Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 7 Social Influence & Group Process Mindmap
Uploaded by
4bh8n2nfmpOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 7 Social Influence & Group Process Mindmap
Uploaded by
4bh8n2nfmpCopyright:
Available Formats
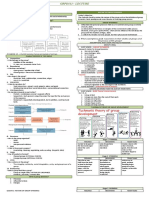
Social Influence & Group Processes
Social Influence
Group
Group Formation
Conformity Compliance Obedience
Why People Join Groups? 2
1. Size of group 1. Foot in the door 1. Roles
2. Size of Minority technique 2. Norms
Group 1. Goal Achievement 2. The deadline 3. Status
2. Provide Knowledge & Information 3. Nature of Task technique
1. Crowd 4. Cohesiveness
3. Security 4. Expression of behaviour 3. Door in the face
2. Teams
4. Status 5. Personality technique
3. Audience
4. Mob
5. Self-esteem GPS4
6. Satisfaction
Influence of group on Individual Behaviour
Social Facilitation
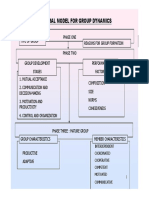
Group Formation
An individual performing an activity alone in the presence of others
How Stages Group Structure Cooperation & Competition
Social Loafing (Latane)
Forming An individual performing an activity along with the others as part of a 1. Reward
Proximity Storming Roles larger group 2. Interpersonal Communication
Similarity Norming Norms 3. Reciprocity
Common Motives Performing Status
Adjourning Cohesiveness
Group Polarisation
It has been found that groups are more likely to take extreme decisions than Individuals
alone
Social Identity
Types of Group (SP - IF - IO) Group Think
SP IF IO Groupthink is characterised by the appearance of consensus or unanimous agreement with
a group
Primary Group Formal Group Ingroup
Secondary Group Informal Group Outgroup Intergroup Conflicts
Bandwagon Effect
When any view is also favored by others, we feel that this view is validated by the public thus
it has to be right.
You might also like
- Teamwork - OB Group 3 - FinalDocument24 pagesTeamwork - OB Group 3 - FinalferdialrfNo ratings yet
- Group Dynamics and Group ProcessesDocument84 pagesGroup Dynamics and Group ProcessesDZ LARIZA100% (4)
- Chapter 7 Groups and TeamsDocument38 pagesChapter 7 Groups and TeamsJohn Leo Caballero DagcutanNo ratings yet
- SWP6: Social Work Practice With GroupsDocument12 pagesSWP6: Social Work Practice With GroupsEdezean Tenebro Balabat100% (2)
- Work GroupsDocument56 pagesWork Groupsbharatsoni007100% (1)
- Work Group BehaviourDocument21 pagesWork Group BehaviourAlie GabianaNo ratings yet
- Leadership and Management Art - Case Study in Cambodia Leadership & Management Art - PHEAK SIENGHUO 彭胜华Document4 pagesLeadership and Management Art - Case Study in Cambodia Leadership & Management Art - PHEAK SIENGHUO 彭胜华Sienghuo PheakNo ratings yet
- Solving Word Problems Involving Subtraction of Whole Numbers Including Money With or Without RegroupingDocument3 pagesSolving Word Problems Involving Subtraction of Whole Numbers Including Money With or Without Regroupingsaticao100% (2)
- 100 Group Games: Skills in Facilitating Group GamesFrom Everand100 Group Games: Skills in Facilitating Group GamesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 3 in Group DynamicsDocument3 pagesLesson 1 3 in Group DynamicsAC NaurgenNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Human Language and Animal CommunicationDocument5 pagesDifferences Between Human Language and Animal CommunicationRafikNo ratings yet
- High-Impact Tools for Teams: 5 Tools to Align Team Members, Build Trust, and Get Results FastFrom EverandHigh-Impact Tools for Teams: 5 Tools to Align Team Members, Build Trust, and Get Results FastRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Session 1-6 PDFDocument25 pagesSession 1-6 PDFSHREYA UNNIKRISHNAN PGP 2019-21 BatchNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Group Decision Support and Groupware TechnologiesDocument31 pagesChapter 5: Group Decision Support and Groupware TechnologiesRetno Aulia VinartiNo ratings yet
- Group: Two or More Individuals, Interacting and Interdependent, Who Come Together To Achieve Particular ObjectivesDocument68 pagesGroup: Two or More Individuals, Interacting and Interdependent, Who Come Together To Achieve Particular ObjectivesRahul RastogiNo ratings yet
- Ob-Ii: Return To Independence Feeling of Team Spirit Is ExperiencedDocument29 pagesOb-Ii: Return To Independence Feeling of Team Spirit Is ExperiencedSoumya HalderNo ratings yet
