0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views11 pagesForce Worksheet
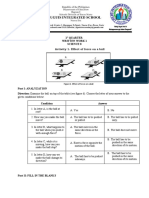
The document consists of a worksheet focused on various physics concepts related to forces, Newton's laws of motion, pressure calculations, hydrostatic pressure, buoyancy, and Pascal's law. It includes scenarios for identifying types of forces, examples of Newton's laws, calculations for net force, pressure exerted by objects, and applications of Archimedes' and Pascal's laws. The worksheet is structured with questions, calculations, and spaces for answers, aimed at reinforcing understanding of fundamental physics principles.
Uploaded by
Nilam AnindythaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views11 pagesForce Worksheet
The document consists of a worksheet focused on various physics concepts related to forces, Newton's laws of motion, pressure calculations, hydrostatic pressure, buoyancy, and Pascal's law. It includes scenarios for identifying types of forces, examples of Newton's laws, calculations for net force, pressure exerted by objects, and applications of Archimedes' and Pascal's laws. The worksheet is structured with questions, calculations, and spaces for answers, aimed at reinforcing understanding of fundamental physics principles.
Uploaded by
Nilam AnindythaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd