Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prothrombin Time (PT) :: INR (Patient's PT / Mean Normal PT)
Uploaded by
oem.osmOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prothrombin Time (PT) :: INR (Patient's PT / Mean Normal PT)
Uploaded by
oem.osmCopyright:
Available Formats
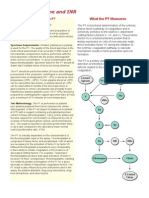
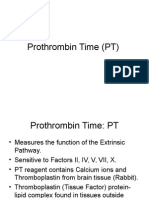
Prothrombin Time (PT):
Prothrombin time is a laboratory test that measures the time it takes for blood plasma to clot. More
specifically, PT assesses the activity of the extrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade, a series of
events that lead to the formation of a blood clot. The extrinsic pathway is primarily triggered by external
trauma that causes bleeding.
During the PT test, a blood sample is mixed with a substance called thromboplastin, which initiates the
clotting process. The time it takes for fibrin strands to form in the blood sample is then measured. Fibrin
strands are essential for clot formation and play a crucial role in stopping bleeding.
INR (International Normalized Ratio):
INR is a standardized unit of measurement for PT results. The need for standardization arises from the
fact that PT values can vary among different laboratories due to differences in reagents, equipment, and
testing methodologies. INR was introduced to provide a uniform system for reporting PT results,
ensuring consistency and comparability across various labs.
Formula for INR Calculation:
INR = (Patient's PT / Mean Normal PT) ISI
The INR formula includes three main components:
1. Patient's PT: This is the prothrombin time of the individual being tested, representing their
blood clotting time.
2. Mean Normal PT: This is the average prothrombin time of a group of healthy individuals. It
serves as a reference point to which the patient's PT is compared.
3. ISI (International Sensitivity Index): This is a correction factor specific to the thromboplastin
reagent used in the PT test. Different thromboplastin reagents have varying sensitivities to
clotting factors, and the ISI adjusts for these differences.
The formula allows for the normalization of PT results, making them comparable across different
laboratories and testing conditions. The resulting INR value provides a standardized way to interpret and
manage anticoagulation therapy.
Significance of Using INR:
1. Standardization: INR enables standardization of PT results, ensuring consistency and reliability in
interpreting coagulation status.
2. Inter-laboratory Comparisons: Health professionals can compare INR results from different
laboratories more confidently, facilitating consistent patient care.
3. Anticoagulation Therapy Management: INR is crucial for monitoring patients on anticoagulant
therapy (e.g., warfarin). Maintaining INR within a target therapeutic range helps balance the risk
of bleeding and clotting.
You might also like
- Pathe Projector Pathe Baby User ManualDocument23 pagesPathe Projector Pathe Baby User ManualzakskenNo ratings yet
- Pathromtin SLDocument8 pagesPathromtin SLJoseline Alejandra Bravo Bravo100% (1)
- K3M 2008 - Form 6Document15 pagesK3M 2008 - Form 6SeanNo ratings yet
- Construction Quality Control Plan DraftDocument24 pagesConstruction Quality Control Plan Draftmozartjr22No ratings yet
- Case: Commercializing The Kunst 1600 Dry Piston Vacuum Pump: Submitted By: Ratandeep Burman - PGP/21/346Document3 pagesCase: Commercializing The Kunst 1600 Dry Piston Vacuum Pump: Submitted By: Ratandeep Burman - PGP/21/346SK CHANDANo ratings yet
- Owner'S Manual: Operation Maintenance Parts ListDocument130 pagesOwner'S Manual: Operation Maintenance Parts ListDmitryNo ratings yet
- Prothrombin TimeDocument8 pagesProthrombin Timeps piasNo ratings yet
- Optimizing The Verification of Mean Normal Prothrombin Time (MNPT) and International Sensitivity Index (ISI) For Accurate Conversion of Prothrombin Time (PT) To International Normalized Ratio (INR)Document16 pagesOptimizing The Verification of Mean Normal Prothrombin Time (MNPT) and International Sensitivity Index (ISI) For Accurate Conversion of Prothrombin Time (PT) To International Normalized Ratio (INR)supervisor procesoNo ratings yet
- Standardization of Prothrombin Time:International Normalized Ratio (PT:INR)Document8 pagesStandardization of Prothrombin Time:International Normalized Ratio (PT:INR)GABRIELA HERRERANo ratings yet
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Document2 pagesP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Yogi Agil MurdjitoNo ratings yet
- PT InrDocument3 pagesPT InrJeniah Lerios OcsioNo ratings yet
- Quick and Owren PDFDocument5 pagesQuick and Owren PDFpieterinpretoria391No ratings yet
- Clinical Use PT and APTTDocument25 pagesClinical Use PT and APTTMustakim DuharingNo ratings yet
- Clotting Factors Blood Liver Prothrombin TimeDocument2 pagesClotting Factors Blood Liver Prothrombin TimeArindah Dinar SafitriNo ratings yet
- HemosIL PT Brochure Rev1 Oct 07Document4 pagesHemosIL PT Brochure Rev1 Oct 07Kath ONo ratings yet
- Thrombin Time, PT, APTT, Fibrin, DdimerDocument24 pagesThrombin Time, PT, APTT, Fibrin, DdimerEma ErvanNo ratings yet
- Prothrombin Time (Protime) : Activity #9Document20 pagesProthrombin Time (Protime) : Activity #9Kei Ef SiNo ratings yet
- Coaguchek & International Normalization Ratio (Inr) : SpeakerDocument26 pagesCoaguchek & International Normalization Ratio (Inr) : Speakerswaraj sharma100% (1)
- PT - MazenDocument8 pagesPT - MazenOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Quick and Owren Prothrombin Time With Regard To The Harmonisation of The International Normalised Ratio (INR) SystemDocument5 pagesComparison of Quick and Owren Prothrombin Time With Regard To The Harmonisation of The International Normalised Ratio (INR) SystemOngNo ratings yet
- Bivalirudin Anticoagulant1Document6 pagesBivalirudin Anticoagulant1walid hassanNo ratings yet
- Fresh Frozen Plasma: Indications For Transfusion 211Document3 pagesFresh Frozen Plasma: Indications For Transfusion 211Kamran AfzalNo ratings yet
- Abstrak TiikgDocument12 pagesAbstrak TiikgAnggiLiesHalimNo ratings yet
- Background Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy Is An Easy, Safe, Autologous, and Cheap BiologicDocument10 pagesBackground Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy Is An Easy, Safe, Autologous, and Cheap BiologicsandhiNo ratings yet
- International Normalized Ratio (INR) : AuthorsDocument9 pagesInternational Normalized Ratio (INR) : AuthorsMasri YaniNo ratings yet
- War Farina, RevisionDocument12 pagesWar Farina, Revisiontsuarez88No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledPamela Carherine Barreda CNo ratings yet
- Clinical Use of Coagulation TestsDocument36 pagesClinical Use of Coagulation TestsOleOhhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 42 Laboratory ValuesDocument4 pagesLesson 42 Laboratory ValuesDarren RossNo ratings yet
- Prothrombin Time Dan Activated Prothrombin TimeDocument9 pagesProthrombin Time Dan Activated Prothrombin TimemieraelNo ratings yet
- Coagulation ProfileDocument8 pagesCoagulation ProfileEsraa Abd ElmenemNo ratings yet
- Eurofins HemocompatbilityDocument2 pagesEurofins HemocompatbilityFVNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument6 pagesResearch Proposaldr.ahsanabid22No ratings yet
- J.jhep.2009.04.01420160516 7753 11ag9zr With Cover Page v2Document9 pagesJ.jhep.2009.04.01420160516 7753 11ag9zr With Cover Page v2amazinggraceNo ratings yet
- Troponin Testing - Analytical Considerations - UpToDateDocument20 pagesTroponin Testing - Analytical Considerations - UpToDateMiguel Angel PugaNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma As Conservative Treatment in Orthopaedicsa Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument12 pagesEfficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma As Conservative Treatment in Orthopaedicsa Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisAmrullahNo ratings yet
- Impact of Low Volume Citrate Tubes On Results of First Line Hemostasis TestingDocument6 pagesImpact of Low Volume Citrate Tubes On Results of First Line Hemostasis TestingSidney WatersNo ratings yet
- Pre-And Post-Analytical PhasesDocument8 pagesPre-And Post-Analytical PhasesDiana EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Prompt Prediction of Fibrinogen Concentration During Cardiopulmonary BypassDocument8 pagesPrompt Prediction of Fibrinogen Concentration During Cardiopulmonary Bypassjuajimenez55No ratings yet
- Aptt 1Document21 pagesAptt 1Diantari PrawertiNo ratings yet
- Hemolyzed Sample Should Be Processed For Coagulation Studies: The Study of Hemolysis Effects On Coagulation ParametersDocument2 pagesHemolyzed Sample Should Be Processed For Coagulation Studies: The Study of Hemolysis Effects On Coagulation ParameterssithaNo ratings yet
- 4 ISI and INRDocument15 pages4 ISI and INRJohnmar AquinoNo ratings yet
- Nefrología CríticaDocument10 pagesNefrología CríticaDobson Flores AparicioNo ratings yet
- Routine Laboratory Evaluation of CoagulationDocument32 pagesRoutine Laboratory Evaluation of CoagulationArshie08No ratings yet
- Correlación de Valores de TTPaDocument6 pagesCorrelación de Valores de TTPaomarpatNo ratings yet
- Gc0082 Moh Clinical-Guidance FinalsendpdfDocument16 pagesGc0082 Moh Clinical-Guidance Finalsendpdfmohamed zeegoNo ratings yet
- APTT & PT Mixing StudiesDocument9 pagesAPTT & PT Mixing StudiesmarrowbiopsyNo ratings yet
- Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia: Original ArticleDocument11 pagesJournal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia: Original ArticleRicardoNo ratings yet
- Prothrombin Time and International Normalized Ratio (PT - INR) - Lab Tests OnlineDocument11 pagesProthrombin Time and International Normalized Ratio (PT - INR) - Lab Tests OnlineAlyaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Article 1439Document8 pages2016 Article 1439302895No ratings yet
- Ajcp 2Document6 pagesAjcp 2margaruzzaNo ratings yet
- NguyenDangPhuocDocument8 pagesNguyenDangPhuocBủ Lờ MaoNo ratings yet
- PT-INR TestDocument5 pagesPT-INR Testmandawa786No ratings yet
- Activity 9 - ProtimeDocument10 pagesActivity 9 - ProtimeKei Ef SiNo ratings yet
- Prothrombin Time: Reference Range, Interpretation, Collection and ..Document3 pagesProthrombin Time: Reference Range, Interpretation, Collection and ..Francis Polycarp DiazNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Tests of Thyroid Function - Uses and Limitations PDFDocument16 pagesLaboratory Tests of Thyroid Function - Uses and Limitations PDFMansouri HichemNo ratings yet
- Inserto TP Thromborel S SIEMENSDocument6 pagesInserto TP Thromborel S SIEMENSedson flores100% (2)
- Monitoring UHF With APTTDocument6 pagesMonitoring UHF With APTTbeniMuhammadNo ratings yet
- BEST Kidney StudyDocument10 pagesBEST Kidney StudyJoseph Zenas JungNo ratings yet
- Thromborel SDocument8 pagesThromborel SJoseline Alejandra Bravo Bravo100% (2)
- Lesson 8Document3 pagesLesson 8GelaaaNo ratings yet
- PRP Review TemplateDocument15 pagesPRP Review TemplatedermoNo ratings yet
- Dental Update 2004. Management of Dental Patients On Warfarin Therapy in A Primary Care SettingDocument5 pagesDental Update 2004. Management of Dental Patients On Warfarin Therapy in A Primary Care Settingdeepak sharmaNo ratings yet
- Dade Innovin: Intended Use Summary and ExplanationDocument8 pagesDade Innovin: Intended Use Summary and ExplanationĐạt PhạmNo ratings yet
- Management of Hemostasis and Coagulopathies for Surgical and Critically Ill Patients: An Evidence-Based ApproachFrom EverandManagement of Hemostasis and Coagulopathies for Surgical and Critically Ill Patients: An Evidence-Based ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Atmel 11121 32 Bit Cortex A5 Microcontroller SAMA5D3 DatasheetDocument1,710 pagesAtmel 11121 32 Bit Cortex A5 Microcontroller SAMA5D3 DatasheetCan CerberusNo ratings yet
- Works) : SABS 1200Document10 pagesWorks) : SABS 1200Palesa TshetlanyaneNo ratings yet
- Double-Blind Test of The Effects of Distant Intention On Water Crystal FormationDocument4 pagesDouble-Blind Test of The Effects of Distant Intention On Water Crystal Formationpmarcelopontes0% (1)
- Mobility Driven Network Slicing: An Enabler of On Demand Mobility Management For 5GDocument12 pagesMobility Driven Network Slicing: An Enabler of On Demand Mobility Management For 5GgirishryenniNo ratings yet
- Tut 1Document5 pagesTut 1foranangelqwertyNo ratings yet
- Typical Malfunctions of BWMSDocument2 pagesTypical Malfunctions of BWMSPyaeSoneHtunNo ratings yet
- SAE AS4059F Table1Document2 pagesSAE AS4059F Table1CherryNo ratings yet
- Rr320306 Heat TransferDocument8 pagesRr320306 Heat TransferandhracollegesNo ratings yet
- Electrical Systems Instructions Manual Sames DRT6364 UkDocument26 pagesElectrical Systems Instructions Manual Sames DRT6364 UkGermando NUNESNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document5 pagesModule 4Ivan PaulinoNo ratings yet
- Quality India Magazine (July To September, 2022)Document59 pagesQuality India Magazine (July To September, 2022)YNR LLPNo ratings yet
- Seaside Elementary School Lunch Menu LewisDocument1 pageSeaside Elementary School Lunch Menu Lewisapi-345910065No ratings yet
- Silo - Tips Modbus Rtu Master CommunicationsDocument35 pagesSilo - Tips Modbus Rtu Master CommunicationsAhmed TalaatNo ratings yet
- Computer Science 9608Document6 pagesComputer Science 9608Krishna Seewooruttun100% (2)
- Weather and Climate-Cs VersionDocument19 pagesWeather and Climate-Cs VersionjtNo ratings yet
- OTC-10860-MS Overview of The Cantarell Field Development Program - GoodDocument9 pagesOTC-10860-MS Overview of The Cantarell Field Development Program - GoodGilbert OmittaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Functional Grammar: A First Step Into The Theory:, IncludingDocument31 pagesSystemic Functional Grammar: A First Step Into The Theory:, Includingnona nonaNo ratings yet
- Gandolfi - L'Eclissi e L'orbe Magno Del LeoneDocument24 pagesGandolfi - L'Eclissi e L'orbe Magno Del LeoneberixNo ratings yet
- Florence Nightingales Environmental TheoryDocument5 pagesFlorence Nightingales Environmental TheoryRoshin Tejero100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1sibi samsonNo ratings yet
- Niir Modern Technology Petroleum Greases Lubricants Petro Chemicals 2nd Revised EditionDocument8 pagesNiir Modern Technology Petroleum Greases Lubricants Petro Chemicals 2nd Revised EditionM.ASNo ratings yet
- Pertcpm 4Document70 pagesPertcpm 4John BanielNo ratings yet
- Script For UptDocument9 pagesScript For UptJohn CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Spring 2019 PDFDocument56 pagesSpring 2019 PDFMayyage LokayaNo ratings yet
- Bevel Gear Drive Screw Jack 6000Document5 pagesBevel Gear Drive Screw Jack 6000Elias YeshiwasNo ratings yet