Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 9 (CHP 9)
Uploaded by
Zulizah NatashaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 9 (CHP 9)
Uploaded by
Zulizah NatashaCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 9 (chp 9)
1. An ideal diesel engine has a compression ratio of 20 and uses air as the working fluid.
The state of air at the beginning of the compression process is 90 kPa and 20°C. If the
maximum temperature in the cycle is not to exceed 2200 K, determine
(a) cut off ratio and the thermal efficiency
(b) produced work and the mean effective pressure.
Assume constant specific heats for air at room temperature. 300K.
(Ans: 2.3, 64%, 784 kJ/kg, 884 kPa)
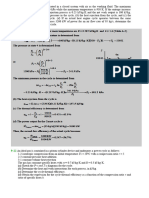
2. Refrigerant-134a is used as the working fluid in a simple ideal Rankine cycle which
operates the boiler at 2000 kPa, while the condenser is operated at 24C (in and out).
The refrigerant enters the pump as a saturated liquid. Note that, the refrigerant at the
exit turbine has a quality of 93 percent. Determine the turbine inlet temperature and
the cycle thermal efficiency. (refer to standard diagram of ideal rankine cycle).
(Ans: 67.5, 10.7)
3. A refrigerator uses refrigerant-134a as the working fluid and operates on the ideal
vapor-compression refrigeration cycle except for the compression process. The
refrigerant enters the evaporator at 100 kPa with a quality of 35 percent and leaves the
compressor at 70C. If the compressor consumes 450 W of power, determine (a) the
mass flow rate of the refrigerant, (b) the refrigeration load and COP of the
refrigerator.
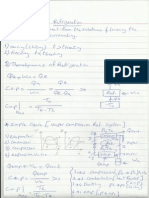
4. An ideal vapor-compression refrigeration cycle that uses refrigerant-134a as its
working fluid maintains a condenser at 800 kPa and the evaporator at -12C. The
refrigerant enters the compressor as a saturated vapor at the evaporator pressure, and
leaves the condenser as saturated liquid at the condenser pressure. Determine the
amount of power required to service a 150 kW cooling load and the system’s COP
(refer to standard diagram ideal vapor-compression Refrigeration cycle)
(Ans: 30.8 kW, 4.9)
Presentation by;
Group A-Q1
Group BC-Q2
Group DE-Q3
Q4-in class discussion
You might also like
- EME2146 Tutorial 6Document2 pagesEME2146 Tutorial 6iwqb0% (1)
- HW-3, Ch-11Document6 pagesHW-3, Ch-11Tshepho Ketshepha KeisangNo ratings yet
- Assignment 12Document7 pagesAssignment 12Anonymous mqIqN5zNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2-Questions (Air-Craft ARC) : Simple Gas Refrigeration CycleDocument3 pagesTutorial 2-Questions (Air-Craft ARC) : Simple Gas Refrigeration CycleRajaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration cycle calculations and COP analysisDocument8 pagesRefrigeration cycle calculations and COP analysisFilianti Gianita0% (1)
- TutorialX RefrigerationCycleDocument1 pageTutorialX RefrigerationCycleAnurag Kumar0% (1)
- Assignment IIDocument3 pagesAssignment IIannukiitNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Processes and Equipment Tutorial with Refrigeration Cycle AnalysisDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer Processes and Equipment Tutorial with Refrigeration Cycle AnalysisHoài ThươngNo ratings yet
- Answers: (A) 0.434, (B) 21.4 KW, (C) 0.478Document2 pagesAnswers: (A) 0.434, (B) 21.4 KW, (C) 0.478Neil BrionesNo ratings yet
- Tutorials for Canot RefrigirationDocument3 pagesTutorials for Canot Refrigirationsphesihlemchunu40No ratings yet
- Problem Set in Exergy Brayton and RefDocument2 pagesProblem Set in Exergy Brayton and RefVan LimNo ratings yet
- Otto & Diesel ProblemsDocument2 pagesOtto & Diesel ProblemsRimarkZanoriaNo ratings yet
- Ar Cycle 2Document4 pagesAr Cycle 2ELEONOR TABLINGONNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Process Tutorial 4 1Document2 pagesThermodynamic Process Tutorial 4 1Boon Khai ChienNo ratings yet
- GP CycleDocument11 pagesGP Cyclerajasekar KNo ratings yet
- AdsorptionDocument3 pagesAdsorptionali105No ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Heat Pump Systems HomeworkDocument1 pageRefrigeration & Heat Pump Systems Homeworkefeln1No ratings yet
- Tut 4Document1 pageTut 4me21b105No ratings yet
- Lectut MIN 106 PDF MI 106 Tutorial VIII - BcPSc3PDocument2 pagesLectut MIN 106 PDF MI 106 Tutorial VIII - BcPSc3PPritam PaulNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Refrigeration Cycle & R-134a Vapor Compression Refrigerator PerformanceDocument3 pagesIdeal Gas Refrigeration Cycle & R-134a Vapor Compression Refrigerator Performanceanask15No ratings yet
- Termo2 PR3 2013Document3 pagesTermo2 PR3 2013Faiz FebriantoNo ratings yet
- Wor ShopDocument4 pagesWor ShopDavid Santiago Ayala RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 2Document2 pagesAssignment No 2ISHPAL singhNo ratings yet
