Professional Documents
Culture Documents
تقرير الالكترونيك استاذ مصطفى
Uploaded by
saif1989top0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesتقرير الالكترونيك استاذ مصطفى
Uploaded by
saif1989topCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
1-List the difference between Ge and Si diodes
The main differences between a germanium (Ge)
diode and a silicon (Si) diode lie in their material
properties. Germanium diodes have a lower forward
voltage drop and higher reverse leakage current
compared to silicon diodes. Silicon diodes, on the
other hand, are more temperature-stable and have a
higher thermal conductivity than germanium diodes.
Additionally, silicon diodes are more widely used in
modern electronic devices due to their superior
performance and availability.
2-Types of diodes
There are various types of diodes, each designed for specific
applications. Some common types include:
1-Rectifier Diodes: Convert AC to DC
2-Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs): Emit light when a current
flows through them.
3-Zener Diodes: Designed to operate in the reverse-biased
breakdown region for voltage regulation.
4-Schottky Diodes: Known for their fast switching speed and
low forward voltage drop.
5-Varactor Diodes: Used as voltage-controlled capacitors in
electronic circuits.
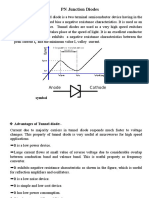
6-Tunnel Diodes: Exhibit negative resistance and are used
in high-frequency oscillators.
7-Photodiodes: Generate a current when exposed to light,
commonly used in light detection.
8-PIN Diodes: Feature a p-type layer, intrinsic (undoped)
layer, and an n-type layer, suitable for RF and microwave
applications.
9-Avalanche Diodes: Operate in the avalanche breakdown
region and are used in applications like noise generation.
10 - Gunn Diodes: Used in microwave oscillators and
amplifiers
These diodes serve diverse purposes in electronic circuits
based on their unique characteristics.
3-applications of diodes
Diodes find applications across various electronic
circuits due to their ability to control the flow of
current. Here are some common applications:
1-Rectification: Diodes are crucial in converting AC
(alternating current) to DC (direct current) in rectifier
circuits, essential for many electronic devices.
2-Voltage Regulation: Zener diodes are used for
voltage regulation in electronic circuits, maintaining a
constant output voltage.
3-Signal Demodulation: Diodes are used in
demodulation circuits to extract information from
modulated signals in communication systems.
4-Logic Gates: Diodes are components in the
construction of logic gates, forming the building
blocks of digital circuits and processors.
5-Light Emission: Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are
used for indicator lights, display screens, and lighting
applications.
6-Clipping and Clamping: Diodes are employed in
clipping and clamping circuits to limit signal
amplitudes or shift signal levels.
7-Switching: Fast-switching diodes, like Schottky
diodes, are used in high-frequency applications and
switching power supplies.
8-Voltage Multipliers: Diodes are part of voltage
multiplier circuits, which generate higher DC voltages
from AC sources.
9-Photovoltaic Cells: Photodiodes are used in solar
cells to convert light energy into electrical energy.
10-Temperature Sensors: Diodes with temperature-
dependent characteristics, like the forward voltage
drop, are used in temperature-sensing applications.
These applications showcase the versatility of diodes
in various electronic systems.
You might also like
- BasicDocument22 pagesBasicharshecomerceNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Diodes - Their Circuit Symbols & ApplicationsDocument22 pagesDifferent Types of Diodes - Their Circuit Symbols & ApplicationsPye PhyoNo ratings yet
- High Speed Diodes and Power SemiconductorsDocument50 pagesHigh Speed Diodes and Power SemiconductorsSudesh Fernando Vayanga SubasinghaNo ratings yet
- Class Notes For DIodesDocument2 pagesClass Notes For DIodesCedric MontianoNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DevicesDocument83 pagesSemiconductor Devicesramil.bocaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Components and Their UsesDocument14 pagesBasic Electronics Components and Their UsesSkNo ratings yet
- All DiodeDocument18 pagesAll DiodeMild SteelNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Diodes and Their ApplicationsDocument24 pagesDifferent Types of Diodes and Their Applicationsphoool100% (8)
- AaaaDocument6 pagesAaaaHussien AlaaNo ratings yet
- Isi PembahasanDocument8 pagesIsi Pembahasandiah lestariNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors - Module - 02 (2.5 LED 2.6 LASER DIODA)Document40 pagesSemiconductors - Module - 02 (2.5 LED 2.6 LASER DIODA)Niken Arina PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors Module 02 PDFDocument40 pagesSemiconductors Module 02 PDFRDWELN RDWELNNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors Module 02Document40 pagesSemiconductors Module 02derejeNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices PresentationDocument14 pagesElectronic Devices PresentationAbdullah Bin Ali 1811858642No ratings yet
- Diode: Is An Electronic Device That Allows The Flow of Current in Only One Direction Other Term IsDocument7 pagesDiode: Is An Electronic Device That Allows The Flow of Current in Only One Direction Other Term IsLeunam SalpadNo ratings yet
- Diode and Its TypesDocument4 pagesDiode and Its TypesSaqib IqbalNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument9 pagesZener DiodeDave SmithNo ratings yet
- DiodeDocument10 pagesDiodefewpew LumanglasNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument7 pagesElectronicsJules inayNo ratings yet
- Diodos MergedDocument17 pagesDiodos MergedCyspagro de la CuencaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of DiodesDocument10 pagesDifferent Types of DiodesGopinathan MNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument18 pagesPower ElectronicsMaysara BalakiNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument11 pagesZener Diodeusama saleemNo ratings yet
- Power Diodes Nascene and CliftonDocument12 pagesPower Diodes Nascene and CliftonSnehasis BarikNo ratings yet
- Unit Four (Cuarta Unidad)Document7 pagesUnit Four (Cuarta Unidad)Madewill DuránNo ratings yet
- Smart Street Light System PDFDocument22 pagesSmart Street Light System PDFDevesh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ? ? ? 6/PERO ? ? ? RqvwuxfwlrqDocument7 pages? ? ? 6/PERO ? ? ? RqvwuxfwlrqLasam CagayanNo ratings yet
- Application of Schotkky DiodeDocument2 pagesApplication of Schotkky DiodeHema lathaNo ratings yet
- EEE 2308 Lecture 1 - IntroductionDocument11 pagesEEE 2308 Lecture 1 - IntroductionIAMMARKSNo ratings yet
- Types of DiodesDocument11 pagesTypes of DiodesElisha LopezNo ratings yet
- Types of DiodeDocument12 pagesTypes of DiodeGopinathan MNo ratings yet
- Function of DiodeDocument5 pagesFunction of DiodeSitiKhusnulKhatimahNo ratings yet
- Golden Gate CollegesDocument4 pagesGolden Gate Collegeshucyg63No ratings yet
- 06 DiodeDocument3 pages06 DiodeJoven Andrei R. LagahitNo ratings yet
- Electronic Card Lock System Final Year Ece Project ReportDocument17 pagesElectronic Card Lock System Final Year Ece Project ReportSunny Prasanth100% (3)
- Name: Vandhana.M USN: 1BM18EI060 Report: Aat Topic: DiodeDocument12 pagesName: Vandhana.M USN: 1BM18EI060 Report: Aat Topic: DiodePayal karakotiNo ratings yet
- Alejandrino, Michael S. Bsee-3ADocument14 pagesAlejandrino, Michael S. Bsee-3AMichelle AlejandrinoNo ratings yet
- PN Junction DiodesDocument18 pagesPN Junction DiodesPulkitNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor PhysicsDocument6 pagesSemiconductor PhysicsJAYSON GREGORIOSNo ratings yet
- Types of DiodeDocument34 pagesTypes of DiodeAfolabiNo ratings yet
- Diodes: Intramuros, Manila College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument8 pagesDiodes: Intramuros, Manila College of Engineering and TechnologyRalph SeminianoNo ratings yet
- DiodeDocument35 pagesDiodeEdelrose LapitanNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC Motor by 555 Timer ICDocument22 pagesSpeed Control of DC Motor by 555 Timer ICSuvam Sinha100% (2)
- Try Ko LNG PoDocument8 pagesTry Ko LNG PoManarex Rhe'nzz Lad-aoNo ratings yet
- Experiment-1 - To Make A Center-Tap Full-Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesExperiment-1 - To Make A Center-Tap Full-Wave RectifierSKMNo ratings yet
- ELectrical Systems WorkDocument7 pagesELectrical Systems Workshamarasharpe48No ratings yet
- Electronics Technology ResearchDocument7 pagesElectronics Technology ResearchInigo PanesNo ratings yet
- Practical LP-4 (CAR66 4.1.1) : Objective:-Familiarization of Diode Symbols, Diode Characteristics and Uses. DescriptionDocument2 pagesPractical LP-4 (CAR66 4.1.1) : Objective:-Familiarization of Diode Symbols, Diode Characteristics and Uses. DescriptionPravin HandeNo ratings yet
- Diodes: FunctionDocument4 pagesDiodes: Functionrasheed313No ratings yet
- Adaptive Light SystemDocument54 pagesAdaptive Light SystemAliza KhanNo ratings yet
- Remote Control LED: Final ProjectDocument18 pagesRemote Control LED: Final ProjectNoman MustafaNo ratings yet
- Cad Lab Project ReportDocument4 pagesCad Lab Project ReportMuhammad Zargham AliNo ratings yet
