Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Common Foodborne Pathogens
Uploaded by
O PCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Common Foodborne Pathogens
Uploaded by
O PCopyright:
Available Formats
Hazards and Controls
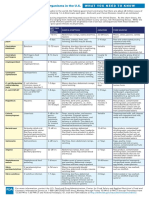
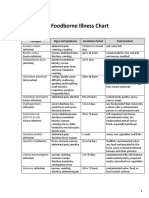
Common Foodborne Pathogens*
Pathogen Common Name of Cause of Illness Incubation Symptoms Possible sources Steps for Prevention
Illness Period
Bacillus cereus B. cereus food large molecular 30 minutes Watery diarrhea, Meats, milk, Proper holding
poisoning weight protein to 15 hours abdominal vegetables, fish, temperatures
(diarrheal type) or cramps, nausea, rice, potatoes,
highly heat-stable and vomiting pasta, and
toxin (emetic type) (emetic type) cheese
Campylobacter Campylobacteriosis Infection, even with One to Nausea, fever, Raw milk, eggs, Pasteurize milk; cook
jejuni low numbers seven days abdominal poultry, raw foods properly; prevent
cramps, diarrhea, beef, cake icing, cross-contamination.
headache - water
varying in severity
Clostridium Botulism Toxin produced by 12 to 36 Nausea, vomiting, Low-acid canned Properly can foods
botulinum Clostridium hours diarrhea, fatigue, foods, meats, following
botulinum headache, dry sausage, fish recommended
mouth, double procedures; cook foods
vision, muscle properly.
paralysis,
respiratory failure
Clostridium Clostridium Inadequate cooling, 8 to 22 abdominal Meats and Rapid cooling and
perfringens perfringens food improper reheating, hours cramps and gravies reheating. Not holding
poisoning holding diarrhea, some product in temperature
temperatures include range allowing growth
dehydration
Escherichia coli E. coli infection Strain of Two to four Hemorrhagic Ground beef, raw Thoroughly cook meat;
O157:H7 enteropathic days colitis, possibly milk no cross-
E. coli hemolytic uremic contamination.
syndrome
Hepatitis A Hepatitis Hepatitis A Virus 2 to 4 fever, malaise, Water, fruits, Proper hand washing
weeks nausea, vegetables, iced before after using a
abdominal pain, drinks, shellfish, restroom and before
yellow eyes and and salads preparing food
skin
Inspection Methods 35-1
Hazards and Controls
Pathogen Common Name of Cause of Illness Incubation Symptoms Possible sources Steps for Prevention
Illness Period
Listeria Listeriosis Infection with Two days to Flu-like Vegetables, milk, Purchase
monocytogenes Listeria three weeks symptoms, cheese, meat, pasteurized dairy
monocytogenes meningitis, deli meat, hot products; cook foods
septicemia, dogs, seafood, properly; no cross-
miscarriage RTE products, contamination; use
Post Lethality sanitary practices.
Exposed
Norwalk, Viral Infection with Between 12 Nausea, vomiting, Raw Adequate and proper
Norwalk-like, or gastroenteritis, Norwalk virus and 48 diarrhea and oysters/shellfish, treatment and disposal
Norovirus winter diarrhea, hours (avg abdominal water and ice, of sewage, appropriate
acute non-bacterial 36 hours); cramps, fever, salads, frosting, chlorination of water,
gastroenteritis, duration, headache person-to-person restriction of infected
food poisoning, 12-60 hours contact food handlers from
and food infection working with food until
they no longer shed
virus.
Salmonella Salmonellosis Infection with 12 to 24 Nausea, diarrhea, Meat, poultry, Cook thoroughly; avoid
Salmonella species hours abdominal pain, egg or milk, raw cross-contamination;
fever, headache, or undercooked use sanitary practices.