- GROUP DYNAMICS ReviewerDocument8 pagesGROUP DYNAMICS ReviewersugarxglossNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Group Behavior: Defining Groups Classifying Groups (Cont'd)Document5 pagesFoundation of Group Behavior: Defining Groups Classifying Groups (Cont'd)Quyên HạnhNo ratings yet
- BPT Unit 1 752884140Document14 pagesBPT Unit 1 752884140sanjai_rahulNo ratings yet
- Group TeamsDocument22 pagesGroup TeamsnainaNo ratings yet
- Group Dynamic: Merry Indah SariDocument16 pagesGroup Dynamic: Merry Indah SariAmatsuka RizuNo ratings yet
- Groups in OrganizationDocument31 pagesGroups in OrganizationparimalamNo ratings yet
- Kasturba Gandhi Nursing College Class Teaching ON Group DynamicsDocument14 pagesKasturba Gandhi Nursing College Class Teaching ON Group DynamicsFriends ThamizhaNo ratings yet
- A General Model For Group Dynamics: Interdependent Coordinated Cooperative Competent Motivated CommunicativeDocument10 pagesA General Model For Group Dynamics: Interdependent Coordinated Cooperative Competent Motivated CommunicativeSRIRAMA VKNo ratings yet
- (SUMMARY) Perilaku Keorganisasian (Chapter 9)Document6 pages(SUMMARY) Perilaku Keorganisasian (Chapter 9)taqi taqaNo ratings yet
- Kasturba Gandhi Nursing College Class Teaching ON Group DynamicsDocument13 pagesKasturba Gandhi Nursing College Class Teaching ON Group DynamicsFriends ThamizhaNo ratings yet
- PPT Kelompok 3Document22 pagesPPT Kelompok 3NoviNo ratings yet
- 2.1 - Group & TeamDocument32 pages2.1 - Group & Team727822TPMB005 ARAVINTHAN.SNo ratings yet
- HBO Module No. 9Document5 pagesHBO Module No. 9Ruby A BarrogaNo ratings yet
- YRahmawati MP W15Document28 pagesYRahmawati MP W15sofia fiersNo ratings yet
- Group BehaviorDocument22 pagesGroup BehaviorIdris SaifeeNo ratings yet
- SlidesDocument117 pagesSlidesJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- An Overview of OBDocument37 pagesAn Overview of OBDevrajNo ratings yet
- Pinoy Development of Groups and TeamsDocument19 pagesPinoy Development of Groups and TeamsSarah Jane SeñaNo ratings yet
- Group DynamicsDocument19 pagesGroup DynamicskomalpreetNo ratings yet
- Last Teaching PDFDocument15 pagesLast Teaching PDFFriends ThamizhaNo ratings yet
- Team LeadershipDocument31 pagesTeam Leadershipapi-3782823No ratings yet
- Group: Prof. Khagendra Bulmim, New DelhiDocument57 pagesGroup: Prof. Khagendra Bulmim, New DelhiSwati SahuNo ratings yet
- GROUP Chapter 9Document39 pagesGROUP Chapter 9samiyaNo ratings yet
- SAQ'S and StudiesDocument3 pagesSAQ'S and StudiesAlia BibiNo ratings yet
- PTKN CLC 2020 - Chapter 5 Teamwork - K59CLCDocument11 pagesPTKN CLC 2020 - Chapter 5 Teamwork - K59CLCThanh-Phu TranNo ratings yet
- Groups and Teams2021Document39 pagesGroups and Teams2021Sai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Group Formation and Development Types of Groups Why Individual Join The Group? Group Structure Group CohesivenessDocument4 pagesGroup Formation and Development Types of Groups Why Individual Join The Group? Group Structure Group CohesivenessEunice ManayagNo ratings yet
- P119 - Module 1Document18 pagesP119 - Module 1Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P119 - Module 1 - 7Document21 pagesP119 - Module 1 - 7Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- The Learning Organisation: Rishabh Tiwari MBA F&C - Ivth Sem Roll No - 14Document14 pagesThe Learning Organisation: Rishabh Tiwari MBA F&C - Ivth Sem Roll No - 14Ravi BhartiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Group BehaviourDocument24 pagesUnit 3 Group BehaviourMichelle Gozon100% (2)
- Chapter 7 Group DynamicsDocument21 pagesChapter 7 Group DynamicsChao Kim100% (1)
- Presentation 1Document31 pagesPresentation 1Rohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Security 2. Inability To Control Self and Others 3. Respect Between Parties 4. Limited Resources 5. FrustrationsDocument6 pagesSecurity 2. Inability To Control Self and Others 3. Respect Between Parties 4. Limited Resources 5. FrustrationsNor-Safinah DimaNo ratings yet
- Organisational Behaviour - AnDocument37 pagesOrganisational Behaviour - Ansk5335No ratings yet
- Week 13 - 15 The Social Group in IndustryDocument10 pagesWeek 13 - 15 The Social Group in IndustryzamudiowhelNo ratings yet
- 5 Cohesion and DevelopmentDocument19 pages5 Cohesion and Developmentjohnpaolo mercadoNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Group BehaviorDocument12 pagesFoundations of Group BehaviordokiparthipraveenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7hboDocument10 pagesChapter 7hboJenNo ratings yet
- Module IV: Behavioral Pattern of Group: Creativity For Team ExcellenceDocument78 pagesModule IV: Behavioral Pattern of Group: Creativity For Team Excellenceprati pNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - Groups & IndividualsDocument29 pagesLecture 8 - Groups & IndividualsHaz ZiraNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument52 pagesFinaljonna timonanNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Group Behavior and Work Teams: Lecturer: Do Tien Long 09 04 51 54 46Document29 pagesFoundations of Group Behavior and Work Teams: Lecturer: Do Tien Long 09 04 51 54 46km12286No ratings yet
- Group Dynamics and BehaviourDocument26 pagesGroup Dynamics and BehaviourMelody ShekharNo ratings yet
- Group Behavior, Terms, Teams AndconflictDocument7 pagesGroup Behavior, Terms, Teams Andconflictvillyn011595No ratings yet
- Unit 11Document27 pagesUnit 11Alexandra Bachero BeltránNo ratings yet
- Child Without Tomorrow: Pergamon General Psychology SeriesFrom EverandChild Without Tomorrow: Pergamon General Psychology SeriesNo ratings yet
- Hanna Horvat Artifact Multicultural Lesson ActivityDocument5 pagesHanna Horvat Artifact Multicultural Lesson Activityapi-549584276No ratings yet
- Pepe TehDocument11 pagesPepe TehAlwin lantinNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument5 pagesThesisMeenakshi SundariNo ratings yet
- Profit Prediction On MSME Using Least Square MethodDocument5 pagesProfit Prediction On MSME Using Least Square MethodInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Academic Guidebook Electrical Engineering 2017Document173 pagesAcademic Guidebook Electrical Engineering 2017Adelon LeopoldNo ratings yet
- Maiers,+W + (2021) +crisis+and+re-Foundation+of+psychologyDocument17 pagesMaiers,+W + (2021) +crisis+and+re-Foundation+of+psychologyCarlos S.Z.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Shela Mae LibandoNo ratings yet
- Whitebread ET AL 2007Document24 pagesWhitebread ET AL 2007Rubén Páez DíazNo ratings yet
- Reflection On George KellyDocument3 pagesReflection On George KellyMalaika NoorNo ratings yet
- University of Madras B.A. Degree Course in Sociology (With Effect From The Academic Year 2008-2009)Document25 pagesUniversity of Madras B.A. Degree Course in Sociology (With Effect From The Academic Year 2008-2009)Sam PeterNo ratings yet
- 1-Integrated Curriculum AY 2021-2022Document34 pages1-Integrated Curriculum AY 2021-2022Cyryhl GutlayNo ratings yet
- Urban Transportation Modeling System (UTMS) : Engr. Francis F. VillarealDocument164 pagesUrban Transportation Modeling System (UTMS) : Engr. Francis F. VillarealGiacomo EllieNo ratings yet
- AI - Lec 02Document13 pagesAI - Lec 02Manish GuleriaNo ratings yet
- Etymology: Biology Is TheDocument2 pagesEtymology: Biology Is TheJohn Kenneth Escober BentirNo ratings yet
- A Program Evaluation of Performing Arts Instruction Used To Impro - CleanedDocument249 pagesA Program Evaluation of Performing Arts Instruction Used To Impro - CleanedErwin GasparNo ratings yet
- Journal of International Students 2017 JIS Volume 7 Issue 2Document285 pagesJournal of International Students 2017 JIS Volume 7 Issue 2STAR ScholarsNo ratings yet
- Writing An Informal Proposal SampleDocument4 pagesWriting An Informal Proposal SampleBannawag HS North CotabatoNo ratings yet
- Culture - Ethics PresentationDocument6 pagesCulture - Ethics PresentationKatrina Alexis AlbaNo ratings yet
- Students' Attainment Level-Maths 6Document38 pagesStudents' Attainment Level-Maths 6Earl Jon Mari BagacinaNo ratings yet
- Dorothy JohnsonDocument5 pagesDorothy JohnsonJoanna Marie TulioNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Chapter 1 5 - 12 Escoffier 2Document26 pagesGroup 1 Chapter 1 5 - 12 Escoffier 2Florence DolorNo ratings yet
- Flipped ClassroomDocument15 pagesFlipped ClassroomRhea OleNo ratings yet
- Building Resources and CapabilitiesDocument5 pagesBuilding Resources and CapabilitiesBasari OdalNo ratings yet
- SOE Lesson 1 INTRO TO SOCIOLOGY For TMD 20Document27 pagesSOE Lesson 1 INTRO TO SOCIOLOGY For TMD 20given kalukanguNo ratings yet
- BME PHD Program (2017) - FinalDocument13 pagesBME PHD Program (2017) - FinalWubshet ShimelsNo ratings yet
- Journal - INDUSTRY 4.0 - ARE WE READYDocument17 pagesJournal - INDUSTRY 4.0 - ARE WE READYElaine SumangNo ratings yet
- Woldia University Faculty of Business and Economics Departement of ManagementDocument34 pagesWoldia University Faculty of Business and Economics Departement of ManagementFiteh KNo ratings yet