Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parts Od Speech
Uploaded by
pinkpotatoh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesParts Od Speech
Uploaded by
pinkpotatohCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
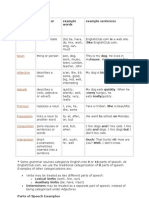
PARTS OF SPEECH
Words are divided into different kinds or classes, called
Parts of Speech, according to their use; that is, according
to the work they do in a sentence. The parts of speech are
eight in number:
1. Noun.
2. Adjective.
3. Pronoun.
4. Verb.
5. Adverb.
6. Preposition.
7. Conjunction.
8. Interjection.
1. A Noun is a word used as the name of a person, place,
or thing; as,
Akbar was a great King.
Kolkata is a big city.
The rose smells sweet.
2. An Adjective is a word used to add something to the
meaning of a noun; as,
He is a brave boy.
There are twenty boys in this class.
3. A Pronoun is a word used instead of a noun; as,
John is absent, because he is ill.
The book are where you left them.
4. A Verb is a word used to express an action or state;
as
The girl wrote a letter to her cousin.
Kolkata is a big city.
Iron and copper are useful metals.
5. An Adverb is a word used to add something to the
meaning of a verb, an adjective, or another adverb;
as,
He worked the sum quickly.
This flower is very beautiful.
She pronounced the word quite correctly.
6. A Preposition is a word used with a noun or a
pronoun to show how the person or thing denoted
by the noun or pronoun stands in relation to
something else; as,
There is a cow in the garden.
The girl is fond of music.
A fair little girl sat under a tree.
7. A Conjunction is a word used to join words or
sentences; as,
Rama and Hari are cousins.
I ran fast, but missed the train.
8. An Interjection is a word which expresses some
sudden feeling; as,
Hurrah! We have won the game.
Alas! She is dead.
9. Some modern grammars include determiners among
the parts of speech.
Determiners are words like a, an, the, this, that, these,
those, every, each, some, any, my, his, one, two, etc., which
determine or limit the meaning of the nouns that follow.
As words are divided into different classes according to the
work they do in sentences, it is clear that we cannot say to
which part of speech a word belongs unless we see it used
in a sentence.
They arrived soon after. (Adverb)
They arrived after us. (Preposition)
They arrived after we had left. (Conjunction)
You might also like
- Comprehensive English Grammar Guide: From Basics to Competitive ExcellenceFrom EverandComprehensive English Grammar Guide: From Basics to Competitive ExcellenceNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument2 pagesParts of SpeechSwatiNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument2 pagesParts of SpeechgelcodoNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 CsDocument14 pagesUnit-1 Csaoiaoashi44No ratings yet
- Lec 2Document9 pagesLec 2Azeem NawazNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Sentences: Little Jack Horner Sat in A CornerDocument7 pagesKinds of Sentences: Little Jack Horner Sat in A CornerparthibanNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: Guided by Mamta Mam Submitted by Teena Vishwakarma Class-9 A'Document7 pagesEnglish Grammar: Guided by Mamta Mam Submitted by Teena Vishwakarma Class-9 A'Jitendra YadavNo ratings yet
- English 1: Parts of SpeechDocument2 pagesEnglish 1: Parts of SpeechJahangir MalikNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: Chapter - 1Document3 pagesParts of Speech: Chapter - 1SakshiNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: Prepared By: Carmella L. Mullo BSED 3 EnglishDocument22 pagesParts of Speech: Prepared By: Carmella L. Mullo BSED 3 EnglishMullo CarmellaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument48 pagesParts of SpeechAmna ShoukatNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech NewtitleDocument77 pagesParts of Speech NewtitleAna Maria PopescuNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument18 pagesParts of SpeechSakunthala RajeshNo ratings yet
- 20 Parts of SpeechDocument12 pages20 Parts of SpeechRamuguhaNo ratings yet
- The Sentence of EnglishDocument16 pagesThe Sentence of EnglishBilal HassanNo ratings yet
- Partsof Speechin English GrammarDocument16 pagesPartsof Speechin English GrammarToledo, Denise Klaire M.100% (1)
- The Sentence: Kinds of SentencesDocument11 pagesThe Sentence: Kinds of SentencesAbhinav SwarajNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: Proper NounDocument4 pagesParts of Speech: Proper NounNoman IrshadNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech - Full BookDocument45 pagesParts of Speech - Full BookAISHWARYA EDUCATIONNo ratings yet
- Superior University Nursing Campus SoniDocument48 pagesSuperior University Nursing Campus SoniAmna ShoukatNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech With Examples PDFDocument6 pagesParts of Speech With Examples PDFHasen MediaNo ratings yet
- Meaningful Building-Block of Language: Name: Ajeng Yupika NIM: 1185030011 Class: 3ADocument7 pagesMeaningful Building-Block of Language: Name: Ajeng Yupika NIM: 1185030011 Class: 3AAjeng YupikaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document22 pagesLesson 2HoussamNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech HandoutDocument7 pagesParts of Speech HandoutSafya BnhNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech ProjectsDocument13 pagesParts of Speech ProjectsdoudouthekillerNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech in EnglishDocument30 pagesParts of Speech in EnglishRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech PDF BookDocument77 pagesParts of Speech PDF BookAmna ShoukatNo ratings yet
- Contoh (Paper) English GrammarDocument7 pagesContoh (Paper) English GrammarKristabella RachelindhaNo ratings yet
- Nur Haziah Latief (F22119072)Document9 pagesNur Haziah Latief (F22119072)Nur Haziah LatiefNo ratings yet
- RT of SpeechDocument7 pagesRT of SpeechDavid Vijay ColeNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument2 pagesParts of Speechtahasheikh822No ratings yet
- Semester 3 AKLDocument3 pagesSemester 3 AKLimranNo ratings yet
- Phrase...., Word Formation and SpectrosDocument6 pagesPhrase...., Word Formation and SpectrosSoumyajit NandiNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Grammar SentencesDocument9 pagesActivity 1 Grammar SentencesIsmeniaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Grammar - POS, Phrases, ClausesDocument2 pagesIntro To Grammar - POS, Phrases, Clausesmohitguptabtech100% (1)
- Parts of Speech TableDocument4 pagesParts of Speech TableEmir XHNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Grade 7Document1 pageGrammar - Grade 7Saira FaisalNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech in EnglishDocument20 pagesParts of Speech in EnglishAyu Putri Masito100% (2)
- Project ReportDocument10 pagesProject ReportgraciousNo ratings yet
- Gramatyka Opisowa (Ściąga)Document64 pagesGramatyka Opisowa (Ściąga)Adam DmochowskiNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Tugas BingDocument2 pagesParts of Speech Tugas BingArdian S.LNo ratings yet
- CONTOH SOAL Foundation of English GrammarDocument4 pagesCONTOH SOAL Foundation of English GrammarFajar PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Identifying Heads and Modifiers of Noun Phrases in A Novel of Alice's Adventures in WonderlandDocument4 pagesIdentifying Heads and Modifiers of Noun Phrases in A Novel of Alice's Adventures in WonderlandKamilatul BadriyahNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument22 pagesParts of Speechjethalal worldNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument18 pagesParts of SpeechAarushi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Notes Figures of Speech 69Document5 pagesNotes Figures of Speech 69abhishek pathakNo ratings yet
- PARTS of SPEECH With ExerciseDocument2 pagesPARTS of SPEECH With ExerciseTHE BÂSSNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4,5 PHRASES AND CLAUSESDocument41 pagesLecture 4,5 PHRASES AND CLAUSESjehoshua35No ratings yet
- English VocabularyDocument16 pagesEnglish VocabularyPriya ChughNo ratings yet
- Final Document PDFDocument202 pagesFinal Document PDFmilkoviciusNo ratings yet
- Article About GrammarDocument2 pagesArticle About GrammarRiska YolandaNo ratings yet
- Essentials of CommunicationDocument71 pagesEssentials of CommunicationAparajita RoyNo ratings yet
- MAJOR 9 LESSON 1 - Parts of Speech in English GrammarDocument9 pagesMAJOR 9 LESSON 1 - Parts of Speech in English GrammarRegine Montiano Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- The Eight Parts of SpeechDocument7 pagesThe Eight Parts of SpeechJasmin Binauhan Niegos-TrongcoNo ratings yet
- English CompositionDocument98 pagesEnglish Compositionesmailasad100% (1)
- Parts of SpeechDocument4 pagesParts of SpeechAlicia Joy TalaveraNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech With Examples PDFDocument4 pagesParts of Speech With Examples PDFFouzia Aziz100% (2)
- LESSON 1 PARTS OF SPEECH LessonDocument22 pagesLESSON 1 PARTS OF SPEECH LessonWane DavisNo ratings yet
- Unit 01Document24 pagesUnit 01Youtube NewsNo ratings yet