0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views1 pageRocket Mass and Forces Analysis
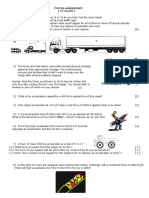
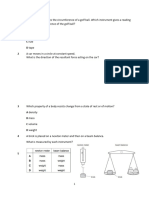
A rocket has a mass of 500 kg. Its weight on Earth is 5000 N and its initial acceleration from a 25,000 N upward force is 50 m/s^2. A falling raindrop experiences a downward force of gravity (force A) and an opposing upward force of air resistance (force B). When these two forces are equal, the raindrop falls with a constant velocity. Powerful engines and lightweight materials allow racing cars to accelerate rapidly even with small engines.
Uploaded by
physics.oalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views1 pageRocket Mass and Forces Analysis
A rocket has a mass of 500 kg. Its weight on Earth is 5000 N and its initial acceleration from a 25,000 N upward force is 50 m/s^2. A falling raindrop experiences a downward force of gravity (force A) and an opposing upward force of air resistance (force B). When these two forces are equal, the raindrop falls with a constant velocity. Powerful engines and lightweight materials allow racing cars to accelerate rapidly even with small engines.
Uploaded by
physics.oalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd