Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tinywow - Nursing - Qs - 42487884 - 3
Uploaded by
juliuscezarquinayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tinywow - Nursing - Qs - 42487884 - 3
Uploaded by
juliuscezarquinayCopyright:
Available Formats
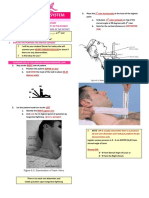
COMMON MEDICAL INTRAMUSCULAR INJECTION SITES 5 P’S OF
ABBREVIATIONS M ID -D ELTOID A REA CIRCULATORY CHECKS
The recommended boundaries of the injection area Pain
ABG arterial blood gas
P
form a rectangle bounded by the lower edge of the
a.c. before meals acromion process on the top to a point on the later- Pallor
ADL activities of daily living al side of the arm opposite the axilla or armpit on Paralysis
ad lib the bottom. Avoid the acromion and humerus, as Paresthesia
as desired Pulse
AP anteroposterior well as the brachial veins and arteries. Limit the
A&P anterior and posterior number of injections here as the area is small and
cannot tolerate repeated injections or large quantities
ASHD arteriosclerotic heart disease
AV arteriovenous, atrioventricular
of medications >1 ml. EDEMA
b.i.d. twice a day POSTERIOR GLUTEAL AREA (DORSOGLUTEAL) Assess by placing thumb over the dorsum
bpm beats per minute The most common site for injections. Restrict of the foot or tibia for 5 seconds
c with injections to that portion of the gluteus medius 0 No edema
CAD coronary artery disease which is above and outside of a diagonal line 1+ Barely discernible depression
cc chief complaint, cubic centimeter drawn from the greater trochanter of the femur to 2+ A deeper depression (less
the posterior superior iliac spine. than 5 mm) accompanied by
cm centimeter
normal foot and leg contours
C&S culture and sensitivity 3+ Deep depression (5 to 10
CSF cerebrospinal fluid VENTROGLUTEAL AREA mm) accompanied by foot
CT computed tomography A good site as it is removed from major nerves and vas-
cular structures. Palpate to find the greater trochanter, and leg swelling
cu cubic the anterior superior iliac spine and the iliac crest. When 4+ An even deeper depression
DIC disseminated intravascular coagulation injecting into the left side of the patient, place the palm of (more than 1 cm) accompanied
DSA digital subtraction angiography the right hand on the greater trochanter and the index finger by severe foot and leg swelling
FUO fever of undetermined origin on the anterior superior iliac spine. Spread the middle finger
g, gm gram posteriorly away from the index finger as far as possible
along the iliac crest, as shown in the drawing. A “V” space
gr grain or triangle between the index and middle finger is PULSES
gt, gtt drop, drops formed. The injection is made in the center of the triangle Peripheral pulses should be com-
HS at bedtime, hour of sleep with the needle directed slightly upward toward the crest of pared for rate, rhythm, and quality.
ICS intercostal space the ilium. (When injecting into the right side of the Pulses are graded as follows:
patient, use your left hand for placement).
IU international unit 0 Absent
kg kilogram VASTUS LATERALIS AREA +1 Weak and thready
KVO, KO keep vein open, keep open A relatively safe injection site free from major nerves and +2 Normal
KUB kidneys, ureters, and bladder blood vessels. This injection area is bounded by the mid- +3 Full
l liter anterior thigh on the front of the leg, the mid-lateral thigh +4 Bounding
lb pound on the side, a hand’s breadth below the greater trochanter of
LUQ left upper quadrant the femur at the proximal end and another hand’s breadth
above the knee at the distal end.
M molar DOSAGE CUP
m meter, minim Z-TRACK TECHNIQUE
µ micron A Z-track technique is used for administering any irritating fluid to ‘seal’ med-
mEq milliequivalent ication in the muscle. Figure A shows the normal tissue before the injection. As
mg milligram in figure B, retract the tissue, insert the needle, administer medication, remove
µg microgram the needle, and release tissue. Note in figure C, the tissue relationships after the
ml milliliter angled Z-tract left by the needle.
