Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dev of Tooth
Uploaded by
sabreennafiya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesThe document summarizes the development of teeth from the 6th week of intrauterine life. It describes the formation of the primary epithelial band which divides into the vestibular lamina and dental lamina. The dental lamina shows proliferation leading to dental placodes, which represent future tooth sites. Tooth development then progresses through bud, cap, and bell stages as the enamel organ grows. During the bell stage, hard structures such as dentin and enamel begin to form through signaling between odontoblasts and ameloblasts, leading to mineralization and the formation of dentinoenamel junction.
Original Description:
Original Title
Dev of tooth (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the development of teeth from the 6th week of intrauterine life. It describes the formation of the primary epithelial band which divides into the vestibular lamina and dental lamina. The dental lamina shows proliferation leading to dental placodes, which represent future tooth sites. Tooth development then progresses through bud, cap, and bell stages as the enamel organ grows. During the bell stage, hard structures such as dentin and enamel begin to form through signaling between odontoblasts and ameloblasts, leading to mineralization and the formation of dentinoenamel junction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesDev of Tooth
Uploaded by
sabreennafiyaThe document summarizes the development of teeth from the 6th week of intrauterine life. It describes the formation of the primary epithelial band which divides into the vestibular lamina and dental lamina. The dental lamina shows proliferation leading to dental placodes, which represent future tooth sites. Tooth development then progresses through bud, cap, and bell stages as the enamel organ grows. During the bell stage, hard structures such as dentin and enamel begin to form through signaling between odontoblasts and ameloblasts, leading to mineralization and the formation of dentinoenamel junction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
EXCEL BDS
Development and growth of teeth
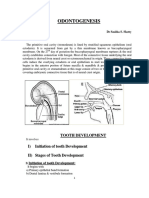
DEVELOPMENT OF TOOTH
• Development of tooth begins in the stomodeum.
• During the 6th week of intra uterine life the stomodeum shows the formation of
primary epithelial band.
• On the 7th week of intra uterine life the primary epithelial band is divided into
two structures such as the vestibular lamina and dental lamina.
a. Vestibular lamina: It forms the vestibule.
The two vestibules formed are the buccal vestibule and the lingual vestibule.
b. Dental Lamina: The dental lamina shows proliferation of cells. At certain points
the dental lamina shows increased proliferation which is called as dental placodes.
The dental placodes represent the future tooth.
Morphologic stages of tooth development:
There are three developmental stages such as the
A. Bud stage
B. Cap stage
C. Bell stage
A. Bud stage: 00.05.28
• The extension of dental placode is called as the enamel organ.
• Based on the proliferation of the enamel organ the stages of tooth development
are named.
• The enamel organ is similar to a bud hence it is called as the bud stage.
• This is the first stage of tooth development.
• The bud stage has two sets of cells of which the outer cells are cuboidal cells
which then transform into low columnar shape cells and the centrally placed
cells polygonal cells.
• Surrounding cells shows condensation of ectomesenchyme which is called as
dental papilla.
• Dental papilla forms the dentin and pulp.
• Enamel organ helps in the formation of enamel.
B. Cap stage: 00.08.10
The enamel organ in this stage shows a downward growth.
• The growth of cells in this stage is uneven.
• The proliferation of the cells is seen on two ends of enamel organ assuming a
cap shaped structure.
• The cells which cover the convexity of the cap is called as the outer enamel
epithelium. The cells which cover the concavity is called as the inner enamel
epithelium.
Excel BDS Notes 1
EXCEL BDS Development and growth of teeth
• The outer enamel epithelium is cuboidal in shape and the inner enamel epithe-
lium cells are tall columnar in shape.
• The centrally placed cells assume a star shape that occur due to the hydrophilic
nature of the cells. These cells absorb the water into them and swell.
• The cells also try to separate from each other to accommodate the water.
• The centrally placed cells also try to act as cushion or shock absorber.
• These cells are maintaining the cytoplasmic extension and are called as stellate
reticulum cells.
• Dental papilla forms the dentin and pulp.
• Ectomesenchyme that covers the outer enamel epithelium forms the dental
sac/dental follicle.
• The dental follicle gives rise to structures such as cementum, periodontal liga-
ment and alveolar bone.
Bell stage: 00.13.06
a. Early bell stage
• The proliferation of cells is continued and the enamel organ assumes a bell
shape.
• The stellate reticulum is going on increasing because of absorption of water.
• Extension of dental lamina is completely lost leaving behind few remnants
which are called as cell rests of serre.
• Cells rests of serre on stimulation can lead to formation of any cyst or tumour.
• There is shift in the nucleus of tall columnar cells.
• Few cells of the inner enamel epithelium has divided into ameloblasts.
Inner enamel epithelium
Signal↓
Dental papilla
↓
Odontoblasts
↓
Dentin formation
• Outer enamel epithelium changes from cuboidal to low cuboidal in shape.
• Outer to enamel epithelium there is appearance of stratum intermedium.
Advanced bell stage:
• Collapsing of stellate reticulum begins.
• Due to the coalesce outer enamel epithelium and odontoblasts leads to the
formation of dentinoenamel junction(DEJ).
• Opposition or mineralization starts such as the hard structures are formed in
this stage along with root formation.
• 1st layer of dentin is laid down which is called as the mantle dentin.
2 Excel BDS Notes
EXCEL BDS Development and growth of teeth
• Dentin signals the ameloblasts to form enamel.
• Dentin formation moves pulpully towards the root surface or towards pulp.
• The enamel formation is over the dentin which is moving towards the cusps or cuspally.
Excel BDS Notes 3
You might also like
- Development of TeethDocument17 pagesDevelopment of Teethhanisha patelNo ratings yet
- Cholesteatoma, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCholesteatoma, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Development and Growth of Teeth: Dr. Madhusudhan ReddyDocument48 pagesDevelopment and Growth of Teeth: Dr. Madhusudhan ReddysiyaNo ratings yet
- Development of Teeth and TongueDocument79 pagesDevelopment of Teeth and TongueOmanakuttan Kr100% (1)
- Development of TeethDocument25 pagesDevelopment of TeethDrShweta Saini100% (1)
- Tooth Development 1Document14 pagesTooth Development 1ahmedfawakh0No ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy and OcclusionDocument53 pagesDental Anatomy and OcclusionIlinca LupuNo ratings yet
- Development of ToothDocument68 pagesDevelopment of ToothMamatha M KarthikNo ratings yet
- Tooth DevelopmentDocument15 pagesTooth DevelopmentSascha WuNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-06-01 at 4.29.14 PMDocument63 pagesScreenshot 2023-06-01 at 4.29.14 PMAyesha AzamNo ratings yet
- Zahn Entwicklung EnglDocument10 pagesZahn Entwicklung EnglinfoNo ratings yet
- Development of TeethDocument30 pagesDevelopment of TeethsiyaNo ratings yet
- 01 Dentin and PulpDocument135 pages01 Dentin and PulpMinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- 1.tooth Development Edited1Document6 pages1.tooth Development Edited1drpnnreddy100% (4)
- ToothDocument34 pagesToothfathimanesrin537No ratings yet
- Development of TeethDocument20 pagesDevelopment of TeethSubhashini RajshekarNo ratings yet
- Development of Dentition: - G.Shekar Subramanian Iyr MdsDocument96 pagesDevelopment of Dentition: - G.Shekar Subramanian Iyr MdsShekar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Development of Tooth and Its Supporting TissuesDocument68 pagesDevelopment of Tooth and Its Supporting TissuesSaud IqbalNo ratings yet
- Development of Teeth 1Document37 pagesDevelopment of Teeth 1Muli MaroshiNo ratings yet
- Development of TeethDocument20 pagesDevelopment of TeethMehri Aisha ShanavasNo ratings yet
- Stages of Tooth DevelopmentDocument6 pagesStages of Tooth DevelopmentSOUMYA A DR, DEPT.OF DENTAL SCIENCES,SRIHERNo ratings yet
- Biology of The Dental Pulp and Periradicular TissuesDocument34 pagesBiology of The Dental Pulp and Periradicular TissuesFatima SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Development of Teeth: by - Dr. Priyanka Singh. M.D.S I YearDocument61 pagesDevelopment of Teeth: by - Dr. Priyanka Singh. M.D.S I YearJerry TurtleNo ratings yet
- DCH Notebook Development of ToothDocument8 pagesDCH Notebook Development of ToothmanujNo ratings yet
- Tooth DevelopmentDocument20 pagesTooth DevelopmentArslan Jokhio0% (1)
- Development and Growth of TeethDocument69 pagesDevelopment and Growth of TeethRamli Abdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Tooth Development (Odontogenesis) : By: Hasu - ChaudhariDocument17 pagesTooth Development (Odontogenesis) : By: Hasu - ChaudharisusanthNo ratings yet
- DevelopmentalDocument27 pagesDevelopmentalمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- Histology Digestive System Oral CavityDocument60 pagesHistology Digestive System Oral CavityAimie DagaleaNo ratings yet
- null ١-١Document26 pagesnull ١-١moh.ahm3040No ratings yet
- Development of ToothDocument57 pagesDevelopment of ToothDr.Rakshith BkNo ratings yet
- Development of TeethDocument13 pagesDevelopment of TeethFaith ChepoghishoNo ratings yet
- Odonto Gens IsDocument8 pagesOdonto Gens Ismary frisanNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy and Occlusion NuggetsDocument53 pagesDental Anatomy and Occlusion Nuggetssethrb100% (5)
- Tooth Development Lecture 4Document9 pagesTooth Development Lecture 4eveNo ratings yet
- Tooth DevelopmentDocument2 pagesTooth Developmentxv2yccj585No ratings yet
- Seminar 3Document96 pagesSeminar 3Dilip Kumar ChevuriNo ratings yet
- Odontogenesis: Dr. Brian E. EsporlasDocument20 pagesOdontogenesis: Dr. Brian E. EsporlasJhonatan Alfaro RondinelNo ratings yet
- Amelogenesis & Dentinogenesis: DR Sana JavedDocument19 pagesAmelogenesis & Dentinogenesis: DR Sana Javedshahzeb memonNo ratings yet
- Enamel HandoutDocument93 pagesEnamel HandoutIqra EjazNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - 1Document9 pagesLecture 2 - 1ahmedfawakh0No ratings yet
- Development of ToothDocument68 pagesDevelopment of Toothpvspartan0933% (3)
- Teeth Development IIDocument65 pagesTeeth Development IIggNo ratings yet
- Development of Tooth Lecture-1Document63 pagesDevelopment of Tooth Lecture-1Dimple KashyapNo ratings yet
- Amelogenesis... : "The Beginnings".Document98 pagesAmelogenesis... : "The Beginnings".Bamidele FamurewaNo ratings yet
- Developmentofteeth StagesDocument45 pagesDevelopmentofteeth Stagesimi4100% (1)
- Colorful Creative Social Media Brainstorm PresentationDocument24 pagesColorful Creative Social Media Brainstorm PresentationSatria MandalaNo ratings yet
- Teeth DevelopmentDocument12 pagesTeeth DevelopmentMostafa El GendyNo ratings yet
- Oral Hist1Document21 pagesOral Hist1saleemshaikh23No ratings yet
- Tooth DevelopmentDocument36 pagesTooth DevelopmentDaffa YudhistiraNo ratings yet
- Teeth Development: Bud StageDocument7 pagesTeeth Development: Bud Stageburdall100% (1)
- Embryologie DentaireDocument23 pagesEmbryologie DentaireElmassal SergeoNo ratings yet
- DENT215 Embryological Development of The Dental Pulp Prof. Dr. Işıl KüçükayDocument29 pagesDENT215 Embryological Development of The Dental Pulp Prof. Dr. Işıl Küçükayezoafaneh0No ratings yet