- Ciclo Brayton Turbina de Gas RegenerativaDocument6 pagesCiclo Brayton Turbina de Gas RegenerativaSebastiánGarcía100% (1)
- Tugas 29 April 2016Document3 pagesTugas 29 April 2016api-316036600No ratings yet
- Tutorials Refrigiration and Heat Pumps 2024 ThermoDocument2 pagesTutorials Refrigiration and Heat Pumps 2024 Thermosphesihlemchunu40No ratings yet
- Problem Set in Exergy Brayton and RefDocument15 pagesProblem Set in Exergy Brayton and RefCheng PasionNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 10 ProblemsDocument2 pagesTutorial 10 ProblemsRudhraa.RNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document3 pagesSheet 1Esmail AnasNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration cycle analysis and optimizationDocument5 pagesRefrigeration cycle analysis and optimizationReina Grace PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Local Media1133470422700059155Document6 pagesLocal Media1133470422700059155Billy JhunNo ratings yet
- 7.1.prob - Sheet Gas Power CyclesDocument3 pages7.1.prob - Sheet Gas Power CyclesAnonymous mXicTi8hB0% (1)
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Pallav AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Vapor Power Cycles Chapters 10 & 11Document2 pagesVapor Power Cycles Chapters 10 & 11MaykaMidreliDeandraLigutomNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 7 (IC Engine)Document6 pagesTutorial - 7 (IC Engine)Vaikunth PatelNo ratings yet
- ME-103 Tutorial Refrigeration CycleDocument1 pageME-103 Tutorial Refrigeration CycleKusmakarNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument2 pagesSample QuestionsnakatsuswanNo ratings yet
- Homework: Chapter 11 Refrigeration CyclesDocument1 pageHomework: Chapter 11 Refrigeration CyclesanikfaisalNo ratings yet
- EMH332 Tutorial 4Document1 pageEMH332 Tutorial 4Chris ZiyuenNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument16 pagesThermoİBRAHİM HAZAR AYTULUNNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Air Conditioning (1) - Sheets SolutionDocument25 pagesRefrigeration & Air Conditioning (1) - Sheets SolutionMohamed Maher100% (3)
- Contoh Soal 1-7Document2 pagesContoh Soal 1-7Tsamara PutraNo ratings yet
- RAC Exam Questions on Refrigeration SystemsDocument2 pagesRAC Exam Questions on Refrigeration SystemsSDvidyaNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT Me PDFDocument3 pagesASSIGNMENT Me PDFmahfuzNo ratings yet
- Ref Review ProblemsDocument3 pagesRef Review ProblemsGiancarlo SantosNo ratings yet
- RAC (ME 802) by Prof. Sangeev S. TomarDocument9 pagesRAC (ME 802) by Prof. Sangeev S. Tomarapi-19832143No ratings yet
- End Prob. CengelDocument5 pagesEnd Prob. CengelErvz MissionNo ratings yet
- Cap 04Document3 pagesCap 04Jorge PozoNo ratings yet
- RAC Tutorial Sheet 2Document3 pagesRAC Tutorial Sheet 2Ankur Sachdeva0% (1)
- B7: Applied Thermodynamics: Hilary Term 2018 Richard StoneDocument4 pagesB7: Applied Thermodynamics: Hilary Term 2018 Richard StoneMoemen MetwallyNo ratings yet
- ITK-233-6 - Power Production & RefrigerationDocument30 pagesITK-233-6 - Power Production & RefrigerationAndy Noven KrisdiantoNo ratings yet
- Assignment On RefregrationDocument1 pageAssignment On Refregrationwardi tubeNo ratings yet
- VHP Phase 4Document142 pagesVHP Phase 4kristan7No ratings yet
- ENSC 14a Problem Set 2Document4 pagesENSC 14a Problem Set 2deusleanNo ratings yet
- Thermo of MechDocument2 pagesThermo of MecheyobNo ratings yet
- RAC Tutorial Sheet 4Document3 pagesRAC Tutorial Sheet 4Ankur SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (Introduction To Course) Sem 1 2023-24Document29 pagesLesson 1 (Introduction To Course) Sem 1 2023-24Zulizah NatashaNo ratings yet
- TheResponseofAccessibilityInfrastructuresforPWDtoNationalDisabilityPoliciesinHigherInstitutionsofDevelopingCountriesCaseStudyofAhmaduBelloUniversityZar PDFDocument17 pagesTheResponseofAccessibilityInfrastructuresforPWDtoNationalDisabilityPoliciesinHigherInstitutionsofDevelopingCountriesCaseStudyofAhmaduBelloUniversityZar PDFZulizah NatashaNo ratings yet
- KG12403 CHP2 (Part 1)Document20 pagesKG12403 CHP2 (Part 1)Zulizah NatashaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (Introduction To Course) Sem 1 2023-24Document29 pagesLesson 1 (Introduction To Course) Sem 1 2023-24Zulizah NatashaNo ratings yet
- TheResponseofAccessibilityInfrastructuresforPWDtoNationalDisabilityPoliciesinHigherInstitutionsofDevelopingCountriesCaseStudyofAhmaduBelloUniversityZar PDFDocument17 pagesTheResponseofAccessibilityInfrastructuresforPWDtoNationalDisabilityPoliciesinHigherInstitutionsofDevelopingCountriesCaseStudyofAhmaduBelloUniversityZar PDFZulizah NatashaNo ratings yet
- KG12403 CHP2 (Part 1)Document20 pagesKG12403 CHP2 (Part 1)Zulizah NatashaNo ratings yet