chills, prostration products
Staphylococcus Staphylococcal Toxin produced by One to six Severe vomiting, Custard-filled Refrigerate foods; use
aureus food poisoning certain strains of hours diarrhea, baked goods, sanitary practices
Staphylococcus abdominal ham, poultry,
aureus cramping Fermented
sausage,
dressing, gravy,
eggs, potato
salad, sandwich
fillings
*compiled from Iowa State University Extension Food Safety Project, FDA Bad Bug Book, and Foodborne Illness-Causing Organisms in the U.S. What You Need to Know
Inspection Methods 35-2
Hazards and Controls
LIMITING CONDITIONS FOR PATHOGEN GROWTH*
MIN AW MAX. % MIN. MAX
MIN OXGEN
PATHOGEN (USING MAX PH WATER TEMP. TEMP
PH REQUIREMENT
SALT) PHASE SALT (°F) (°F)
facultative
BACILLUS CEREUS 0.92 4.3 9.3 10 39.2 131
anaerobe
C. BOTULINUM TYPE A,
AND PROTEOLYTIC TYPES 0.935 4.6 9 10 50 118.4 anaerobic
B&F
C. BOTULINUM TYPE E,
AND NONPROTEOLYTIC 0.97 5 9 5 37.9 113 anaerobic
TYPES B & F
C. PERFRINGENS 0.93 5 9 7 50 125.6 anaerobic
PATHOGENIC STRAINS OF facultative
0.95 4 10 6.5 43.7 120.9
ESCHERICHIA COLI anaerobe
LISTERIA facultative
0.92 4.4 9.4 10 31.3 113
MONOCYTOGENES anaerobe
facultative
SALMONELLA SPP. 0.94 3.7 9.5 8 41.4 115.22
anaerobe
STAPHOLOCCUS AUREUS facultative
0.83 4 10 20 44.6 122
GROWTH anaerobe
STAPHYLOCOCCUS
facultative
AUREUS TOXIN 0.85 4 9.8 10 50 118
anaerobe
FORMATION
CAMPYLOBACTER JEJUNI 0.987 4.9 9.5 1.7 86 113 micro aerophilic
*Other Conditions Optimal Fish and Fishery Products Hazards and Controls Guide-references in Guide
Inspection Methods 35-3
You might also like
- Types of Food ContaminationDocument13 pagesTypes of Food ContaminationHelena MbangoNo ratings yet
- Food PoisoningDocument30 pagesFood PoisoningFitz BaniquedNo ratings yet
- Food Poisoning by BacteriaDocument3 pagesFood Poisoning by Bacteriamichael biwotNo ratings yet
- Food Borne IllnessesDocument18 pagesFood Borne IllnessesMaria AbigailNo ratings yet
- Bahaya Biologis Dan Penyakit Bawaan Makanan: Pertemuan 4Document29 pagesBahaya Biologis Dan Penyakit Bawaan Makanan: Pertemuan 4Ratih PurwasihNo ratings yet
- Foodborne IllnessesDocument30 pagesFoodborne IllnessesNicoel100% (6)
- Juanito's Kitchen Safety ManualDocument62 pagesJuanito's Kitchen Safety ManualJessan Sinadhan LimosneroNo ratings yet
- Intoxicaciones Alimentarias - ConsumidorDocument2 pagesIntoxicaciones Alimentarias - ConsumidorMartha Patricia López PimentelNo ratings yet
- 2-1. Bacterial Food Poisoning (Infective)Document53 pages2-1. Bacterial Food Poisoning (Infective)lectureslides22No ratings yet
- CKCLEC001 I. Haccp System Flowchart II. Characteristic of Bacteria IllnessDocument4 pagesCKCLEC001 I. Haccp System Flowchart II. Characteristic of Bacteria IllnessGrace de los SantosNo ratings yet
- Datasheet: Pathogenic Bacteria:: Campylobacter JejuniDocument2 pagesDatasheet: Pathogenic Bacteria:: Campylobacter JejuniDutch CharmingNo ratings yet
- Top Foodborne Illness Organisms in the U.SDocument1 pageTop Foodborne Illness Organisms in the U.SHappy'No ratings yet
- Lum Bang Activity 1Document4 pagesLum Bang Activity 1Hoshi KwonNo ratings yet
- Table Biological HazardDocument2 pagesTable Biological HazardStanislava Kanjevac100% (1)
- FBD 2021Document99 pagesFBD 2021Ruth Mary PadaNo ratings yet
- FDA FoodborneIllness Final PDFDocument1 pageFDA FoodborneIllness Final PDFlindaNo ratings yet
- 1-FDA - FoodborneIllness - Final (8 Files Merged)Document326 pages1-FDA - FoodborneIllness - Final (8 Files Merged)Hazal HazalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2mason.rudd05No ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Food MicrobiologyDocument6 pagesUnit - 1 Food Microbiologyfarhan79054No ratings yet
- Foodborne Illness: Also Called Food PoisoningDocument25 pagesFoodborne Illness: Also Called Food PoisoningHappy'No ratings yet
- 08 Infectious DiarrheaDocument5 pages08 Infectious DiarrheaVincent De AsisNo ratings yet
- Food PoisoningDocument23 pagesFood PoisoningEsther NyawiraNo ratings yet
- Food poisoning bacteriaDocument1 pageFood poisoning bacteriaaariya.kothariNo ratings yet
- FOOD POISONING - ProjectDocument23 pagesFOOD POISONING - ProjectIshika SinghNo ratings yet
