0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views4 pagesThree Phase
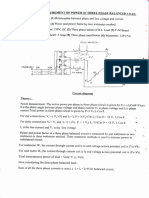
The document describes a laboratory experiment to measure power in a three-phase circuit using the two wattmeter method. Students will connect a balanced three-phase circuit with a variable resistive load to two wattmeters and measure voltage, current, and wattmeter readings at different load settings to calculate power. They will then analyze the results, limitations of the two wattmeter method, and conditions that produce negative wattmeter readings.
Uploaded by
Saket KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views4 pagesThree Phase
The document describes a laboratory experiment to measure power in a three-phase circuit using the two wattmeter method. Students will connect a balanced three-phase circuit with a variable resistive load to two wattmeters and measure voltage, current, and wattmeter readings at different load settings to calculate power. They will then analyze the results, limitations of the two wattmeter method, and conditions that produce negative wattmeter readings.
Uploaded by
Saket KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd