Professional Documents
Culture Documents
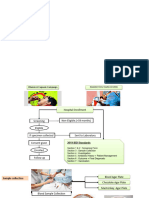
Would A Loss of Control Lead To Risk of Illness or Injury: Decision Tree
Uploaded by
201253200 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesOriginal Title
CCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesWould A Loss of Control Lead To Risk of Illness or Injury: Decision Tree
Uploaded by
20125320Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Would a loss of control lead to risk of illness or injury
Yes No
Is there a later step that this hazard
is or can be controlled?
Yes No
Not CCP
CCP Not
DECISION TREE
Results of determination tree for CCP Determination
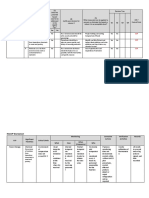
Ste Process step Hazards Control Contro
p measures l point
1(a) Receive milk Presence of Microbiologic CP
microorganism al analysis
s Keep records
for each
tanker route
1(b) Raw milk(Release Antibiotics Rosa test CCP
tests) Foreign Kundrat test
materials In line filter
Inspect tanker
before off
loading
Quality of
gaskets
1(c) Raw cooling milk Microbial Temperature CP
1(d) Silo release raw milk Microbial Temperature CP
Chemical risks and time
Cleaning GMP
2(a) Cream separation Chemical risk Cleaning GMP
3(a) Homogenisation Chemical risk Cleaning GMP
4(a) Pasteurization Microbial Tempertature CCP
and time
4(b) Pasteurization(Transf Microbial Cleaning GMP
er to tank)
5 Loading milk(mixing) Microbial Cleaning GMP
6 Powder mixing Physical Production GMP
foreign and process
materials control
7 T105 to storage tank Microbial Cleaning GMP
8 Pasteurization and Microbial Time and CCP
homogenisation temperature
9 Cooling down to Microbial Temperature CCP
maturation
temperature, ferment
addition
10 Maturation, breaking Microbial Cleaning GMP
of curd
11 Cooling, Smoothing, Microbial Cleaning GMP
Transfer to tank
12 Adding sterile apple Microbial Cleaning GMP
pieces
13 Packing Microbial Cleaning GMP
14 Storage Microbial Lab test CP
15 Dispatch Microbial Temperature CP
CCPs of apple yogurt production
-The presence of antibiotics, and foreign materials in raw milk
-Effective pasteurization and homogenization
-Keeping the fermentation temperature
You might also like
- Technical Manual: 110 125US 110M 135US 120 135UR 130 130LCNDocument31 pagesTechnical Manual: 110 125US 110M 135US 120 135UR 130 130LCNKevin QuerubinNo ratings yet
- Man Machine Interface SafetyDocument9 pagesMan Machine Interface SafetyVidyesh Viswanathan NairNo ratings yet
- D6a - D8a PDFDocument168 pagesD6a - D8a PDFduongpn63% (8)
- HACCP Plan Template FermentationDocument18 pagesHACCP Plan Template FermentationAugustina AnaglateyNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Lantape, Ryan Luis P. RISK 111 Balandang, Jymel Gabriel Submitted To: Mrs. Mylene Dela Cruz Palmares, Vincent RileyDocument3 pagesSubmitted By: Lantape, Ryan Luis P. RISK 111 Balandang, Jymel Gabriel Submitted To: Mrs. Mylene Dela Cruz Palmares, Vincent RileyJhon Rommel Dela Cruz-OdiamanNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Corrective Action Verification Procedure Documentat IONDocument3 pagesMonitoring Corrective Action Verification Procedure Documentat IONKimberly Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- EMI-EMC - SHORT Q and ADocument5 pagesEMI-EMC - SHORT Q and AVENKAT PATILNo ratings yet
- HACCPExample1 PDFDocument6 pagesHACCPExample1 PDFSaraa HusainNo ratings yet
- Chocolate Liquor HACCPDocument5 pagesChocolate Liquor HACCPKSXNo ratings yet
- Section 5-2 HACCP PLANDocument3 pagesSection 5-2 HACCP PLANshamroz khanNo ratings yet
- HACCP Plan ExampleDocument20 pagesHACCP Plan ExampleMenna WahedNo ratings yet
- HACCP For Yoghurt ProductionDocument29 pagesHACCP For Yoghurt ProductionLim Che YanNo ratings yet
- HACCP Plan GHEEDocument20 pagesHACCP Plan GHEEMaryam AhmedNo ratings yet
- I.V. FluidDocument4 pagesI.V. FluidOdunlamiNo ratings yet
- Process Step HACCPDocument2 pagesProcess Step HACCPMeha RajNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Ultrapure Water Systems - : Igor GorskyDocument36 pagesPharmaceutical Ultrapure Water Systems - : Igor GorskyunknownNo ratings yet
- Safety in The Process Industries: College of Arts and Engineering Chemical Engineering DepartmentDocument8 pagesSafety in The Process Industries: College of Arts and Engineering Chemical Engineering DepartmentJaynie Lee VillaranNo ratings yet
- 13.2 HACCP Plans ExamplesDocument10 pages13.2 HACCP Plans ExamplesRodgers MtongaNo ratings yet
- LC HAGroundBeefDocument2 pagesLC HAGroundBeefAnar MahmudovNo ratings yet
- CCP For Dairy Fill in Haccp AnalysisDocument2 pagesCCP For Dairy Fill in Haccp AnalysisKiara JamesNo ratings yet
- Haccpofmilkpasteurizationbyumairahmad 190430145242 PDFDocument14 pagesHaccpofmilkpasteurizationbyumairahmad 190430145242 PDFUzair Aslam KhanNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE HACCP PLAN FOR NO COOK FOOD Prepared byDocument2 pagesSAMPLE HACCP PLAN FOR NO COOK FOOD Prepared byyounelNo ratings yet
- FMCB - HACCP Yoghurt PDFDocument10 pagesFMCB - HACCP Yoghurt PDFEdelin Nilsa PutriNo ratings yet
- HACCP ImplementationDocument25 pagesHACCP ImplementationAronn SiamNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat SheetDocument16 pagesPython Cheat Sheetphamxtien3741No ratings yet
- HACCP Plan Template Cook ChillDocument21 pagesHACCP Plan Template Cook ChillAnastasia IonasNo ratings yet
- Abc Restaurant: Haccp PlanDocument18 pagesAbc Restaurant: Haccp PlanTrelospapasse BaftisedenyparxeisNo ratings yet
- Haccp ApplicationDocument10 pagesHaccp ApplicationMaryamNo ratings yet
- Samikshya PresentationDocument10 pagesSamikshya PresentationUmesh ThapaNo ratings yet
- Lunchbox HACCP PlanDocument18 pagesLunchbox HACCP PlanFooTraGoNo ratings yet
- BVD PCR Technical Review 2 08Document2 pagesBVD PCR Technical Review 2 08Pablo HenrriquezNo ratings yet
- BFHTDocument192 pagesBFHTManvi SinghNo ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis & HACCP WorksheetsDocument3 pagesHazard Analysis & HACCP WorksheetsJohn Cedric DullaNo ratings yet
- Media BPW MerckDocument1 pageMedia BPW MerckKesmavet UPTDLKKNo ratings yet
- Haccp Implentation in Milk IndustriesDocument22 pagesHaccp Implentation in Milk IndustriesUzair Aslam KhanNo ratings yet
- Scope of The HACCP PlanDocument2 pagesScope of The HACCP PlanrajaNo ratings yet
- Curacen EngDocument19 pagesCuracen Engstanescu_radu_mirceaNo ratings yet
- Insert CRP4 0108057591190c503 V5 enDocument4 pagesInsert CRP4 0108057591190c503 V5 enVegha NedyaNo ratings yet
- HPFB MFHPB-19 April 2002 ENDocument13 pagesHPFB MFHPB-19 April 2002 ENThư YJsNo ratings yet
- Syllabus DDTDocument11 pagesSyllabus DDTelvismorey9721No ratings yet
- Kogene Food SafetyDocument24 pagesKogene Food SafetyChandra Mohan RajendranNo ratings yet
- Quantiphy - Handbook v07.2017Document16 pagesQuantiphy - Handbook v07.2017Anisoara HolbanNo ratings yet
- Campylobacter Agar Base Blood Free (CCDA) ISO: Industry RegulationsDocument2 pagesCampylobacter Agar Base Blood Free (CCDA) ISO: Industry RegulationsDOKTER HEWAN TVNo ratings yet
- crp4 2020-03 v1Document4 pagescrp4 2020-03 v1Thempy ccNo ratings yet
- UJI STERILITAS FarmakopeDocument55 pagesUJI STERILITAS FarmakopeRiska Jati AstutiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Course No.: CFPE 3212 Course Title: Food Microbiology & Molecular CellDocument31 pagesLaboratory Manual: Course No.: CFPE 3212 Course Title: Food Microbiology & Molecular CellShovonNo ratings yet
- 1301 en 2Document2 pages1301 en 2lgoNo ratings yet
- Stability of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) DNA in PreservCyt® at 4ºC and Room Temperature, As Detected by The Roche AMPLICOR® HPV TestDocument1 pageStability of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) DNA in PreservCyt® at 4ºC and Room Temperature, As Detected by The Roche AMPLICOR® HPV TestAlbertoNo ratings yet
- Manual Mother DairyDocument89 pagesManual Mother DairyFahimNo ratings yet
- VM980473 MP enDocument2 pagesVM980473 MP enNguyen Minh SonNo ratings yet
- CIP Checklist: CIP Unit Preparation (In CIP Room)Document1 pageCIP Checklist: CIP Unit Preparation (In CIP Room)Rizwan SultanNo ratings yet
- Grobig Brazil 2016Document66 pagesGrobig Brazil 2016Adib MustofaNo ratings yet
- هاسب تصنيع الشيكولاتةDocument20 pagesهاسب تصنيع الشيكولاتةMuhammed aNo ratings yet
- Market Milk ManualDocument74 pagesMarket Milk ManualNamraNo ratings yet
- HACCP Study 3Document7 pagesHACCP Study 3Karissa Evangelista33% (3)
- Raw Milk Balance Between Hazards and Benefits Carvalho Full Download ChapterDocument51 pagesRaw Milk Balance Between Hazards and Benefits Carvalho Full Download Chapterclyde.alsberry705100% (14)
- 7 Milk Leaflet English PDFDocument4 pages7 Milk Leaflet English PDFsishu21No ratings yet
- A Ceramic Hydroxyapatite-Based Purification Platform Bulletin - RP0033Document8 pagesA Ceramic Hydroxyapatite-Based Purification Platform Bulletin - RP0033Sairam EdupugantiNo ratings yet
- Thc2: Risk Management As Applied To Safety, Sanitation and Security Bshm-IDocument5 pagesThc2: Risk Management As Applied To Safety, Sanitation and Security Bshm-ISheena HarrienNo ratings yet
- Genome Sequencing PresentationDocument18 pagesGenome Sequencing Presentationsamhossain1907No ratings yet
- USP-NF 61 Microbiological Examination of Nonsterile Products - Microbial Enumeration TestsDocument7 pagesUSP-NF 61 Microbiological Examination of Nonsterile Products - Microbial Enumeration TestsALEXÁNDER MOSQUERA CÓRDOBANo ratings yet
- 182-Article Text-1113-1-10-20201201Document4 pages182-Article Text-1113-1-10-20201201Neni Sri GunartiNo ratings yet
- Unit Name Food Fermentation Technology (ITP321)Document3 pagesUnit Name Food Fermentation Technology (ITP321)brianfoldNo ratings yet
- Proteomics in Food Science: From Farm to ForkFrom EverandProteomics in Food Science: From Farm to ForkMichelle Lisa ColgraveNo ratings yet
- Appleyard ResúmenDocument3 pagesAppleyard ResúmenTomás J DCNo ratings yet
- Carry Trade Calculator 1.54Document3 pagesCarry Trade Calculator 1.54Gabriel RomanNo ratings yet
- TRX Documentation20130403 PDFDocument49 pagesTRX Documentation20130403 PDFakasameNo ratings yet
- Scheme Bidirectional DC-DC ConverterDocument16 pagesScheme Bidirectional DC-DC ConverterNguyễn Quang KhoaNo ratings yet
- Chap 06 Ans Part 2Document18 pagesChap 06 Ans Part 2Janelle Joyce MuhiNo ratings yet
- Learner Guide HDB Resale Procedure and Financial Plan - V2Document0 pagesLearner Guide HDB Resale Procedure and Financial Plan - V2wangks1980No ratings yet
- CW February 2013Document60 pagesCW February 2013Clint FosterNo ratings yet
- SVPWM PDFDocument5 pagesSVPWM PDFmauricetappaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Geophysics: Class One Amin KhalilDocument13 pagesMathematical Geophysics: Class One Amin KhalilAmin KhalilNo ratings yet
- Computer System Sevicing NC Ii: SectorDocument44 pagesComputer System Sevicing NC Ii: SectorJess QuizzaganNo ratings yet
- Adjectives With Cork English TeacherDocument19 pagesAdjectives With Cork English TeacherAlisa PichkoNo ratings yet
- Design of Open Channels US Department of Agriculture SCSDocument293 pagesDesign of Open Channels US Department of Agriculture SCSMiguelGuavitaRojasNo ratings yet
- Part A Plan: Simple Calculater Using Switch CaseDocument7 pagesPart A Plan: Simple Calculater Using Switch CaseRahul B. FereNo ratings yet
- Catalog enDocument292 pagesCatalog enSella KumarNo ratings yet
- Nasoya FoodsDocument2 pagesNasoya Foodsanamta100% (1)
- 11 TR DSU - CarrierDocument1 page11 TR DSU - Carriercalvin.bloodaxe4478100% (1)
- Aisc Research On Structural Steel To Resist Blast and Progressive CollapseDocument20 pagesAisc Research On Structural Steel To Resist Blast and Progressive CollapseFourHorsemenNo ratings yet
- Harga H2H Pula-Paket Data - Saldo EWallet v31012022Document10 pagesHarga H2H Pula-Paket Data - Saldo EWallet v31012022lala cemiNo ratings yet
- DevelopmentPermission Handbook T&CPDocument43 pagesDevelopmentPermission Handbook T&CPShanmukha KattaNo ratings yet
- Rundown Rakernas & Seminar PABMI - Final-1Document6 pagesRundown Rakernas & Seminar PABMI - Final-1MarthinNo ratings yet
- Sun Hung Kai 2007Document176 pagesSun Hung Kai 2007Setianingsih SENo ratings yet
- Omae2008 57495Document6 pagesOmae2008 57495Vinicius Cantarino CurcinoNo ratings yet
- 0901b8038042b661 PDFDocument8 pages0901b8038042b661 PDFWaqasAhmedNo ratings yet
- MML3 Journal To CapcomDocument103 pagesMML3 Journal To CapcomFer BarcenaNo ratings yet
- Study of Means End Value Chain ModelDocument19 pagesStudy of Means End Value Chain ModelPiyush Padgil100% (1)