- Food Sanitation Document AnalysisDocument7 pagesFood Sanitation Document AnalysisRiezel dgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1b IntroductionDocument57 pagesChapter 1b IntroductionDorothy LimNo ratings yet
- CD TransDocument85 pagesCD TransDhang Cerilo AparenteNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea UpdatedDocument66 pagesDiarrhea UpdatedAna KarlaNo ratings yet
- Food ContaminationDocument19 pagesFood Contaminationfarmasi_hm100% (2)
- Gastrointestinal Tract Pathogens and Microbiology AssignmentDocument8 pagesGastrointestinal Tract Pathogens and Microbiology AssignmentWame Cynthia KNo ratings yet
- Thermobacteriology I: Food Microbiology and Public HealthDocument28 pagesThermobacteriology I: Food Microbiology and Public HealthHasan TheMcNo ratings yet
- Basic Food Hygiene Level 1Document77 pagesBasic Food Hygiene Level 1g5nbNo ratings yet
- Food PoisoningDocument20 pagesFood PoisoningNgọcNo ratings yet
- Datasheet: Pathogenic Bacteria:: Bacillus CereusDocument2 pagesDatasheet: Pathogenic Bacteria:: Bacillus CereusDutch CharmingNo ratings yet
- Food Borne IllnessesDocument14 pagesFood Borne Illnesseswnz9dn8gt6No ratings yet
- Waterborne Diseases: Group 2Document21 pagesWaterborne Diseases: Group 2Jay RickNo ratings yet
- Basic Food Safety With New Logo-HandoutDocument67 pagesBasic Food Safety With New Logo-HandoutAwiz AmaralNo ratings yet
- Asmi 03 0557Document8 pagesAsmi 03 0557Mulubrhan OkbaiNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Food PoisoningDocument40 pagesBacterial Food Poisoningdigracia manatigaNo ratings yet
- B CereusDocument5 pagesB CereusMyles ResumaNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Nuevo de CuliDocument14 pagesTrabajo Nuevo de CulijanNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGICAL SAFETY OF FOODS: KEY FOODBORNE PATHOGENS AND PREVENTIONDocument42 pagesMICROBIOLOGICAL SAFETY OF FOODS: KEY FOODBORNE PATHOGENS AND PREVENTIONRidhu SehgalNo ratings yet
- Tabel Makanan BacteriaDocument4 pagesTabel Makanan BacteriaSyifa KhalisaNo ratings yet
- FOOD SAFETY & GMP (Refresher Course) 2018Document156 pagesFOOD SAFETY & GMP (Refresher Course) 2018QA SpicemixNo ratings yet
- FOOD SAFETY & GMP (Refresher Course) 2018Document156 pagesFOOD SAFETY & GMP (Refresher Course) 2018QA SpicemixNo ratings yet
- Food Poisoning Symptoms and CausesDocument2 pagesFood Poisoning Symptoms and CausesEllieNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Major Foodborne Illnesses Caused by Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi and ParasitesDocument37 pagesTopic 2 Major Foodborne Illnesses Caused by Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi and Parasitesedison aguilarNo ratings yet
- What Is Food Poisoning?: W Hotel Talents 6 April 2016Document10 pagesWhat Is Food Poisoning?: W Hotel Talents 6 April 2016Dhani AnggaraNo ratings yet
- Foodborne Illness What Consumers Need To KnowDocument4 pagesFoodborne Illness What Consumers Need To KnowAnthony MoralesNo ratings yet
- Listeriosis: Powered by Estland Food Control AuthorityDocument1 pageListeriosis: Powered by Estland Food Control AuthorityMCHADNo ratings yet
- Escherichia - Coli 0157Document2 pagesEscherichia - Coli 0157Tamar KobaliaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet: Pathogenic Bacteria:: Escherichia - Coli 0157Document2 pagesDatasheet: Pathogenic Bacteria:: Escherichia - Coli 0157Dutch CharmingNo ratings yet
- Datasheet: Pathogenic Bacteria:: Clostridium PerfringensDocument2 pagesDatasheet: Pathogenic Bacteria:: Clostridium PerfringensDutch CharmingNo ratings yet
- (GI) A Child With DiarrheaDocument59 pages(GI) A Child With DiarrheaJo casNo ratings yet
- Microbes and More - Creative LPDocument28 pagesMicrobes and More - Creative LPAshleigh LynNo ratings yet
- Foodborne Illness Chart PDFDocument2 pagesFoodborne Illness Chart PDFdanicaNo ratings yet
- 004 Microbiological Spoilage of Food and Beverages PDFDocument69 pages004 Microbiological Spoilage of Food and Beverages PDFNadiya ShiyamahNo ratings yet
- Yersiniosis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments of Foodborne DiseaseDocument13 pagesYersiniosis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments of Foodborne DiseasemicrobzNo ratings yet
- Food Contamination 1709801411Document19 pagesFood Contamination 1709801411Giang Pham Thi ThuyNo ratings yet
- Role Play Influeza Bhs InggrisDocument4 pagesRole Play Influeza Bhs InggrisYuna PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Latent TBDocument24 pagesLatent TBLouis FortunatoNo ratings yet
- Expert Smart Lab Tests and DiscountsDocument148 pagesExpert Smart Lab Tests and DiscountsEma PetrescuNo ratings yet
- Acute CervicitisDocument9 pagesAcute CervicitisVicobeingoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Basic and Clinical Principles: First EditionDocument110 pagesMicrobiology: Basic and Clinical Principles: First EditionDawn DixonNo ratings yet
- DR Lal Pathlabs: LPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini Delhi 110085Document2 pagesDR Lal Pathlabs: LPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini Delhi 110085Vivek PatelNo ratings yet
- ANA Diagnostico IIFTDocument40 pagesANA Diagnostico IIFTCEAR ReumatologíaNo ratings yet
- DR Ediyono SP P Sub Dep Paru RSAL DR Ramelan: Farmasi UBY S2 April 2016Document132 pagesDR Ediyono SP P Sub Dep Paru RSAL DR Ramelan: Farmasi UBY S2 April 2016Sukmawati Eka Bima SahputriNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis: Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesAnaphylaxis: Learning Objectivesmohamed fahmyNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank Part 1 & 2Document28 pagesBlood Bank Part 1 & 2rathisNo ratings yet
- CHN MidtermsDocument9 pagesCHN Midtermsanjie kamidNo ratings yet
- Testing For Non-Celiac Gluten Intolerance: Dr. Stephen Wangen Founder, IBS Treatment CenterDocument62 pagesTesting For Non-Celiac Gluten Intolerance: Dr. Stephen Wangen Founder, IBS Treatment CenterNikola StojsicNo ratings yet
- ImunofarmakologiDocument63 pagesImunofarmakologiShafiraNo ratings yet
- E Streptococcus STDocument52 pagesE Streptococcus STArleen MatincaNo ratings yet
- Standard Price List: Products PackageDocument2 pagesStandard Price List: Products PackageYuli NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Hand Hygiene: The Key to Infection PreventionDocument35 pagesHand Hygiene: The Key to Infection PreventionNur IkhsanNo ratings yet
- In Mu No ModulationDocument10 pagesIn Mu No Modulationmaxi392No ratings yet
- Transfusion Products: ImmunohematologyDocument12 pagesTransfusion Products: ImmunohematologyDiana Gabriela NinaNo ratings yet
- Size: 137 X 218 MM: Rapid Test For The Detection of Dengue NS 1 Antigen in Human Serum/plasma DeviceDocument4 pagesSize: 137 X 218 MM: Rapid Test For The Detection of Dengue NS 1 Antigen in Human Serum/plasma DeviceMatibar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument50 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionKaushik ghoshNo ratings yet
- Cluster of DifferentiationDocument4 pagesCluster of Differentiationajie354No ratings yet
- Immune Cell Guide BrochureDocument84 pagesImmune Cell Guide BrochureNathália LuísaNo ratings yet
- School Immunization Consent FormDocument2 pagesSchool Immunization Consent FormRasha ElbannaNo ratings yet
- ImmunoSeroLab M1 M4 MergedDocument14 pagesImmunoSeroLab M1 M4 Mergedela kikayNo ratings yet
- Assure Covid-19 Igg/Igm Rapid Test Device: Optional MaterialsDocument4 pagesAssure Covid-19 Igg/Igm Rapid Test Device: Optional MaterialsJohn UebersaxNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Graft Versus Host DiseaseDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Graft Versus Host DiseasePriMaNo ratings yet
- Medical Report For Foreign Worker Health ScreeningDocument7 pagesMedical Report For Foreign Worker Health ScreeningP Venkata SureshNo ratings yet
- Clinical Review - KEDRABDocument97 pagesClinical Review - KEDRABcoolchapNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Multisystem Nature of Celiac DiseaseDocument93 pagesUnderstanding the Multisystem Nature of Celiac DiseaseamolsdNo ratings yet
- Who Dengue Classification and Differentials ModuleDocument14 pagesWho Dengue Classification and Differentials ModuleKevin AgbonesNo ratings yet