0% found this document useful (0 votes)
126 views1 pageTransformer Working Principles Explained
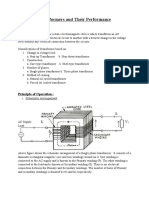
A transformer transfers electric energy between circuits by electromagnetic induction. It works by applying an alternating current to the primary winding, which creates an alternating magnetic flux linking the secondary winding and inducing an electromotive force in it. Transformers are used to increase or decrease voltages for power transmission or operating low-voltage devices.
Uploaded by
roniahmed119219Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
126 views1 pageTransformer Working Principles Explained
A transformer transfers electric energy between circuits by electromagnetic induction. It works by applying an alternating current to the primary winding, which creates an alternating magnetic flux linking the secondary winding and inducing an electromotive force in it. Transformers are used to increase or decrease voltages for power transmission or operating low-voltage devices.
Uploaded by
roniahmed119219Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd