Revision | Algebra
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines - Answers
Question Answer
Group A Skill Questions
State the equation of a line that is parallel
to the given equation.
1) 𝑦 = 2𝑥 1) 𝑦 = 2𝑥 + 𝑐
2) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 + 5 2) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 + 𝑐
3) 𝑦 = 7𝑥 − 3 3) 𝑦 = 7𝑥 + 𝑐
1
4) 𝑦 =
1
𝑥+4 4) 𝑦 = 2
𝑥+𝑐
2
5)𝑦 =− 𝑥 + 3 5) 𝑦 =− 𝑥+𝑐
6) 𝑦 =− 5𝑥 − 3 6) 𝑦 =− 5𝑥 + 𝑐
7) 𝑦 = 6 − 𝑥 7) 𝑦 =− 𝑥+𝑐
8) 𝑦 = 3 − 2𝑥 8) 𝑦 =− 2𝑥 + 𝑐
1
9) 𝑦 =
𝑥
+7 9) 𝑦 = 5
𝑥+𝑐
5
1
10) 2𝑦 − 9 = 𝑥 10) 𝑦 = 2
𝑥+𝑐
11) 3𝑦 + 4𝑥 = 10 11) 𝑦 =−
4
𝑥+𝑐
3
12) 2(𝑥 − 𝑦) = 15
12) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 𝑐
Group B State the gradient that is perpendicular to
the given equation. 1) 𝑛 =− 1
1) 𝑦 = 𝑥 2) 𝑛 =−
1
4
2) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 3) 𝑛 =−
1
6
3) 𝑦 = 6𝑥 + 1
1
4) 𝑛 =− 2
4) 𝑦 = 𝑥 1
2 5) 𝑛 = 3
5) 𝑦 =− 3𝑥 1
6) 𝑦 =− 2𝑥 + 7 6) 𝑛 = 2
7) 𝑦 =−
1
𝑥 7) 𝑛 = 5
5 5
2 8) 𝑛 =−
8) 𝑦 = 5
𝑥 2
5
9) 𝑦 = 0. 6𝑥 + 0. 25 9) 𝑛 =− 3
2
10) 𝑦 = 1
1
𝑥 + 3 10) 𝑛 =− 3
2
4
11) 𝑦 =− 2
3
𝑥 11) 𝑛 = 11
4
5
12) 𝑦 =− 3. 6𝑥 + 5 12) 𝑛 = 18
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 7
GCSE Maths Revision | Algebra
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines - Answers
Question Answer
Group C Skill Questions
Show that the two straight line equations
are parallel, perpendicular or neither.
1) 𝑦 = 2𝑥 + 4, 𝑦 = 2𝑥 + 9 1) Parallel
2) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 + 3, 𝑦 =− 𝑥 + 3 2) Neither
3) 𝑦 =− 2𝑥, 𝑦 =
1
𝑥 3) Perpendicular
2
4) 𝑦 = 3𝑥 + 5, 𝑦 = 3 + 5𝑥 4) Neither
5) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 + 6, 2𝑦 = 8𝑥 + 18 5) Parallel
6) 𝑦 = 4 − 𝑥, 𝑦 = 𝑥 − 4 6) Perpendicular
2 3
7) 𝑦 = 3
𝑥 + 2, 𝑦=6− 2
𝑥 7) Perpendicular
1
8) 3𝑦 = 4𝑥 + 1, 𝑦 =− 12
𝑥+8 8) Neither
9) 𝑥 + 𝑦 = 1, 𝑥−𝑦=1 9) Perpendicular
𝑥 𝑥
10) 3𝑦 = 6 − 2
, 5𝑦 = 10 − 2
10) Neither
11) 𝑦 − 0. 6𝑥 = 17, 𝑦 =
3
𝑥 + 14 11) Parallel
5
12) 5𝑦 =− 2𝑥 + 6, 𝑦 = 2. 5𝑥 + 7 12) Perpendicular
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 8
GCSE Maths Revision | Algebra
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines - Answers
Question Answer
Applied Questions
1) a) Given that the two lines A and B are parallel a) Gradient of line B is 1
and the equation of line A is 𝑦 = 3 + 𝑥, Y-intercept of line B is -2
calculate the equation of line B. 𝑦=𝑥−2
b) b) Gradient of line C is -1
Show that line C is perpendicular to lines A 1 ×− 1 =− 1
and B. The lines are perpendicular as
the product of their gradients
is equal to -1..
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 9
1
2) a) Use the lines 𝑦 = 𝑥 and 𝑦 = 4
𝑥 to state the a)
value of 𝑚 for the line 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥.
b) Draw the line that is perpendicular to the line b) The gradient of the
𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 at the origin, using your answer to part
perpendicular line n is equal
a) to help you. 1
to 𝑛 =− 1 ÷ 2
=− 2
The y intercept is 0.
3) a) Line A is parallel to the 𝑥 axis. State the a) 𝑦 = 5
equation of line A.
b) Line B is perpendicular to line A at the point b) 𝑥 = 4
(4,5). State the equation of line B.
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 10
4) a) Construct the perpendicular bisector to the line a)
1
𝑦= 3
𝑥 + 1 on the set of axes below going
through the coordinate (9,4).
Hence calculate the gradient of the 1
b) b) 𝑛 =− 1 ÷ =− 1 × 3 =− 3
perpendicular bisector. 3
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 11
GCSE Maths Revision | Algebra
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines - Answers
Question Answer
Exam Questions
1) (a) The line A is the tangent to the circle (a) 𝑚 = 4−0
= 1 (1)
4−0
of centre 𝑂. The tangent meets the 𝑛 =− 1 ÷ 1 =− 1 (1)
circle at the coordinate (4,4).
Calculate the gradient of the tangent.
(b) Line B is parallel to the 𝑥 axis going (b) (− 4, 4) (1)
through the point (4,4). State the
coordinate P.
2) (a) The equation of a line A is (a) -2 (1)
2y+4x=11. Another line B is parallel
to line A. What is the gradient of line
B? Circle the correct answer.
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 12
(b) Line C is perpendicular to line A. (b) 1 (1)
2
What is the gradient of line C? Circle
the correct answer.
3) Two lines A and B are perpendicular. Line B: (1)
6−0 1
They intersect at the point P. Gradient 𝑚 = =−
0−12 2
Calculate the coordinate P. Y-intercept 𝑐 = 6
(1)
1
Line B equation: 𝑦 =− 2
𝑥+ 6
Line A: (1)
1
Gradient 𝑛 =− 1 ÷− 2
=2
Y-intercept 𝑐 = 0
(1)
Line A equation: 𝑦 = 2𝑥
Coordinate P:
(1)
(1)
(1)
When 𝑥 = 2. 4,
𝑦 = 2 × 2. 4 = 4. 8
P=(2.4,4.8) (1)
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 13
4) Show that the shape ABCD is a Line AB:
square using parallel and 𝑦 =− 𝑥 + 3 or 𝑦 = 3 − 𝑥 (1)
perpendicular lines.
Line BC:
𝑦=𝑥−3 (1)
Line CD:
𝑦 =− 𝑥 − 3 (1)
Line AD:
𝑦=𝑥+3 (1)
A square has 2 sets of parallel sides: (1)
Line AB and CD have the same gradient and
so they are parallel.
Line BC and AD have the same gradient and
so they are parallel.
A square contains four 90 ° angles:
(2)
Line AB and BC are perpendicular as
1 ×− 1 =− 1 (the product of their
gradients is -1)
Line BX and CD are perpendicular
1 ×− 1 =− 1 (the product of their
gradients is -1)
Line CD and AD are perpendicular as
1 ×− 1 =− 1 (the product of their
gradients is -1)
Line AD and AB are perpendicular as
1 ×− 1 =− 1 (the product of their
gradients is -1)
The diagonals are the same length:
AC=BD=6 units
(1)
Therefore ABCD is a square .
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 14
Do you have KS4 students who need additional support in maths?
Our specialist tutors will help them develop the skills they need to succeed at GCSE in weekly one to one online
revision lessons. Trusted by secondary schools across the UK.
Visit thirdspacelearning.com to find out more.
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 15
You might also like
- Past Year SPM Vectors QuestionsDocument6 pagesPast Year SPM Vectors QuestionsAnonymous wksd8qcaZ50% (2)
- Third Space Learning Solving Equations GCSE WorksheetDocument6 pagesThird Space Learning Solving Equations GCSE WorksheetZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- SCI101SC - PHA101SC - (B) - Assessment - 202101 - Joy and FisherDocument6 pagesSCI101SC - PHA101SC - (B) - Assessment - 202101 - Joy and FisherAhmed Sami YounisNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Solving Linear Equations GCSE Worksheet 1Document8 pagesThird Space Learning Solving Linear Equations GCSE Worksheet 1erin zietsmanNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Quadratic Simultaneous Equations GCSE Worksheet 1Document9 pagesThird Space Learning Quadratic Simultaneous Equations GCSE Worksheet 1Sabrin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Equations and Subject of The Formula Worksheet With SolutionsDocument11 pagesEquations and Subject of The Formula Worksheet With SolutionsCamille ComasNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Completing The Square GCSE WorksheetDocument11 pagesThird Space Learning Completing The Square GCSE Worksheetisaaceden24No ratings yet
- Differential Calculus Practice TestDocument8 pagesDifferential Calculus Practice Testchirantha150No ratings yet
- Seeta High School Post - 2023 S.6 Pure Mathematics Paper 1Document3 pagesSeeta High School Post - 2023 S.6 Pure Mathematics Paper 1vanessablessed999100% (1)
- XII Math - 2Document6 pagesXII Math - 2M A T T H Y D E NNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Quadratic Graphs GCSE WorksheetDocument15 pagesThird Space Learning Quadratic Graphs GCSE WorksheetZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- P3 JAN 21 Revision Worksheet All ChaptersDocument3 pagesP3 JAN 21 Revision Worksheet All ChaptersSheikh HassanNo ratings yet
- Test 7 SMKCH Ques&AnsDocument8 pagesTest 7 SMKCH Ques&AnsLIM YEE WEN MoeNo ratings yet
- University of Petra: Faculty of Arts and Sciences Department of MathematicsDocument2 pagesUniversity of Petra: Faculty of Arts and Sciences Department of MathematicsLeen AlghubariNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Maths Test 1 Term 1Document1 pageGrade 11 Maths Test 1 Term 1Karla LeemansNo ratings yet
- 2019-1-NS-KGV Section A (45 Marks) Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument10 pages2019-1-NS-KGV Section A (45 Marks) Answer All Questions in This Sectionbdcyl1No ratings yet
- Group Written AssignmentDocument1 pageGroup Written AssignmentKailurNo ratings yet
- Line (Set A) - 1-2Document2 pagesLine (Set A) - 1-2Zidane ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Linear Geometry WorksheetDocument2 pagesLinear Geometry WorksheetEnash ManakkilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 QuizDocument6 pagesChapter 18 QuizBruce ZhouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 BookletDocument20 pagesChapter 4 Bookletgabriel loNo ratings yet
- Algebraic FractionsDocument11 pagesAlgebraic FractionsSafiya Shiraz ImamudeenNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations - Worksheet: Skill Group A - Factorising Quadratics 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 2 6) 2 7) 2 8) 3 9) 2Document10 pagesQuadratic Equations - Worksheet: Skill Group A - Factorising Quadratics 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 2 6) 2 7) 2 8) 3 9) 2erin zietsmanNo ratings yet
- 3D MCQ TestDocument2 pages3D MCQ TestChetanNo ratings yet
- Xii PB 2023 Maths 281123Document6 pagesXii PB 2023 Maths 281123HarshwardhanNo ratings yet
- Inverse Functions - Worksheet: Find: ( )Document10 pagesInverse Functions - Worksheet: Find: ( )erin zietsmanNo ratings yet