- Tooth Origin and Formation - by Bugnariu Paul, Buterchi Codrut, Chit-Stinean AdonisDocument73 pagesTooth Origin and Formation - by Bugnariu Paul, Buterchi Codrut, Chit-Stinean AdonisVlad FlaviusNo ratings yet
- Development of UmDocument40 pagesDevelopment of UmMisbah Kokab100% (1)
- Dental HistologyDocument65 pagesDental HistologyMustafa H. KadhimNo ratings yet
- Pulp Dentin ComplexDocument187 pagesPulp Dentin ComplexHitesh Chopra100% (1)
- Odontogenesis 3Document75 pagesOdontogenesis 3mennaitaNo ratings yet
- Oral Cells and Tissues PDFDocument427 pagesOral Cells and Tissues PDFAdriana Cristina Rocha Haerber100% (1)
- Tooth Development, Eruption & Applied Aspects: Saurabh Roy 09.03.2016Document95 pagesTooth Development, Eruption & Applied Aspects: Saurabh Roy 09.03.2016reema aslamNo ratings yet
- Deve of Tooth OSPE With AnswersDocument21 pagesDeve of Tooth OSPE With AnswersAffan AbbasNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Oral Biology 1st Year BDSDocument29 pagesStudy Guide Oral Biology 1st Year BDSFatima ShahNo ratings yet
- Janat00041 0262bDocument2 pagesJanat00041 0262bFranky YehNo ratings yet
- @MBmedicalbook DentalDocument337 pages@MBmedicalbook DentalBeakal TsegaiNo ratings yet
- Endodontics MCQsDocument68 pagesEndodontics MCQsFâtîmá Âl Zâhrää94% (18)
- Cementum: Avisha AgrawalDocument109 pagesCementum: Avisha AgrawalpoojaNo ratings yet
- Development of DentitionDocument8 pagesDevelopment of DentitionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Oral Histology Lec.2Document18 pagesOral Histology Lec.2imi40% (1)
- Cementum in Health and DiseaseDocument161 pagesCementum in Health and DiseaseRazvan UngureanuNo ratings yet
- Development of Teeth: January 2018Document13 pagesDevelopment of Teeth: January 2018Tesa RafkhaniNo ratings yet
- Kwon 2018Document11 pagesKwon 2018fatimahNo ratings yet
- Pit and Fissure Sealants PDFDocument180 pagesPit and Fissure Sealants PDFBBB HUYT100% (3)
- Regenerative Approaches in Dentistry - An Evidence-Based Perspective (2021)Document276 pagesRegenerative Approaches in Dentistry - An Evidence-Based Perspective (2021)Mohammad Ibrahim100% (2)
- Tooth Development Lecture 4Document9 pagesTooth Development Lecture 4eveNo ratings yet
- Regenerative EndodonticsDocument37 pagesRegenerative EndodonticsJainath JainNo ratings yet
- Maji - Josh .Dental-Book PDFDocument614 pagesMaji - Josh .Dental-Book PDFMohammed hisham khan92% (13)
- Essentials of Oral Biology PDFDocument614 pagesEssentials of Oral Biology PDFRudra VermaNo ratings yet
- The Periodontal PocketDocument9 pagesThe Periodontal Pocketpatricia sotoNo ratings yet
- Development of PeriodontiumDocument24 pagesDevelopment of Periodontiumpalak sharma100% (1)
- 7 - Dentinogenesis PDFDocument14 pages7 - Dentinogenesis PDFHãnëën Twalbeh83% (12)
- AmelogenesisDocument5 pagesAmelogenesisBooMinhPhanNo ratings yet
- Development of Tooth Lecture-1Document63 pagesDevelopment of Tooth Lecture-1Dimple KashyapNo ratings yet
- ODONTOGENESISDocument7 pagesODONTOGENESISAngierika CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Oral Histology 2nbsped 9788131254844 8131254844Document143 pagesAtlas of Oral Histology 2nbsped 9788131254844 8131254844Dhikra PikaNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From Anna B. Fuks, Benjamin Peretz Eds. Pediatric Endodontics Current Concepts in Pulp Therapy For Primary and Young Permanent TeethDocument7 pagesExtracted Pages From Anna B. Fuks, Benjamin Peretz Eds. Pediatric Endodontics Current Concepts in Pulp Therapy For Primary and Young Permanent TeethMona CameliaNo ratings yet
- Enamel: Physical PropertiesDocument18 pagesEnamel: Physical PropertiesRajat NangiaNo ratings yet