Professional Documents
Culture Documents
All About VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
Uploaded by
syarifah atika0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesAll About VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
Uploaded by
syarifah atikaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
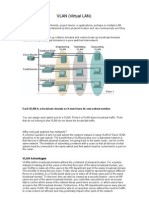
VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks)
Definition of VLAN (Virtual LAN)
A virtual LAN or VLAN is a group of devices on one or more LANs that are configured (using
management software) so that they can communicate as if they were connected to the same
line, when in fact the devices are on a number of different LAN segments.
VLAN is also defined as a network model that is not limited to physical locations such as
LAN, this causes a network to be configured virtually without having to obey the physical
location of the equipment.
The use of VLANs will make network settings very flexible where segments can be made
depending on the organization or department, without depending on the location of the
workstation.
VLAN types
Membership in a VLAN can be classified based on the port
used, MAC address, protocol type.
By Port
Membership in a VLAN can be based on the port used by
those VLANs. For example, on a bridge/switch with 4 ports, ports 1, 2,
and 4 is VLAN 1 while port 3 belongs to VLAN 2, see table:
Ports and VLAN table
Ports 1 2 3 4
VLANs 2 2 1 2
The downside is that users can't move around, if they have to
switch, the Network administrator must reconfigure.
Based on MAC Address
Membership of a VLAN is based on the MAC address of each workstation/computer owned
by the user. The switch detects/records all MAC addresses owned by each Virtual LAN. The
MAC address is a part that is owned by the NIC (Network Interface Card) on each
workstation.
The advantage is that if the user moves, he will still be configured as a member of the VLAN.
While the drawback is that each machine must be configured manually, and for a network
that has hundreds of workstations, this type is less efficient to do.
MAC address and VLAN table
MAC address 132516617738 272389579355 536666337777 24444125556
VLANs 1 2 2 1
Based on the type of protocol used
VLAN membership can also be based on the protocol used, see table
Protocol and VLAN table
IPX IP protocol
VLANs 1 2
Based on IP Subnet Address
The subnet IP address on a network can also be used to classify a VLAN
IP Subnet and VLAN table
IP subnet 22.3.24 46.20.45
VLANs 1 2
This configuration is not related to routing on the network and also does not matter the
function of the router. The IP address is used to map VLAN membership. The advantage is
that a user does not need to reconfigure his address on the network when moving places, it's
just that because he works at a higher layer it will be a little slower to forward packets than
using MAC addresses.
Based on other applications or combinations
It is possible to define a VLAN based on the application being run, or a combination of all of
the above types to apply to a network. For example: the FTP (file transfer protocol)
application can only be used by VLAN 1 and Telnet can only be used on VLAN 2.
The application of a VLAN technology allows a network to be more flexible to support
business goals. Here are some advantages of using VLANs:
security
Departments that have sensitive data separated from the existing network, will reduce the
opportunity for breaches of access to confidential and important information.
Cost reduction
Cost savings result from the absence of the need for expensive network upgrades and
efficient use of available bandwidth and uplink.
Higher performance
By dividing the layer 2 network into several workgroups logically (broadcast domains) it
reduces unnecessary traffic on the network and improves performance.kjk
Broadcast storm mitigation
Splitting a network into VLANs reduces the number of devices participating in broadcast
storms.
Improved IT staff efficiency
With VLAN network management is easier, because users with the same network needs
share the same VLAN.
Simpler project or application management
Having separate functions makes it easier to manage a project or work with a specific
application.
You might also like
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- Cisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewFrom EverandCisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- VLANDocument4 pagesVLANIsmail ChorNo ratings yet
- Why Use VLAN's?: Passmore Et Al (3com Report)Document5 pagesWhy Use VLAN's?: Passmore Et Al (3com Report)Shavin AvinNo ratings yet
- Vlan Membership: Static VlansDocument5 pagesVlan Membership: Static VlansJing Jie LeimNo ratings yet
- GECH NT ConfigDocument10 pagesGECH NT ConfigGebrie BeleteNo ratings yet
- Vlans Come in A Variety of Shapes and SizesDocument8 pagesVlans Come in A Variety of Shapes and SizesKenth ShiratsuchiNo ratings yet
- Switching & Wireless: Switching Introduction To Switching VLAN: Virtual Local Area NetworkDocument88 pagesSwitching & Wireless: Switching Introduction To Switching VLAN: Virtual Local Area NetworkGilbert MUHIRENo ratings yet