- Coord Geo RevisionDocument1 pageCoord Geo Revisionadhrit1mitraNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 AM WA3 Mock Exam 2023Document10 pagesSec 3 AM WA3 Mock Exam 2023Jayden Chua Qi Ze (Amkss)No ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics Revision Worksheet Month 5Document4 pagesPure Mathematics Revision Worksheet Month 5Le Jeu LifeNo ratings yet
- Secondary 3 A Math WA3 Mock Exam Paradigm MathDocument9 pagesSecondary 3 A Math WA3 Mock Exam Paradigm MathrohNo ratings yet
- Math 1 Mukono Examination CouncilDocument3 pagesMath 1 Mukono Examination CouncilPastor Bahemuka EdwardNo ratings yet
- Curve Sketching Questions Marks 1. 1Document3 pagesCurve Sketching Questions Marks 1. 1Kelvin ChenNo ratings yet
- Functions in Algebra Third Space Learning GCSE WorksheetDocument10 pagesFunctions in Algebra Third Space Learning GCSE WorksheetShalini MishraNo ratings yet
- 20-21 2nd Midterm HBSDocument2 pages20-21 2nd Midterm HBSKurdishNo ratings yet
- Midterm-Math 211fall 2023Document7 pagesMidterm-Math 211fall 2023aalrjl08No ratings yet
- Finding The Equation of A Line From Two PointsDocument9 pagesFinding The Equation of A Line From Two PointsParikNo ratings yet
- St. Francis School, Bhamian Kalan: Class - Xi (Mathematics) Sample Paper SESSION 2022-23Document4 pagesSt. Francis School, Bhamian Kalan: Class - Xi (Mathematics) Sample Paper SESSION 2022-23Manik BholaNo ratings yet
- İnönü Üniversitesi Uluslararasi Öğrenci Sinavi: Inonu University International Students' ExamDocument20 pagesİnönü Üniversitesi Uluslararasi Öğrenci Sinavi: Inonu University International Students' ExamAydin IbrahimovNo ratings yet
- Y9 Summer Block 5 ANS3 Investigate Graphs of Simultaneous EquationsDocument2 pagesY9 Summer Block 5 ANS3 Investigate Graphs of Simultaneous EquationsTitus AnaghoNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Equation of A Tangent To A Circle GCSE WorksheetDocument10 pagesThird Space Learning Equation of A Tangent To A Circle GCSE WorksheetShuayb KhanNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument2 pagesMathsPLAYER100No ratings yet
- FactorisationDocument6 pagesFactorisationSafiya Shiraz ImamudeenNo ratings yet
- Mathematics IIDocument5 pagesMathematics IIitsmeshimrithNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument2 pagesQuadratic EquationsNidhi MehtaNo ratings yet
- Maths 041 Set 3 2022 - 23)Document9 pagesMaths 041 Set 3 2022 - 23)owenknight3456No ratings yet
- Rationals Test ReviewDocument3 pagesRationals Test ReviewAlexis JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Class 8 CH 2 Linear Equations in One Variable May 19Document3 pagesClass 8 CH 2 Linear Equations in One Variable May 19Neha TyagiNo ratings yet
- Types of Graphs GCSE WorksheetDocument20 pagesTypes of Graphs GCSE WorksheetMr dogeNo ratings yet
- Math QP Set 1Document9 pagesMath QP Set 1Manimara PandiyanNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematic Revision Worksheet Month 3Document2 pagesPure Mathematic Revision Worksheet Month 3Le Jeu LifeNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Composite and Inverse Functions GCSE WorksheetDocument10 pagesThird Space Learning Composite and Inverse Functions GCSE Worksheeterin zietsmanNo ratings yet
- P4 MAY BATCH (Upto CH 4)Document2 pagesP4 MAY BATCH (Upto CH 4)Bibi Marium SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- p4 May Batch (Upto CH 4)Document2 pagesp4 May Batch (Upto CH 4)Bibi Marium SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Math Xi Set A First Term 2080 FinalDocument4 pagesMath Xi Set A First Term 2080 Finalrajshgupta01No ratings yet
- 22 (Alg)Document3 pages22 (Alg)Parker SmithNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-08 at 08.35.27Document5 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-08 at 08.35.27alicejessicapreesNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations MCQDocument6 pagesLinear Equations MCQVVS. G.S1074No ratings yet
