Professional Documents
Culture Documents
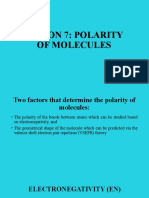
The States of Matter
The States of Matter
Uploaded by
xyrruschloe06Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The States of Matter
The States of Matter
Uploaded by
xyrruschloe06Copyright:
Available Formats
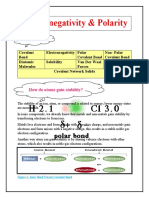
Bond Polarity
WHAT IS BOND POLARITY?
Bond polarity is a measurement of how
much polarity a bond exhibits. A bond
polarity, to put it simply, is a scientific
instrument that helps us understand the
nature of the bonds and the sort of bonding
they will experience to produce compounds.
TYPES OF BONDS
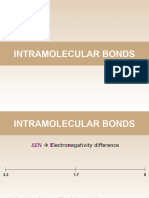
The absolute value of the difference in
electronegativity of two bonded atoms provides a
rough measure of the polarity to be expected in the
bond and, thus, the bond type. When the difference
is very small or zero, the bond is covalent and
nonpolar. When it is large, the bond is polar
covalent or ionic.
APPLICATION OF BONDS
In a polar bond, one atom has a partial electrical charge that is
positive, and the other atom has a partial electrical charge that is
negative. In other words, an electric dipole is created by a polar link.
Atoms share electrons equally in a nonpolar bond, therefore there is
no partial positive or negative charge between them. The difference
between two atoms' electronegativity values determines whether they
join together to create polar or nonpolar bonds.
HOW TO IDENTIFY IF IT IS
NON POLAR OR POLAR?
We define a bond as polar if the difference
between the electronegativity of the atoms in
the bond is more than 0.4. The bond is
effectively nonpolar if the difference in
electronegativity is smaller than 0.4. The
molecule is nonpolar if there are no polar
bonds.
HOW IMPORTANT IS
POLARITY, EXACTLY?
It is a state or a condition of an atom or a
molecule inherent in a body that exhibits
opposite properties or powers in opposite
parts or directions.The term is frequently
used to describe the movement of
electrons in the fields of electricity,
magnetism, chemistry, and electronic
signaling.
GRADE 9
XYRRUS CHLOE P. BAGUIO MENDELEEV
You might also like
- Exploring Polarity of Molecules and Its Properties: Physical Science Quarter 3 Module 2Document18 pagesExploring Polarity of Molecules and Its Properties: Physical Science Quarter 3 Module 2Maricar DimasNo ratings yet
- Chemical PolarityDocument6 pagesChemical PolarityPavan TejNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - The Polarity of Molecule Based On Its StructureDocument48 pagesLesson 4 - The Polarity of Molecule Based On Its Structuretheresa balaticoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Quarter 3 Week 2: Not For SaleDocument7 pagesPhysical Science Quarter 3 Week 2: Not For SaleChristien Kate GonzalesNo ratings yet
- COT Physical Science PamphletDocument2 pagesCOT Physical Science PamphletGabNo ratings yet
- Polarity of MoleculesDocument22 pagesPolarity of MoleculesEstrellita SilvioNo ratings yet
- What is Charge? – The Redefinition of Atom - Energy to Matter ConversionFrom EverandWhat is Charge? – The Redefinition of Atom - Energy to Matter ConversionNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Ms. Grace Monica P. LebrillaDocument40 pagesPhysical Science: Ms. Grace Monica P. LebrillaGabriel James SedanNo ratings yet
- PolarityDocument27 pagesPolarityGiffNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity - MondayDocument17 pagesElectronegativity - MondayJela AlmonedaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - Module 4 (Assignment)Document1 pagePhysical Science - Module 4 (Assignment)CharlesNo ratings yet
- Properties of Covalent BondingDocument9 pagesProperties of Covalent BondingMBOTAKE LawsonNo ratings yet
- Polarity & ForcesDocument13 pagesPolarity & ForcesElsayed ElazazyNo ratings yet
- q1l3 - 2nd Sem Physical ScienceDocument12 pagesq1l3 - 2nd Sem Physical ScienceBilly Jasper DomingoNo ratings yet
- Bond ParametersDocument3 pagesBond ParametersQuenneBelocuraNo ratings yet
- 05 Intramolecular BondsDocument10 pages05 Intramolecular BondsJimmy YeNo ratings yet
- Physci Lesson 2Document14 pagesPhysci Lesson 2wendell john medianaNo ratings yet
- 4-1 Polarity of Bonds Molecular Polarity SlidesDocument15 pages4-1 Polarity of Bonds Molecular Polarity Slidesapi-240915238No ratings yet
- Polar and Nonpolar Compounds: (Son) Kharadar General HospitalDocument2 pagesPolar and Nonpolar Compounds: (Son) Kharadar General HospitalLOVE KUMARNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document29 pagesLesson 2Rhiane AngloNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Polarity of MoleculesDocument56 pagesPhysical Science Polarity of MoleculeskharentaponNo ratings yet
- Ps Module 2Document7 pagesPs Module 2quiwasjNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Physical Science - ReviewerDocument2 pagesModule 2 Physical Science - Reviewercj espinoNo ratings yet
- Polarity of MoleculeDocument35 pagesPolarity of MoleculeAlyson Kate CastillonNo ratings yet
- DLP ElectronegativityDocument6 pagesDLP ElectronegativityRodelyn Dahay CalluengNo ratings yet
- Notes On Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument17 pagesNotes On Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDeepti KashyapNo ratings yet
- Polarity of MoleculesDocument33 pagesPolarity of Moleculeskharentapon10No ratings yet
- General Chemistry I Handout 9.1 Electronegativity Differences and PolarityDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry I Handout 9.1 Electronegativity Differences and PolarityGwyneth CataneNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Chapter # 04Document2 pagesChemical Bonding: Chapter # 04AimanNo ratings yet
- Polar VS Nonpolar MoleculesDocument6 pagesPolar VS Nonpolar MoleculesHerlinNo ratings yet
- Electro NegativityDocument1 pageElectro NegativitySukmaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument20 pagesScienceKath MercadejasNo ratings yet
- Aula Biology Guia 1Document5 pagesAula Biology Guia 1Paulha CastillaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem ReviewerDocument4 pagesGen Chem Revieweraldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Physical Science M2 Polarity of Molecules Part 1Document70 pagesPhysical Science M2 Polarity of Molecules Part 1Evangeline AgtarapNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Graphic Taken From Chemistry, Moore/Stanitski/Jurs, Thomson, 2006, PG 355Document5 pagesChemical Bonding: Graphic Taken From Chemistry, Moore/Stanitski/Jurs, Thomson, 2006, PG 355SevenNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity of An AtomDocument4 pagesElectronegativity of An AtomLindsay AgabasNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent BondsDocument2 pagesIonic and Covalent BondsMeg Dianne V. CañedaNo ratings yet
- Polarity of BondsDocument2 pagesPolarity of BondsGilbert AranaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7: Polarity of MoleculesDocument9 pagesLesson 7: Polarity of MoleculesRAENA MARIE PENDRASNo ratings yet
- PHSC - L3 Bond Polarity and Properties of CompoundsDocument31 pagesPHSC - L3 Bond Polarity and Properties of CompoundsRegene SoledadNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document201 pagesCH 01Khaled OsmanNo ratings yet
- Intramolecular ForcesDocument2 pagesIntramolecular ForcesNarjis FatimaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science UNIT 5 LESSON 5.1 Copy 2Document21 pagesPhysical Science UNIT 5 LESSON 5.1 Copy 2janellekawaii16No ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument19 pagesMolecular PolarityDianne CofinoNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument4 pagesBasic Concepts of Chemical BondingKaren Anne Briones RufinoNo ratings yet
- Specialization: Physical Science: Environment: By: Prof. Crisanta A. OcampoDocument5 pagesSpecialization: Physical Science: Environment: By: Prof. Crisanta A. OcampoApril Joyce Ricamora NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Theories of Covalent Bond and Shapes of MoleculeDocument12 pagesTheories of Covalent Bond and Shapes of Moleculemuhwaqar80No ratings yet
- Notes VSEPR (CH 6)Document21 pagesNotes VSEPR (CH 6)Nestor BalboaNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2Kunai The X GamerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Intermolecular ForcesDocument13 pagesLesson 3 Intermolecular ForcesChristine SenaNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity and Bonding 3.1Document2 pagesElectronegativity and Bonding 3.1Smarty ElephantNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Bonding and Molecular Sructure I Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Bonding and Molecular Sructure I Chemical BondingJonathan SaydeNo ratings yet
- JJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJDocument1 pageJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJBaltazar MarcosNo ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument43 pagesMolecular Polaritychubbskie00No ratings yet
- Molecule PolarityDocument30 pagesMolecule PolarityRexzyl ClajeNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument25 pagesBondingnya72505No ratings yet
- Chemıcal BondsDocument10 pagesChemıcal BondsDesirie MarceloNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity and Polarity - FactsDocument9 pagesElectronegativity and Polarity - FactsAlshaimaa SolimanNo ratings yet