- Essential Electrical Components and How They Work Together To Create Incredible Modern Electrical SystemsDocument13 pagesEssential Electrical Components and How They Work Together To Create Incredible Modern Electrical SystemsSolomon GodwinNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document30 pagesModule 1Sathya Prakash PNo ratings yet
- Diode: Miguel Luis R. Binaday MEE31 ECET320k Engr. Katrina AcapulcoDocument5 pagesDiode: Miguel Luis R. Binaday MEE31 ECET320k Engr. Katrina AcapulcoMiguel BinadayNo ratings yet
- Types of DiodesDocument3 pagesTypes of DiodesPyae Sone PhyoNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 3: Diodes There Are Many Different Types of Diodes That Are Available For Use in ElectronicsDocument3 pagesAssignment - 3: Diodes There Are Many Different Types of Diodes That Are Available For Use in ElectronicsSourav ChandelNo ratings yet
- Remote Override of Traffic Signal in Emergency: Under The Guidance ofDocument23 pagesRemote Override of Traffic Signal in Emergency: Under The Guidance ofDebashishParidaNo ratings yet
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- MS Unstaffing Air Charge IntakeDocument8 pagesMS Unstaffing Air Charge IntakewarryNo ratings yet
- Sent Tutorial 5 Prob OnlyDocument2 pagesSent Tutorial 5 Prob OnlyYu LoengNo ratings yet
- STANLEY 45HW Electrified Mortise LockDocument6 pagesSTANLEY 45HW Electrified Mortise LocksacdawoodNo ratings yet
- Insulation CoDocument26 pagesInsulation Cokishore krishNo ratings yet
- Endress+Hauser FTL20 GBDocument16 pagesEndress+Hauser FTL20 GBGyörgy MurvaiNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids:: R-Cooh, R-Co HDocument43 pagesCarboxylic Acids:: R-Cooh, R-Co HmacybnzNo ratings yet
- Compiled by Rosadonna Trinita Naben: English ModulDocument51 pagesCompiled by Rosadonna Trinita Naben: English Modulprimus agustinusNo ratings yet
- Design of Single Phase To Three Phase Static Power ConverterDocument7 pagesDesign of Single Phase To Three Phase Static Power Converterderbalijalel100% (1)
- Stageverslag - Stefan KloosterDocument46 pagesStageverslag - Stefan KloosterӨтесин БайрамсагатовNo ratings yet
- BMW UpholstryDocument4 pagesBMW UpholstryМіша ШляхтаNo ratings yet
- Design of Cooling SystemDocument5 pagesDesign of Cooling Systemsameerpatel15770100% (1)
- Employee Satisfation at IOCL Project Final ReportDocument67 pagesEmployee Satisfation at IOCL Project Final ReportShivani AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Lab Exe No. 1 - Estimation of Solar Energy ResourceDocument8 pagesLab Exe No. 1 - Estimation of Solar Energy ResourceJamil Mansor M. LaguiabNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Calculations FinalDocument66 pagesChemical Engineering Calculations Finalsiams fadnierhsaNo ratings yet
- Dip-Ee-6th Sem-ImeeDocument94 pagesDip-Ee-6th Sem-ImeeISHAQ RASHIDNo ratings yet
- 132kv 25kv Structure Height QuazigundDocument1 page132kv 25kv Structure Height QuazigundmanishNo ratings yet
- Reff PODocument4 pagesReff POAkhmad ZaelaniNo ratings yet
- Bueno Eaton-Secondary-Unit-Substation-Design-GuideDocument48 pagesBueno Eaton-Secondary-Unit-Substation-Design-GuideGEISON JUNIOR CAJA GUERRANo ratings yet
- Manual Oper Manut Gerador KATO - 350 01001 00Document48 pagesManual Oper Manut Gerador KATO - 350 01001 00Damiao PereiraNo ratings yet
- Energy: Shun Lae Kyaw, Mya Kyar Phyu, Naw Mary NoDocument11 pagesEnergy: Shun Lae Kyaw, Mya Kyar Phyu, Naw Mary NoShun Lae KyawNo ratings yet
- Datasheet - Live: Capacitors With Screw Terminals 105 C B 43 650 B 43 670Document7 pagesDatasheet - Live: Capacitors With Screw Terminals 105 C B 43 650 B 43 670Blendwerk AntikunstNo ratings yet
- Hoja Tecnica Inverter Mcquay Serie Mid MiuDocument3 pagesHoja Tecnica Inverter Mcquay Serie Mid MiuTatiana DiazNo ratings yet
- PDB PresentationDocument64 pagesPDB PresentationMehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- Hopkins, Michael (2007-01-25) - "Saving Time". Nature Magazine, Vol 445, p344-345.Document2 pagesHopkins, Michael (2007-01-25) - "Saving Time". Nature Magazine, Vol 445, p344-345.Save Standard TimeNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument2 pagesDatasheetEdgarNo ratings yet
- R48100G1Document2 pagesR48100G1Cristopher Rojas100% (1)
- MAN Diesel: Tools For Reconditioning 52001-02Document4 pagesMAN Diesel: Tools For Reconditioning 52001-02manuel canas nunezNo ratings yet
- SSED - Solved Problems For Chapter 3Document7 pagesSSED - Solved Problems For Chapter 3MINH NGUYỄN THẾNo ratings yet
- Coal Mill & Fan PerformanceDocument52 pagesCoal Mill & Fan PerformanceManohar TatwawadiNo ratings yet
- Kick Control: BY: Naga Ramesh D. Assistant Professor Petroleum Engineering Dept. KlefDocument13 pagesKick Control: BY: Naga Ramesh D. Assistant Professor Petroleum Engineering Dept. Klefavula43No ratings yet