Professional Documents
Culture Documents
156x216 Math 100
156x216 Math 100
Uploaded by
Skrrtt SkrrttOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
156x216 Math 100
156x216 Math 100
Uploaded by
Skrrtt SkrrttCopyright:
Available Formats
MATH 100 - M6.
1
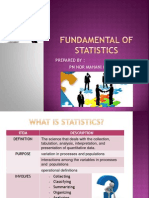
STATISTICS
- A branch of mathematics dealing with the
collection, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of
masses of numerical data.
- A collection of quantitative data.
BRANCHES OF STATISTICS
1. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS is concerned with
summarizing and describing numerical data through
the use of tables, graphs, and charts.
2. INFERENTIAL STATISTICS is concerned with
generalizing information or making inference about a
population based on a sample observed.
MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY
- it is a single value that used to identify the center of
the data and is considered as the typical value in a set of
scores
- can maybe also called a center or location in a
distribution.
- it tends to lie within the center if the observation
(data) are arranged from the lowest to highest or vice
versa.
- 3 measures of tendency are: mean, mode, and
median.
1. mean( x )
- also called as Arithmetic mean or average.
- is the most commonly used measure of central
tendency.
- it is found by taking the sum of all the data values
and then dividing the result by the numbers of values. It
can be affected by extreme scores.
- it is stable, and varies less from sample to sample.
- the mean is the balance point of a score distribution.
MEAN OF UNGROUPED DATA
x 1+x + x +...+ x ∑x
x= 2 3 n
=
n n
To find the mean for a set of data, find the sum of the
data values and divide by the number of data values.
For instance, to find the mean of the 5 salaries
listed below.
$ 43,750 $ 39,500 $ 38,000
$ 41,250 44,000
$ 43,750+ $ 39,500+ $ 38,000
+$ 41,250+ 44,000
5
$ 206,500
¿ =$ 41,300
5
You might also like
- Central Tendency, Measures of Dispersion, NormalDocument31 pagesCentral Tendency, Measures of Dispersion, NormalShad RahmanNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency & VariabilityDocument25 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency & Variabilityelune121No ratings yet
- Ungrouped DataDocument13 pagesUngrouped DataCharlene NazNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Measure of Central TendencyDocument11 pagesLesson 7 - Measure of Central TendencyriniNo ratings yet
- MODULE IN STATISTICS Measures Tendency VariabilityDocument23 pagesMODULE IN STATISTICS Measures Tendency VariabilityFarah Mae Mosquite-GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and DispersionDocument27 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and DispersionmichikoquiachonNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics PDFDocument130 pagesDescriptive Statistics PDFShaheed MorweNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument9 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyJan RusselNo ratings yet
- C22 P04 Statistical AveragesDocument41 pagesC22 P04 Statistical AveragessandeepNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: STT-500 BS (CS) 2A Course InstructorDocument27 pagesStatistics and Probability: STT-500 BS (CS) 2A Course InstructorMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Ecs NotesDocument10 pagesEcs Notes55389740No ratings yet
- Stats 3Document12 pagesStats 3Marianne Christie RagayNo ratings yet
- Physiological StatisticsDocument12 pagesPhysiological StatisticsGerlyn MortegaNo ratings yet
- Istanbul Aydin University: Describing, Exploring, and Comparing DataDocument21 pagesIstanbul Aydin University: Describing, Exploring, and Comparing Dataxxnameless 97No ratings yet
- Instructor'S Manual: Statistical Techniques in Financial ManagementDocument3 pagesInstructor'S Manual: Statistical Techniques in Financial Managementjoebloggs1888No ratings yet
- Statistics For Data ScienceDocument93 pagesStatistics For Data ScienceCesar LobatoNo ratings yet
- Data Description: Elementary StatisticsDocument19 pagesData Description: Elementary StatisticsHabiba AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Modern World Notes PrintableDocument5 pagesMathematics in Modern World Notes PrintableLuna ShiNo ratings yet
- 9 Statistics Class Handout and Test.Document15 pages9 Statistics Class Handout and Test.Suraj PrakashNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 - MMW Statistics - For AsynchDocument18 pagesExercise 5 - MMW Statistics - For AsynchGylene GardonNo ratings yet
- Research 8 Grade 8 Melc 1 q4 Week1Document26 pagesResearch 8 Grade 8 Melc 1 q4 Week1iancyrillvillamer10No ratings yet
- C4 Descriptive StatisticsDocument34 pagesC4 Descriptive StatisticsNAVANEETHNo ratings yet
- RSU - Statistics - Lecture 3 - Final - myRSUDocument34 pagesRSU - Statistics - Lecture 3 - Final - myRSUirina.mozajevaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Business Statistics & AnalyticsDocument25 pagesUnit 1 - Business Statistics & Analyticsk89794No ratings yet
- ChandruDocument27 pagesChandruSidhant BhayanaNo ratings yet
- SINGLE VARIABLE Notes 5.3 Year 10Document9 pagesSINGLE VARIABLE Notes 5.3 Year 10primalp6105No ratings yet
- Module 3: Measures of Central TendencyDocument2 pagesModule 3: Measures of Central TendencyMary Haley Queen BonalosNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency Mean, Mode, Median: DR. Hetal Koringa Assistant ProfessorDocument26 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency Mean, Mode, Median: DR. Hetal Koringa Assistant ProfessorHetal Koringa patelNo ratings yet
- 43hyrs Principles of Statistics 3Document56 pages43hyrs Principles of Statistics 3Russel ShamuyariraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Fin534Document38 pagesChapter 4 Fin5342022876708No ratings yet
- Data Summary: Lesson 4 StatisticsDocument38 pagesData Summary: Lesson 4 StatisticsAndrea Cayetano100% (1)
- Measures Of: Central Tendency & DispersionDocument58 pagesMeasures Of: Central Tendency & DispersionAustine Ampofo TwumasiNo ratings yet
- Inbound 2987877137517492731Document32 pagesInbound 2987877137517492731Angel GedoriaNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument32 pagesStatisticsJEENUPRIYA SAHANo ratings yet
- DM - 02 - 02 - Descriptive Data SummarizationDocument32 pagesDM - 02 - 02 - Descriptive Data SummarizationAnkush LaybarNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument29 pagesStatisticsSakshiNo ratings yet
- Section 6 (Statistics)Document15 pagesSection 6 (Statistics)Javel georgeNo ratings yet
- IMS 504-Week 4&5 NewDocument40 pagesIMS 504-Week 4&5 NewAhmad ShahirNo ratings yet
- Reading - Exploratory Data AnalysisDocument33 pagesReading - Exploratory Data Analysisvaibhavpardeshi55No ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics MBADocument7 pagesDescriptive Statistics MBAKritika Jaiswal100% (2)
- 4 Measures of Centrality: Mean, Median, Mode, Grouped DataDocument18 pages4 Measures of Centrality: Mean, Median, Mode, Grouped DataRejesh MeladNo ratings yet
- Mathematical AnalysisDocument46 pagesMathematical AnalysisGilbert Dwasi100% (1)
- Math4E Week 7 - Lecture 6Document19 pagesMath4E Week 7 - Lecture 6John Cris Lustria PüblicoNo ratings yet
- Calculate Mean, Median, Mode, Variance and Standard Deviation For Column ADocument22 pagesCalculate Mean, Median, Mode, Variance and Standard Deviation For Column AAmol VirbhadreNo ratings yet
- Intro To StatsDocument4 pagesIntro To StatsMakieNo ratings yet
- 1.ungrouped Data Mean, Median&ModeDocument39 pages1.ungrouped Data Mean, Median&ModegccsubjectsNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1-Math 112EDocument13 pagesAssignment 1-Math 112EAshley DestrizaNo ratings yet
- Dsbda Unit 2Document155 pagesDsbda Unit 2king makerNo ratings yet
- Day 01-Basic Statistics - Part (I)Document29 pagesDay 01-Basic Statistics - Part (I)Sparsh VijayvargiaNo ratings yet
- BA 1 - Describing and Summarizing Data PDFDocument4 pagesBA 1 - Describing and Summarizing Data PDFpurwadaNo ratings yet
- Math Majorship Statistics PDFDocument9 pagesMath Majorship Statistics PDFRoberto Esteller Jr.No ratings yet
- Math Majorship StatisticsDocument9 pagesMath Majorship StatisticsMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- A Measure of Central TendencyDocument3 pagesA Measure of Central TendencyJerome ArmedillaNo ratings yet
- Quality ControlDocument33 pagesQuality ControlAydaLeeNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument6 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyAditi ChandraNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Central Tendency and VariabilityDocument28 pagesWeek 2 Central Tendency and VariabilityMuhaimin Abdu AzizNo ratings yet
- Statistics-NCERT Class 11thDocument36 pagesStatistics-NCERT Class 11thporealme.shivalikNo ratings yet
- First Stage: Lecture ThreeDocument14 pagesFirst Stage: Lecture Three翻訳すると、40秒後に死にますOMGITZTWINZNo ratings yet
- ScamDocument1 pageScamSkrrtt SkrrttNo ratings yet
- Soil ChemistryDocument57 pagesSoil ChemistrySkrrtt SkrrttNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument3 pagesProject ProposalSkrrtt SkrrttNo ratings yet
- NSTP 1 L PROJECT PROPOSALDocument2 pagesNSTP 1 L PROJECT PROPOSALSkrrtt SkrrttNo ratings yet