- SMK Sam Tet Mathematics T s2 2021 QDocument2 pagesSMK Sam Tet Mathematics T s2 2021 QZurainiNo ratings yet
- Mat 1123Document4 pagesMat 1123Sujan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Robot Kinematics: - Spatial Descriptions and Transformations - Introduction To MotionDocument24 pagesRobot Kinematics: - Spatial Descriptions and Transformations - Introduction To MotionSehzadNo ratings yet
- Robot Kinematics - TransformationDocument57 pagesRobot Kinematics - TransformationHoney RathoreNo ratings yet
- Guided Notes Triangle Construction MethodsDocument5 pagesGuided Notes Triangle Construction Methodsapi-528525621No ratings yet
- Multi-Sized Sphere Packing: Shuji Yamada Jinko Kanno Miki MiyauchiDocument45 pagesMulti-Sized Sphere Packing: Shuji Yamada Jinko Kanno Miki Miyauchimadden08No ratings yet
- BR Math 11Document3 pagesBR Math 11Phoenix RockiNo ratings yet
- Cone Vs Sphere Vs CylinderDocument3 pagesCone Vs Sphere Vs Cylinderapi-259421821No ratings yet
- Sasmo Grade 7 - EdugainDocument2 pagesSasmo Grade 7 - Edugainnataliaagustina22No ratings yet
- Undergrad Guide TorDocument134 pagesUndergrad Guide TorEugeneNo ratings yet
- GRADE 7 - MATH REVIEWER in Geometry PDFDocument6 pagesGRADE 7 - MATH REVIEWER in Geometry PDFLiam DeeCeeNo ratings yet
- Analytical GeometryDocument78 pagesAnalytical GeometryChinnaGurappaNo ratings yet
- Directions: Solve The Following Problems Correctly. Box Your Final AnswerDocument1 pageDirections: Solve The Following Problems Correctly. Box Your Final AnswerDavid OrtegaNo ratings yet
- SMO Open 16Document4 pagesSMO Open 16JonNo ratings yet
- ",/I/L@L/I!L! 6: Rohrwerk Agitator Agitateur AgitadorDocument2 pages",/I/L@L/I!L! 6: Rohrwerk Agitator Agitateur AgitadorVijay BhureNo ratings yet
- MAE101-ALG-Chapter 4 - Vector GeometryDocument82 pagesMAE101-ALG-Chapter 4 - Vector GeometryHuynh Hoang Ty (K18 CT)No ratings yet
- Weiss Zone Law and Zone AxesDocument4 pagesWeiss Zone Law and Zone AxesthuronNo ratings yet
- Aa Sss and Sas SimilarityDocument24 pagesAa Sss and Sas SimilarityJay Jexter SeldaNo ratings yet
- Tugas 3 Geo Analitik Bidang Dan RuangDocument3 pagesTugas 3 Geo Analitik Bidang Dan RuangPHELIPUS MERENo ratings yet
- Properties of ShapesDocument16 pagesProperties of ShapesMunaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel P34 15-19 VectorsDocument13 pagesEdexcel P34 15-19 Vectorsmgmfcf7m6yNo ratings yet
- 3RD Summative TestDocument4 pages3RD Summative TestJovelynNo ratings yet
- Topper 110 2 3 Maths Question Up202312041558 1701685716 1865Document8 pagesTopper 110 2 3 Maths Question Up202312041558 1701685716 1865Ruby KumariNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Aimon RaufNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Annual Paper.Document4 pagesClass 9 Annual Paper.Vanshh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Similar Shapes Area and Volume QP Edexcel GcseDocument8 pagesSimilar Shapes Area and Volume QP Edexcel GcseYoussef TarekNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic TheoryDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Theory2025eie34palashNo ratings yet
- (1-8) Midpoint FormulaDocument14 pages(1-8) Midpoint Formulagtan@icacademy.orgNo ratings yet
- 2.4: Finding The Sum of Interior Angles of Polygons (Worksheet)Document3 pages2.4: Finding The Sum of Interior Angles of Polygons (Worksheet)Dorsey MathleteNo ratings yet
- Soal Desimal CampuranDocument2 pagesSoal Desimal CampuranMuhimatus Sa'diyahNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02Document5 pagesMaths Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02Anonymous TvppppNo ratings yet