- VLAN Assignment 02Document10 pagesVLAN Assignment 02Aqeel ZaffarNo ratings yet
- Virtual LAN: Applications and TechnologyDocument7 pagesVirtual LAN: Applications and TechnologyJames HeathNo ratings yet
- Virtual LAN NEtworkDocument4 pagesVirtual LAN NEtworkMarinette MedranoNo ratings yet
- What Is A VLAN?: Technology UpdateDocument2 pagesWhat Is A VLAN?: Technology UpdateMubashir ShahNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Virtual Local Area Network Using Network SimulatorDocument6 pagesImplementation of Virtual Local Area Network Using Network SimulatorijsretNo ratings yet
- Virtuella LANDocument18 pagesVirtuella LANanuj_199No ratings yet
- VlanDocument46 pagesVlanchitrang_11No ratings yet
- Virtual Local Area Networks: Varadarajan.5@osu - EduDocument19 pagesVirtual Local Area Networks: Varadarajan.5@osu - EduRahulDevNo ratings yet
- CCNA 3 CHAPTER 3: Introducing VLANsDocument54 pagesCCNA 3 CHAPTER 3: Introducing VLANsSMMSSMMMNo ratings yet
- Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)Document5 pagesVirtual Local Area Network (VLAN)ijsretNo ratings yet
- Virtual Local Area NetworksDocument26 pagesVirtual Local Area Networksamar_mba10No ratings yet
- VLANs: Virtual Local Area Networks ExplainedDocument13 pagesVLANs: Virtual Local Area Networks ExplainedAbed El Rhman Hamed100% (2)
- 8 Types of VLANs ExplainedDocument9 pages8 Types of VLANs ExplainedSyed Rahmath Ali100% (1)
- VLAN Vs LANDocument2 pagesVLAN Vs LANpk1985No ratings yet
- Design A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) Based Network: June 2020Document10 pagesDesign A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) Based Network: June 2020Shafai Media OfficialNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Vlans: Cisco Networking Academy Program at Tstc-WacoDocument36 pagesChapter 3 - Vlans: Cisco Networking Academy Program at Tstc-WacobosnazmajNo ratings yet
- Vlan CcnaDocument50 pagesVlan CcnaPaulNo ratings yet
- VLAN ReportDocument22 pagesVLAN Reportbalaji-reddy-balaji-2837100% (1)
- VLAN BasicsDocument18 pagesVLAN Basicssatyvan2003No ratings yet
- Overview of Routing Between Virtual Lans: What Is A Virtual Lan?Document8 pagesOverview of Routing Between Virtual Lans: What Is A Virtual Lan?Sophia NahozaNo ratings yet
- Cisco VLAN Benefits and TypesDocument17 pagesCisco VLAN Benefits and Typesobamasux1No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Network DesignDocument26 pagesChapter 1 Network DesignnyeluNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 VLAN VTPDocument17 pagesLecture 7 VLAN VTPSadatur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Router On A Stick WikipediaDocument4 pagesRouter On A Stick WikipediaJoe BrownNo ratings yet
- University of Gondar College of Informatics Department of Information TechnologyDocument6 pagesUniversity of Gondar College of Informatics Department of Information TechnologyGebrie BeleteNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Vlans:: Ip Protocols Supports 500 Devices Per VlansDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Vlans:: Ip Protocols Supports 500 Devices Per VlansRajneesh RathorNo ratings yet
- VLANDocument6 pagesVLANBelete TilahunNo ratings yet
- Virtual Local Area Network Technology and Applications: (VLAN)Document4 pagesVirtual Local Area Network Technology and Applications: (VLAN)ahedNo ratings yet
- Vlan TutorialDocument21 pagesVlan Tutorialunix.linux100% (6)
- Routing Between Virtual Lans: What Is A Virtual Lan?Document6 pagesRouting Between Virtual Lans: What Is A Virtual Lan?Sudhir MaherwalNo ratings yet
- VlanDocument28 pagesVlanRakesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document9 pagesExp 2neha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- Re Ea Locală Virtuală: Română Domeniu de Difuzare Rețea Locală Switch de RețeaDocument3 pagesRe Ea Locală Virtuală: Română Domeniu de Difuzare Rețea Locală Switch de RețeaEmanuel RebleanuNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 VLANs FinishedDocument4 pagesExercise 3 VLANs Finishedmysticman0628No ratings yet
- Basic VLAN Configuration: Erik RodriguezDocument2 pagesBasic VLAN Configuration: Erik RodriguezShanagonda Manoj KumarNo ratings yet
- 4270 Vlan TutorialDocument21 pages4270 Vlan TutorialAsma Lata LataNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - VLANDocument45 pagesLecture 7 - VLANAnnatolia ErastoNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document16 pagesModule 3هبة عمار كاظمNo ratings yet
- Overview of Routing Between VLANs (VLANDocument6 pagesOverview of Routing Between VLANs (VLANkasula-sridhar-kumar-7646No ratings yet
- Operation Manual - VLAN Quidway S3900 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510Document16 pagesOperation Manual - VLAN Quidway S3900 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510juliod85No ratings yet
- Objectives: VlansDocument48 pagesObjectives: VlansDiane GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Vlan Basic Concepts Explained With ExamplesDocument7 pagesVlan Basic Concepts Explained With ExamplesManish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Albert-Ludwigs-Universität, Freiburg Institut Fürinformatik: Internetworking Project Vlan Technology"Document26 pagesAlbert-Ludwigs-Universität, Freiburg Institut Fürinformatik: Internetworking Project Vlan Technology"Ankita Agarwal100% (1)
- What Is VLANDocument3 pagesWhat Is VLANtinmyint27No ratings yet
- Vlan Irtual: V LANDocument35 pagesVlan Irtual: V LANHansa JhaNo ratings yet
- Applied Study of Layer 3 Switching Configuration Based On VLAN Among Colleges' Library Network SystemsDocument4 pagesApplied Study of Layer 3 Switching Configuration Based On VLAN Among Colleges' Library Network SystemsAlex Daniel ZadNo ratings yet
- Acn 2Document17 pagesAcn 2Royal TNo ratings yet
- Ch08 Backbone Network Q&ADocument11 pagesCh08 Backbone Network Q&ATuan Doan0% (1)
- Ip Over Atm 3Document8 pagesIp Over Atm 3Rafi AnsariNo ratings yet
- Layer 2 Switching Vlan Tagging and Compactpci2338Document3 pagesLayer 2 Switching Vlan Tagging and Compactpci2338Patrick AngNo ratings yet
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachFrom EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Next-Generation switching OS configuration and management: Troubleshooting NX-OS in Enterprise EnvironmentsFrom EverandNext-Generation switching OS configuration and management: Troubleshooting NX-OS in Enterprise EnvironmentsNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument10 pagesManualSi Brian TohNo ratings yet
- 2014 CYTECH StandAlone DVR PriceDocument25 pages2014 CYTECH StandAlone DVR PriceBrett Walker100% (1)
- DWR 921e1Document3 pagesDWR 921e1TadilakshmikiranNo ratings yet
- Advance Java Final MaterialDocument137 pagesAdvance Java Final MaterialRajesh Kumar100% (1)
- Distributed Systems Characterization and DesignDocument35 pagesDistributed Systems Characterization and DesignkhoadplaNo ratings yet
- Maxis 1store AgreementDocument23 pagesMaxis 1store AgreementFoong Peng PiawNo ratings yet
- HTB vs PCQ comparisonDocument26 pagesHTB vs PCQ comparisonxagitarioNo ratings yet
- Balibago Primero Integrated School: Senior High School Media and Information LiteracyDocument4 pagesBalibago Primero Integrated School: Senior High School Media and Information LiteracybethNo ratings yet
- Ict and Society NotesDocument75 pagesIct and Society Notesbmashik2002896167% (3)
- Electronic Communications Committee (ECC) Within The European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT)Document13 pagesElectronic Communications Committee (ECC) Within The European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT)Nagendra BadamNo ratings yet
- Industrial TrainingDocument26 pagesIndustrial TrainingPrachi DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Virus vs Worm: Understanding the Key DifferencesDocument27 pagesVirus vs Worm: Understanding the Key DifferencesDonnabelle MedinaNo ratings yet
- LicenseDocument6 pagesLicenseThant ZinNo ratings yet
- Data Domanin Command GuideDocument448 pagesData Domanin Command GuideGreivin ArguedasNo ratings yet
- Google Problem in ChinaDocument22 pagesGoogle Problem in Chinamayanksvp100% (1)
- 100+ Useful Websites & BonusesDocument5 pages100+ Useful Websites & BonusesBEN GURION A/L DAVID / UPMNo ratings yet
- WiFi OffloadDocument41 pagesWiFi Offloadmonel_24671100% (2)
- CV Full - Muhammad Aldhi Nuralam Afriyan DaumalDocument1 pageCV Full - Muhammad Aldhi Nuralam Afriyan Daumalmutiaraa LU'LU'ANNo ratings yet
- Data Hub SetupDocument6 pagesData Hub SetupjsinnNo ratings yet
- Salesforce JMeter Test PlanDocument60 pagesSalesforce JMeter Test PlanReX_XaR_No ratings yet
- Case Study Report On Volkswagen IndiaDocument2 pagesCase Study Report On Volkswagen IndiaGabriel de VeraNo ratings yet
- Govt Simplifies ILD and NLD Licences, Reduces FeesDocument3 pagesGovt Simplifies ILD and NLD Licences, Reduces Feesanubhav777No ratings yet
- System Overview Startup System Overview Startup: © 2018 Avaya, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Page 1Document16 pagesSystem Overview Startup System Overview Startup: © 2018 Avaya, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Page 1Leonar Dosis temaNo ratings yet
- Xerox B1022 MFP Sag En-UsDocument105 pagesXerox B1022 MFP Sag En-UsValyo DiNo ratings yet
- Understanding SIP RE-INVITEDocument6 pagesUnderstanding SIP RE-INVITESK_shivamNo ratings yet
- Nexus Interview Question: Nexux - 7K# Show HSRP BR Nexus - 7K# Show HSRP Standb BRDocument12 pagesNexus Interview Question: Nexux - 7K# Show HSRP BR Nexus - 7K# Show HSRP Standb BRvijay6996No ratings yet
- Semester-V BCA 501-Software Engineering (BCA V)Document8 pagesSemester-V BCA 501-Software Engineering (BCA V)Anitha VeeramaneNo ratings yet
- Manual GaokeDocument96 pagesManual GaokegiottoartNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review-2Document97 pagesFinal Exam Review-2Octavian Ciprian Bordeanu80% (5)
- Chapter 5 International Dimensions of CrimeDocument13 pagesChapter 5 International Dimensions of CrimeShinya KogamiNo ratings yet