Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 4 Psychological Disorders
Uploaded by
Kshitij DasariOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 4 Psychological Disorders
Uploaded by
Kshitij DasariCopyright:
Available Formats
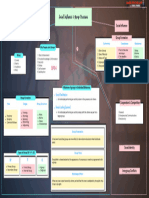
Trauma & Stressor-Related Somatic Symptom & Related
Anxiety DIsorders OCD & Related Disorders Dissociative Disorders Depressive Disorders
Disorders Disorders
A diffuse, vague, very 1. Obsessive Behaviour - PTSD - Post Traumatic These are conditions in 1. Dissociative Amnesia - Major Depressive Disorder -
unpleasant feeling of fear An inability to stop Stress Disorder which there are physical A period of depressed mood
and apprehension
Extensive but selective
symptoms in the absence of
thinking about a particular memory loss with no and / or loss of interest or
a physical disease.
Symptoms - Rapid heart
idea or topic Symptoms - recurrent organic cause. pleasure in most activities.
rate, shortness of breath, 2. Compulsive behaviour - dreams, flashbacks, 2. Dissociative Identity
diarrhoea, loss of appetitte, It is need to perform impaired concentration & 1. Somatic Symptom Disorder (Multiple Symptoms - Change in body
fainting, dizziness, sweating, certain behaviours over & emotional numbing. Disorder - Persistent personality disorder) - weight, constant sleep
sleeplessness, frequent over again often associated with problems, tiredness, inability
body-related symptoms
urination & tremors to think clearly, agitation,
in absence of any medical traumatic experiences in
greatly slowed behaviour,
condition. childhood and thoughts of death &
1. Generalised Anxiety 1. Hoarding disorder 1. Adjustment Disorders 2. Illness anxiety Disorder - 3. Depersonalisation / suicide, excessive guilt or
Disorder 2. Trichotillomania 2. Acute Stress Disorders constantly worrying about Derealisation Disorder - feelings of worthlessness.
2. Panic Disorder 3. Excoriation developing a serious The person experiences a
3. Phobias illness change in his/her sense of
a. Specific Phobias 3. Conversion Disorders - reality & perception of
4 D's - Common Features Factors towards Depression
b. Social Phobias Historical Background reported loss of part or all self.
Deviance 1. Genetic make-up
c. Agoraphobia 1. Supernatural of some basic body
Distress 2. Age
4. Seperation Anxiety 2. Biological or Organic functions.
Dysfunctional 3. Gender
Disorder approach
Danger Factors underlying Abnormal 4. Negative Life Events
3. Psychological approach
4. Organismic approach Behaviour
Psychological
5. Middle Ages 1. Biological factors
Disorders
6. Renaissance period 2. Genetic factors
7. Age of Reason & Enlightment 3. Psychological factors
a. Psychodynamic model Approaches of Abnormal
8. Bio-Psycho-Social Approach Behaviour
(Sigmund Freud)
i. Id Deviation from Social Norms
Schizophrenia Spectrum & Disruptive, Impulse-Control & Maladaptive
Bipolar & Related Disorders Neurodevelopmental Disorders ii. Ego
other Psychotic Disorders Conduct Disorders
iii. Super Ego
1. Bipolar I Disorder b. Behavioural model
1.Attention-Deficit /
Positive Symptoms Hyperactivity Disorder 1. Oppositional Defiant c. Cognitive Model
Mania Depression 1. Delusion (ADHD) Disorder (ODD) - d. Humanistic-existential
a. Delusions of 2.Autism Spectrum Disorder - Age-inappropriate model
2. Bipolar II Disorder persecution Impairments in social amounts of stubbornness, 4. Socio-cultural Model
b. Delusions of reference interaction & communication are irritable, defiant, 5. Diathesis-stress Model Substance Related & Addictive
Mania Depression c. Delusions of grandeur skills disobedient and behave in
Disorders
d. Delusions of control 3.Intellectual Disability (IQ 70 hostile manner.
2. Formal Thought Disorder or below & deficit in adaptive 2. Conduct Disorder - Age- Feeding & Eating Disorders
3. Cyclothymic Disorder a. Loosening of behaviour) inappropriate actions & 1. Alcohol - Drinking
associations 4.Specific Learning Disability - attitudes that violate interferes with their social
Mania Depression b. Neologisms difficulty in perceiving or family expectations, 1. Anorexia nervosa - behaviour and ability to
c. Perseveration processing information societal norms, and the refusing to eat, exercising think & work
3. Hallucinations effectively & accurately personal or property compulsively & 2. Heroin - Dependence,
a. Auditory (Hear) rights of others developing unusual habits withdrawal reaction,
b. Tactile (Touch) a. Verbal Aggression for not eating. paralysed breathing, death
Negative Symptoms c. Somatic (body related) Psychomotor Symptoms b. Physical Aggression 2. Bulimia nervosa - Over 3. Cocaine - Increasing
1. Poverty of speech (Alogia) d. Visual (seeing) 1. Catatonia c. Hostile Aggression eating resistance, withdrawal
2. Blunted affect e. Gustatory (taste) a. Catatonic stupor d. Proactive Aggression 3. Binge eating - frequent symptoms - depression,
3. Flat affect f. Olfactory (smell) b. Catatonic rigidity episodes of out-of- fatigue, sleep problems,
4. Avolition c. Catatonic posturing control eating. irritability & anxiety
You might also like
- NCMHCE Study Supplement PDFDocument348 pagesNCMHCE Study Supplement PDFQuincy Bennett100% (14)
- Summary of Mental IllnessDocument6 pagesSummary of Mental IllnessNelsie Duhilag100% (2)
- Mood Disorders OutlineDocument19 pagesMood Disorders OutlineAki HimeNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric NursingDocument1,800 pagesPsychiatric Nursingkamel abdi100% (3)
- Clinical Differences Among Four Common DementiasDocument2 pagesClinical Differences Among Four Common DementiasIsaac EliasNo ratings yet
- (Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 1010) Xiaochu Zhang, Jie Shi, Ran Tao (Eds.) - Substance and Non-Substance Addiction-Springer Singapore (2017)Document357 pages(Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 1010) Xiaochu Zhang, Jie Shi, Ran Tao (Eds.) - Substance and Non-Substance Addiction-Springer Singapore (2017)Christian Vlad0% (1)
- DSM 1-5Document46 pagesDSM 1-5Dheeraj Kumar ChhillarNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia and PsychoticDocument71 pagesSchizophrenia and Psychoticpunzell eonnieNo ratings yet
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Ocd 1Document16 pagesObsessive Compulsive Disorder Ocd 1Peter SmithNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorders ExplainedDocument11 pagesMood Disorders ExplainedPrincessXFaithNo ratings yet
- Jose Gerardo Los Baños, M.D.: Topic OutlineDocument15 pagesJose Gerardo Los Baños, M.D.: Topic OutlineMaikka IlaganNo ratings yet
- What is psychosisDocument2 pagesWhat is psychosisGrace LNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - NotesDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 4 - NotesAquamsha FahimNo ratings yet
- Psy 214 Lwcture 7Document27 pagesPsy 214 Lwcture 7Hope MashakeniNo ratings yet
- Understanding Depression: Helping Families & Friends Find Better WaysDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Depression: Helping Families & Friends Find Better WaysRajAnandNo ratings yet
- Psych Ch. 7 Notes (Tutor)Document5 pagesPsych Ch. 7 Notes (Tutor)Haylle ThomasNo ratings yet
- Bipolar DisorderDocument1 pageBipolar DisorderNur BalqisNo ratings yet
- Mindmap CH 5 Therapeutic ApproachesDocument1 pageMindmap CH 5 Therapeutic ApproachesKshitij DasariNo ratings yet
- Suicide: A Temporary Solution For A Temporary ProblemDocument20 pagesSuicide: A Temporary Solution For A Temporary ProblemurvashichaudharyNo ratings yet
- MH TermsDocument6 pagesMH TermsWarren MillerNo ratings yet
- Affective Disorders: Moods, Causes and TreatmentsDocument31 pagesAffective Disorders: Moods, Causes and TreatmentsLamyaa Ali HasanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Psychosis and Its DiagnosisDocument52 pagesUnderstanding Psychosis and Its DiagnosisYazan Mahafza100% (1)
- Definition of Terms PDFDocument7 pagesDefinition of Terms PDFkireeeNo ratings yet
- Understanding Neurosis: A Concise Look at the History, Symptoms, and Theories of Neurotic DisordersDocument60 pagesUnderstanding Neurosis: A Concise Look at the History, Symptoms, and Theories of Neurotic DisordersMelda Kusuma WardaniNo ratings yet
- AnxietyDocument4 pagesAnxietyIT’S ME HAYLANo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders I Part 1: Ethel Maureen P. Pagaddu, MDDocument7 pagesAnxiety Disorders I Part 1: Ethel Maureen P. Pagaddu, MDRaiMalsiPilarNo ratings yet
- General Definition, Causes, and Types of Mental IllnessDocument6 pagesGeneral Definition, Causes, and Types of Mental Illnesszahra03762No ratings yet
- Models of Abnormality in PsychopathologyDocument18 pagesModels of Abnormality in PsychopathologyGift MwapeNo ratings yet
- Psych Ch. 5 NotesDocument7 pagesPsych Ch. 5 NotesHaylle ThomasNo ratings yet
- What Is Mental Health?: Risk FactorsDocument2 pagesWhat Is Mental Health?: Risk FactorsElmaRabagoNo ratings yet
- SUICIDEDocument29 pagesSUICIDERizwan ZafarNo ratings yet
- Major Depressive Disorder: Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning and InterventionsDocument25 pagesMajor Depressive Disorder: Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning and InterventionsCath CathNo ratings yet
- Understanding Psychological DisordersDocument148 pagesUnderstanding Psychological Disordersmax lifeNo ratings yet
- Hallucinations and Hearing VoicesDocument4 pagesHallucinations and Hearing VoicesCazacu ParascoviaNo ratings yet
- Kaplan Mood DisorderDocument32 pagesKaplan Mood DisorderSyafruddin SyafruddinNo ratings yet
- Myths and Facts About Mental Health 022007Document2 pagesMyths and Facts About Mental Health 022007Jemimah AlobaNo ratings yet
- Signs and symptoms of mental disorders explainedDocument60 pagesSigns and symptoms of mental disorders explainedgerrgiytryahoo100% (1)
- Handout Chapter15Document3 pagesHandout Chapter15BismahMehdiNo ratings yet
- Major Depressive EpisodeDocument55 pagesMajor Depressive EpisodeKamogelo MakhuraNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric NursingDocument28 pagesPsychiatric NursingRAYMART DENAGANo ratings yet
- GlossaryDocument8 pagesGlossarysnejinka1979No ratings yet
- Somatoform DisordersDocument10 pagesSomatoform Disorderssuresh patilNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument11 pagesAnxiety DisordersMahmoud emadNo ratings yet
- Mental Disorders: Key FactsDocument9 pagesMental Disorders: Key Factssoshi2691loveNo ratings yet
- Helping Anxious Children: A Parent's GuideDocument17 pagesHelping Anxious Children: A Parent's GuideImtiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - 7oct2022 - RDocument22 pagesLecture 6 - 7oct2022 - RAryaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Terms - PsychDocument13 pagesSummary of Terms - Psychapi-642709499No ratings yet
- MSE of Uncooperative PTDocument16 pagesMSE of Uncooperative PTGurvinder KalraNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: Signs and SymptomsDocument38 pagesSchizophrenia: Signs and SymptomsRatu Nurul FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Mental and Emotional HealthDocument2 pagesMental and Emotional HealthEden LacsonNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 Personality DisordersDocument3 pagesNCM 117 Personality DisordersMary Queenie TulinNo ratings yet
- Wikipedia: The Act or An Instance of Taking One's Own Life Voluntarily and IntentionallyDocument9 pagesWikipedia: The Act or An Instance of Taking One's Own Life Voluntarily and Intentionallysubham kumarNo ratings yet
- OCD Types and CompulsionsDocument95 pagesOCD Types and CompulsionsDzarrin100% (3)
- PSYCHIATRIC NURSING: THERAPEUTIC COMMUNICATIONDocument5 pagesPSYCHIATRIC NURSING: THERAPEUTIC COMMUNICATIONElla MejiaNo ratings yet
- ! Light Her Fire Phoenix Editionbv2Document133 pages! Light Her Fire Phoenix Editionbv2AndygggNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology (Chapter 4)Document9 pagesAbnormal Psychology (Chapter 4)Mavy QueenNo ratings yet
- 02 - Community Mental HealthDocument41 pages02 - Community Mental HealthNinad KupwadeNo ratings yet
- Anxiety and Psychosexual Disorders in ChildDocument60 pagesAnxiety and Psychosexual Disorders in ChildAnnalesa BarkerNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology: Definitions, Perspectives, and ClassificationDocument53 pagesAbnormal Psychology: Definitions, Perspectives, and ClassificationcipaxobNo ratings yet
- Schizo ToolDocument3 pagesSchizo Toolsherell220No ratings yet
- Mental Health Lesson Plan Details Common DisordersDocument10 pagesMental Health Lesson Plan Details Common DisordersGladys Javier PatoNo ratings yet
- Anxiety PDFDocument2 pagesAnxiety PDFHussain OtlaNo ratings yet
- Abpsych ReviewerDocument17 pagesAbpsych ReviewerAGNER JASMIN ROSE L.No ratings yet
- PSYCH 9 Reviewer - Chapter 7 Mood Disorders and SuicideDocument5 pagesPSYCH 9 Reviewer - Chapter 7 Mood Disorders and SuicideJoelle Marie GarciaNo ratings yet
- DepressionDocument3 pagesDepressionsarguss14No ratings yet
- Psychiatry Notes - Depressive DisorderDocument2 pagesPsychiatry Notes - Depressive DisorderLiSenNo ratings yet
- Neurodevelopmental Disorders FinalDocument7 pagesNeurodevelopmental Disorders FinalAARON JOHN VIRAYNo ratings yet
- Suicide: Risk Factors, Assessment, Methodological Problems: Sweta Sheth Chair: Dr. Rajesh GopalakrishnanDocument59 pagesSuicide: Risk Factors, Assessment, Methodological Problems: Sweta Sheth Chair: Dr. Rajesh GopalakrishnanpriyagerardNo ratings yet
- Free Trade, Protectionism, International Trade Theories, and Balance of PaymentsDocument25 pagesFree Trade, Protectionism, International Trade Theories, and Balance of PaymentsPravin AjaazNo ratings yet
- Why Do Teens Consider Suicide (EAPP)Document5 pagesWhy Do Teens Consider Suicide (EAPP)michaellamigas04No ratings yet
- AP Psych Unit 4 VocabDocument3 pagesAP Psych Unit 4 Vocabdittman1430No ratings yet
- Clinical Features of Common Psychiatric DisordersDocument21 pagesClinical Features of Common Psychiatric DisordersShivan A.C.No ratings yet
- Understanding schizophrenia definitions and symptomsDocument11 pagesUnderstanding schizophrenia definitions and symptomsDuha B. SalimNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Social Influence & Group Process MindmapDocument1 pageCH 7 Social Influence & Group Process Mindmap4bh8n2nfmpNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Attitudes & Social CognitionDocument1 pageCH 6 Attitudes & Social CognitionKshitij DasariNo ratings yet
- QLM - Debentures 22Document14 pagesQLM - Debentures 22Kshitij DasariNo ratings yet
- SPIL AR2022 23 Complete Annual ReportDocument308 pagesSPIL AR2022 23 Complete Annual ReportHitansh ShahNo ratings yet
- Body Integrity Identity DisorderDocument6 pagesBody Integrity Identity DisorderCarla MesquitaNo ratings yet
- Scientific American MIND, Vol. 32.2 (March-April 2021)Document34 pagesScientific American MIND, Vol. 32.2 (March-April 2021)Aladin1972No ratings yet
- Dulmus L.a.rapp-Paglicci - Handbook of Preventive Interventions For AdultsDocument482 pagesDulmus L.a.rapp-Paglicci - Handbook of Preventive Interventions For AdultsTiara Febriani NurantiNo ratings yet
- Case of DylanDocument5 pagesCase of DylanElaine Joyce PasiaNo ratings yet
- Role of Play Therapy in Childhood Grief: A Case Report: December 2016Document73 pagesRole of Play Therapy in Childhood Grief: A Case Report: December 2016Ram JayNo ratings yet
- Beyond Negative Affectivity A Hierarchical ModelDocument18 pagesBeyond Negative Affectivity A Hierarchical ModelDe La LamaNo ratings yet
- Per. Dev. (Bin-Bin)Document21 pagesPer. Dev. (Bin-Bin)Jayric BanagyoNo ratings yet
- Journal of Child Neurology 4Document7 pagesJournal of Child Neurology 4NEUROLAB ESCALÓNNo ratings yet
- SpedDocument19 pagesSpedLyra CampbilNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders in Children and Adolescents: Assessment and Diagnosis - UpToDateDocument11 pagesAnxiety Disorders in Children and Adolescents: Assessment and Diagnosis - UpToDatePrakhar JainNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Self Learning Guide (Revised)Document24 pagesSpiritual Self Learning Guide (Revised)MARJOHN ESGUERRANo ratings yet
- NCM 117: Long Exam 2: Anxiety & Anxiety Disorders Topic OutlineDocument56 pagesNCM 117: Long Exam 2: Anxiety & Anxiety Disorders Topic OutlineLoren SarigumbaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders: Moges Ayehu, MD, Psychiatrist Assistant Professor, HUCMHDocument38 pagesAnxiety Disorders: Moges Ayehu, MD, Psychiatrist Assistant Professor, HUCMHsoran muzeyinNo ratings yet
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder in Children and Adolescents: Georgina Krebs, Isobel HeymanDocument5 pagesObsessive-Compulsive Disorder in Children and Adolescents: Georgina Krebs, Isobel HeymanRidwan AdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document23 pagesModule 1Franz Simeon ChengNo ratings yet
- Fred Penzel Pliny The Elder Elliott Larson Eleanor RooseveltDocument4 pagesFred Penzel Pliny The Elder Elliott Larson Eleanor Rooseveltam_jaluNo ratings yet
- Anorexia Research Paper - Essay 1Document5 pagesAnorexia Research Paper - Essay 1api-329151535No ratings yet
- ScientificAnalysisofMantra BasedMeditationDocument7 pagesScientificAnalysisofMantra BasedMeditationTomas Meraz MorgenrothNo ratings yet