µl microliter A B C
mm millimeter
NPO nothing by mouth
OTC over the counter
oz ounce
p.c. after meals
PERRLA pupils equal, round, reactive to light
and accommodation CALCULATING I.V. DRIP RATE HOUSEHOLD/APOTHECARY/
P.O. by mouth The physician’s order states: 1,000 ml LRS to infuse METRIC EQUIVALENTS
prn as needed, whenever necessary over 8 hours. The administration set delivers 15 drops Household Apothecary Metric
per milliliter. What should the drip rate be?
PTCA percutaneous transluminal coronary Volume
angioplasty Use the equation: --- = 15-16 minims = 1 milliliter(ml)*
Total no. of ml
_______________ x drip factor = drip rate 1 tsp = 1 fld. dram
q every Total no. of min = 4-5 ml
qh every hour 1 Tbs = 3-4 fld. drams = 15-16 ml
Set up the equation using the given data: 1 cup
q2h every 2 hours 1,000 ml = 8 fld. ounces = 240 ml
_______________ x 15 gtt/ml = X gtt/min 1 pint = 16 fld. ounces
8 hr x 60 min. = 480 ml
q.i.d. four times a day 1 quart = 32 fld. ounces 960 ml
After multiplying the number of hours by 60 minutes =
RLQ right lower quadrant Weight
in the denominator of the fraction, the equation is:
R/O rule out 1,000 ml --- = 1 grain = 60-65 mg
______________ x 15 gtt/ml = X gtt/min
ROM range of motion 480 min --- = 15-16 grains = 1 gram
RUQ right upper quadrant After dividing the fraction, the equation is: --- = 1 dram = 4 grams
2.2 pounds = --- = 1 kg
Rx prescription 2.08 ml/min x 15 gtt/ml = X gtt/min Length
s without The final answer is 31.2 gtt/min, which can be rounded 1 inch = --- 2.54 cm
to 31 gtt/min. The drip rate is 31 drops per minute. =
SC, SQ subcutaneous 39.37 inches = --- = 1 meter
subq subcutaneous
SI International System of Units
SOB short of breath I.V. FLOW RATES CONVERSION FACTORS
ss one-half Vary with the type of administration set and the manufacturer. Weight o o
C F
stat immediately Drops/ Drops/minute to infuse 1 gr = 60-65mg
Mgf. (GTTS) 1 mg 37.0 98.6
sx symptoms cc = 1000 mcg
T&C type and crossmatch 1,000ml 24 hr 20 hr 10 hr 8 hr 6 hr 1 Gm = 1000 mg = 15 gr 37.8 100
cc/hr 42 50 100 125 166 1 kg = 1000 Gm = 2.2 lb 38.4 101.1
t.i.d. three times a day
Abbott 15 10 12 25 31 42 Volume 39 102.2
TPR temperature, pulse, respirations
Baxter 15 or 16
tsp teaspoon 10 7 8 17 21 28 1 ml* = minims 39.6 103.3
Healthcare 5 ml
UA urinalysis = 1 fld. dr = 1 tsp
ung, ungt ointment Cutter 20 14 17 34 42 56 15 ml = 4 fld. dr = 1 tbsp oF = ( oC x 1.8) + 32
IVAC 20 14 17 34 42 56 30 ml = 8 fld. dr = 1 ounce
URI upper respiratory infection * ml and cc oC = ( oF-32) ÷ 1.8
UTI urinary tract infection McGaw 15 10 12 25 31 42 are equivalent
You might also like
- eMRCS MCQ PDFDocument595 pageseMRCS MCQ PDFMMansour88% (8)
- Upper Extremity Nerve Blocks: Transducer Placement Ultrasound Imaging Cross-Sectional AnatomyDocument1 pageUpper Extremity Nerve Blocks: Transducer Placement Ultrasound Imaging Cross-Sectional Anatomyana salasNo ratings yet
- Kaushik Banerjee OrthopaedicsDocument281 pagesKaushik Banerjee OrthopaedicsSwarnadeep Mani50% (4)
- Atls Approach To Pediatric TraumaDocument8 pagesAtls Approach To Pediatric TraumaMakoto KyogokuNo ratings yet
- Time To Synergize Mental Health With Brain Health: CommentDocument3 pagesTime To Synergize Mental Health With Brain Health: Commentsoliveira_149796No ratings yet
- Median NerveDocument40 pagesMedian Nervehumera100% (2)
- Clinical Notes of The Lower LimbDocument12 pagesClinical Notes of The Lower LimbsahrNo ratings yet
- Lower Extremity AmputationsDocument9 pagesLower Extremity AmputationsAisyah DewiNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular System: May I Know Your Name Sir/mam? I Will Be Your Student Doctor For Today Who WillDocument7 pagesCardio Vascular System: May I Know Your Name Sir/mam? I Will Be Your Student Doctor For Today Who WillMDNICNo ratings yet
- Review of Medical AbbreviationsDocument10 pagesReview of Medical AbbreviationsPaula ColeenNo ratings yet
- ACB Dan FIBCDocument21 pagesACB Dan FIBCharjunaNo ratings yet
- Tendon Transfers For Radial Nerve PalsyDocument62 pagesTendon Transfers For Radial Nerve Palsyavinashrao39No ratings yet
- Ultrasound-Guided Axillary Brachial Plexus Block - NYSORADocument12 pagesUltrasound-Guided Axillary Brachial Plexus Block - NYSORAEarn TipananNo ratings yet
- PARENTERAL MEDICATION Part 1Document8 pagesPARENTERAL MEDICATION Part 1Marielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Equipment of Locoregional Anesthesia 13-14Document44 pagesEquipment of Locoregional Anesthesia 13-14Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Parenteral InjectionsDocument7 pagesParenteral InjectionsNashleyah AnayatinNo ratings yet
- SURG 4.04 Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm - Aortic Dissection - Dr. Achurra (Updated + Additional Pics)Document8 pagesSURG 4.04 Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm - Aortic Dissection - Dr. Achurra (Updated + Additional Pics)Monique BorresNo ratings yet
- Radial Nerve Compression RaDocument28 pagesRadial Nerve Compression RaIndra RanteNo ratings yet
- Examination of The HandDocument20 pagesExamination of The HandOtnil DNo ratings yet
- Assessment of HeartDocument4 pagesAssessment of HeartCraigyyNo ratings yet
- Reporte de Un CasoDocument2 pagesReporte de Un CasoDiana AvilesNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 150221070554 Conversion Gate01Document75 pagesPresentation1 150221070554 Conversion Gate01yellymarlianapatuNo ratings yet
- Central Venous AccessDocument21 pagesCentral Venous AccessChrisNo ratings yet
- Otal Aryngectomy: Alexander C VlantisDocument12 pagesOtal Aryngectomy: Alexander C VlantisKumaran Bagavathi RagavanNo ratings yet
- 07 Total-Laryngectomy PDFDocument12 pages07 Total-Laryngectomy PDFEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- DUR - Fracture of The Shaft Radius and UlnaDocument55 pagesDUR - Fracture of The Shaft Radius and UlnaM. Abdurrahman Al-HaraaniNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Direct HerniaDocument7 pagesBilateral Direct HerniaTeja Laksana NukanaNo ratings yet
- Neligan Craniofacial: "Zygoma" Cheek Examination: Anesthesia Untuk FacialDocument10 pagesNeligan Craniofacial: "Zygoma" Cheek Examination: Anesthesia Untuk FacialannisaNo ratings yet
- Radiography of Chest, ASMITADocument74 pagesRadiography of Chest, ASMITAAsmita BhattNo ratings yet
- Mahogany St. Rabe Subdivision, Tagum City Bachelor of Science in NursingDocument4 pagesMahogany St. Rabe Subdivision, Tagum City Bachelor of Science in NursingRoel John Atamosa CasilacNo ratings yet
- Guia de Pontos Motores PDFDocument18 pagesGuia de Pontos Motores PDFDaniel Gonçalves SantosNo ratings yet
- E Vascular (Blue Keyword Pyq)Document3 pagesE Vascular (Blue Keyword Pyq)Irsyad SiddeeqNo ratings yet
- Kirstie Lower LimbDocument79 pagesKirstie Lower LimbVasile OnigaNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Assessment GuideDocument13 pagesUpper Limb Assessment GuidepriyaNo ratings yet
- Transverse Incisions AdvantagesDocument2 pagesTransverse Incisions AdvantagesMonica Blesilda Anne Yvette HernandezNo ratings yet
- Surgery StepsDocument15 pagesSurgery Steps53 - Karthika Devi SNo ratings yet
- Lumbar PunctureDocument25 pagesLumbar Punctureomar kmr97No ratings yet
- Radial Forearm Flap: DR G Avinash Rao Fellow Hand and Microsurgery Skims, SrinagarDocument71 pagesRadial Forearm Flap: DR G Avinash Rao Fellow Hand and Microsurgery Skims, Srinagaravinashrao39No ratings yet
- Mrishoulder 160528142230Document181 pagesMrishoulder 160528142230Risa Marissa100% (1)
- Im Performance ChecklistDocument4 pagesIm Performance ChecklistCarl SantosNo ratings yet
- Presented By:: CC Abegail IbañezDocument42 pagesPresented By:: CC Abegail IbañezAbegail IbañezNo ratings yet
- Harvesting Vascularized Fibula Flap & Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforators (Diep)Document31 pagesHarvesting Vascularized Fibula Flap & Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforators (Diep)Putri PurwanthiNo ratings yet
- Hand Tendon Injuries v1.3Document2 pagesHand Tendon Injuries v1.3CazlpNo ratings yet
- Varicose - VeinsDocument40 pagesVaricose - VeinsBibi MariamNo ratings yet
- Checklist Guide Chest RadiographyDocument2 pagesChecklist Guide Chest Radiographyjturos2003No ratings yet
- Abdominal IncisionsDocument51 pagesAbdominal IncisionsFransisko ReinardNo ratings yet
- I. P A D: Eripheral Rterial IseaseDocument8 pagesI. P A D: Eripheral Rterial IseasevmdcabanillaNo ratings yet
- Cervix DelineationDocument22 pagesCervix Delineationfadli puteraNo ratings yet
- 2645 Clinical Weekly Worksheet s18Document11 pages2645 Clinical Weekly Worksheet s18api-502994344No ratings yet
- TAP Block 2Document5 pagesTAP Block 2Parvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- Rectal Cancer Contouring Guide: Econtour TeamDocument29 pagesRectal Cancer Contouring Guide: Econtour TeamRonna Marie Vijar PamalandongNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment 16Document11 pagesHealth Assessment 16shannon c. lewisNo ratings yet
- 2.physical Exam 2Document118 pages2.physical Exam 2Althea Gabriel CastrosantoNo ratings yet
- Supracondylarfracture PDFDocument40 pagesSupracondylarfracture PDFSurya AbigamikaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound-Guided Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block - NYSORADocument16 pagesUltrasound-Guided Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block - NYSORAEarn TipananNo ratings yet
- Amputation FinalDocument35 pagesAmputation FinalDr Bighnesh DashNo ratings yet
- PolytraumaDocument64 pagesPolytraumaOkkie Mharga SentanaNo ratings yet
- Surgery Cases: CASE 2: Chest Abdominal TraumaDocument3 pagesSurgery Cases: CASE 2: Chest Abdominal TraumaGio Tamaño BalisiNo ratings yet
- Count To Ten Allowing YourselfDocument1 pageCount To Ten Allowing YourselfwisgeorgekwokNo ratings yet
- BEDAH 2 - MANTAP Mei 2019 PDFDocument256 pagesBEDAH 2 - MANTAP Mei 2019 PDFZhraaNo ratings yet
- Final Draft Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesFinal Draft Lesson PlanJannelle Saludo100% (3)
- Hope - 1 Grade 11: Exercise For FitnessDocument6 pagesHope - 1 Grade 11: Exercise For FitnessTABBAL JAN PAOLONo ratings yet
- 9RESPIRATORY THERAPY EQUIPMENT PPTDocument6 pages9RESPIRATORY THERAPY EQUIPMENT PPTJack OneNo ratings yet
- Genre Analysis Outlining Worksheet 1 1Document4 pagesGenre Analysis Outlining Worksheet 1 1api-733516026No ratings yet
- 11 - Reciprocal InnervationDocument20 pages11 - Reciprocal Innervationbreinfout fotosNo ratings yet
- World Vision International Adverst IRS-GFDocument4 pagesWorld Vision International Adverst IRS-GFMwai EstherNo ratings yet
- Final SBFR Training PPT 19th April 2022 MoHDocument113 pagesFinal SBFR Training PPT 19th April 2022 MoHDaniel Firomsa100% (6)
- Crime PaperDocument15 pagesCrime Paperyukta ambasthaNo ratings yet
- Visitation Dos and Don'tsDocument4 pagesVisitation Dos and Don'tsalinachegalatiNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Health Psychology Biopsychosocial Interactions 9th Edition Edward P Sarafino Timothy W Smith PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Health Psychology Biopsychosocial Interactions 9th Edition Edward P Sarafino Timothy W Smith PDF Full Chapterbiscuitunwist20bsg4100% (16)
- Environmental Health and Sustainable Development in Ogoni DR UzorkaDocument30 pagesEnvironmental Health and Sustainable Development in Ogoni DR UzorkaBettyNo ratings yet
- Compensation & Reward ManagementDocument227 pagesCompensation & Reward ManagementjitendersharmajiNo ratings yet
- Physical Activity For or Againts Balneotherapy: By: Andini Tri Wulandari Umdatul Khoiroh Agustini D-Iii PhysiotherapyDocument12 pagesPhysical Activity For or Againts Balneotherapy: By: Andini Tri Wulandari Umdatul Khoiroh Agustini D-Iii PhysiotherapyAyik AsnewenNo ratings yet
- Archery Tips-Home Training - WAEC - TEC-PHY - ENG - V1 - 0 PDFDocument44 pagesArchery Tips-Home Training - WAEC - TEC-PHY - ENG - V1 - 0 PDFjenny12No ratings yet
- Emdad's Answers For SST in PTEDocument9 pagesEmdad's Answers For SST in PTEGlishna Peushan Widanapathirana100% (1)
- Edu 537 Sas CompilationDocument41 pagesEdu 537 Sas CompilationAlden Tagupa EscobidoNo ratings yet
- Health Belief ModelDocument12 pagesHealth Belief Modelmariatul fithriasariNo ratings yet
- Digital Workflow For CAD-CAM Custom Abutments of Immediate Implants Based On Natural Emergence Profile of The Tooth To Be ExtractedDocument23 pagesDigital Workflow For CAD-CAM Custom Abutments of Immediate Implants Based On Natural Emergence Profile of The Tooth To Be ExtractedRAEDNo ratings yet
- University of Caloocan City: Biglang Awa, Corner Cattleya ST., Edsa Caloocan CityDocument19 pagesUniversity of Caloocan City: Biglang Awa, Corner Cattleya ST., Edsa Caloocan CityMaria Luisa BantoyNo ratings yet
- 7 Ways To Treat Chronic Back Pain Without Surgery - Johns Hopkins MedicineDocument3 pages7 Ways To Treat Chronic Back Pain Without Surgery - Johns Hopkins MedicinechhavishNo ratings yet
- FLT Module2 Lesson 2 EngageDocument17 pagesFLT Module2 Lesson 2 EngageKim So-HyunNo ratings yet
- Academic AchievementDocument4 pagesAcademic AchievementMariuxi León MolinaNo ratings yet
- Crying-And-Feeding-Issues - CCG LeafletDocument16 pagesCrying-And-Feeding-Issues - CCG LeafletWaleed AsadNo ratings yet
- Kyoto OjoDocument2 pagesKyoto OjoFernando SanNo ratings yet
- Health Insurance Guidelines 2020-21Document25 pagesHealth Insurance Guidelines 2020-21NIRAJ BAHEKARNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3: Exercise Variables and PrinciplesDocument31 pagesLESSON 3: Exercise Variables and PrinciplesCapulong Kimberly100% (1)
- Sample Dessertation, DR NandanDocument98 pagesSample Dessertation, DR Nandansrilalitha avinashNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Dissertation SampleDocument4 pagesElectrical Engineering Dissertation SampleInstantPaperWriterUK100% (1)
- Social Immersive Learning (Distribution V1)Document15 pagesSocial Immersive Learning (Distribution V1)Aman ChaudharyNo ratings yet