Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aminoacidopathies
Uploaded by
barbiegahibOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aminoacidopathies
Uploaded by
barbiegahibCopyright:
Available Formats
Aminoacidopathies
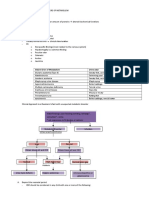
Name Phenylketonuria (PKU) Tyrosinemia Alkaptonuria Maple Syrup Urine Isovaleric Homocystinuria Argininosuccinic Cystinuria
Disease (MSUD) Acidemia Aciduria &
Citrullinemia
Trait autosomal recessive Familial metabolic One of the original hereditary Inherited Genetic defect in the
trait disorder “inborn errors of renal absorption
metabolism” mechanism
Type deficiency deficiency Biochemical defect absence or greatly deficiency Impaired activity Deficiency in urea Defect in amino acid
decrease cycle transport system
Enzyme phenylalanine fumaryl-acetoacetate homogentisate oxidase enzyme branched- Isovaleryl-CoA Cystathione beta- Arginosuccinic acid 20-30 fold ↑ in urinary
hydroxylase (PAH)/ hydrolase (tyrosinemia I); in the tyrosine catabolic chain alpha ketoacid building up synthase leading (ASA) lyase (leading excretion of cysteine;
phenylalanine-4-mono- tyrosine aminotransferase pathway decarboxylase, Isovaleric acid to to ↑ precursors to citrullinemia) ↑ excretion of lysine,
(tyrosinemia II);
oxygenase blocking leucine, toxic level, hemocystein and arginine and ornithine
4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic
(turns phenylalanine to isoleucine and damaging the methionine in due to def. resorption
acid oxidase
tyrosine) (tyrosinemia III) valine in UBC brain and nervous plasma & urine
system
Clinical retarded mental liver damage (infant); ochronosis (tissue failure to thrive “sweaty feet thrombosis, vomiting and high Formation of calculi or
findings development cirrhosis & carcinoma pigmentation) (death in 1st year), odor” osteoporosis, lens ammonia levels, stone (insoluble
muscular rigidity, (↑ glycine dislocation and sometimes mental cysteine precipitate in
mental retardation, conjugate of mental retardation (MR) kidney tubules)
keto-acidosis and isovaleric acid, retardation (MR)
hypoglycemia isovaleryl glycine)
Diagnosis >1200 umol/L of excretion of urine darkening of urine upon Maple syrup/ burnt Physical defects
Indicator phenylalanine in the tyrosine and its standing at room temp sugar odor of the develop gradually
blood; catabolities -in connective tissues urine, breath and with age
musty odor of urine seen microscopically skin.
-4mg/dl of leucine
Screening Guthrie Bacterial Modified Guthrie Citrulline is a
test Inhibition Assay (B. Test (4-azaleucine- diagnostic marker;
subtilis spores & β2- antagonist) dramatically ↑ in
thienylalanine -increase leucine citrullinemia,
antagonist) level overcome the milder ↑
[B.subtilis cannot grow activity of 4- Arginosuccinic
in agar plate containing azaleucine allowing aciduria (ASAuria)
β2-thienylalanine, but bacterial growth.
blood phenylalanine
level is higher the
4mg/dl counteracts the
antagonist β2-
thienylalanine and the
bacteria will grow (+).
Diagnosis HPLC HPLC (Amino acid Chromatography Cyanide-nitroprusside,
Test analysis) react sulfhydryl group
You might also like
- Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument13 pagesInborn Error of MetabolismKuzhandai VeluNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument12 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic DisordersMitch Ibay100% (1)
- Aub F Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument4 pagesAub F Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersRomie SolacitoNo ratings yet
- New Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument45 pagesNew Inborn Error of Metabolismmannan mangal100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Urine Screening For Metabolic Disorders: Phenylalanine/Tyrosine Metabolic PathwayDocument1 pageChapter 8 Urine Screening For Metabolic Disorders: Phenylalanine/Tyrosine Metabolic PathwayChynna Izzabelle Alcantara AbellanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 TransDocument8 pagesUnit 6 TransGrace FernandoNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Disorders 01Document41 pagesMetabolic Disorders 01Brent LagartoNo ratings yet
- Ek Ah YG EIA: AlbuminDocument1 pageEk Ah YG EIA: AlbuminRebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic Disorders: Phenylalanine HydroxylaseDocument5 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic Disorders: Phenylalanine HydroxylaseNORAINE PRINCESS TABANGCORANo ratings yet
- Kelainan Metabolisme BawaanDocument19 pagesKelainan Metabolisme BawaannurmultazamNo ratings yet
- Metabolic-Disorders NotesDocument8 pagesMetabolic-Disorders NotesKeannu HavanaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument22 pagesDrugsPAUL MICHAEL G. BAGUHINNo ratings yet
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Dengan Chronic Kidney DiseasesDocument24 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Dengan Chronic Kidney DiseasestidaktahudiriNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument9 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic DisordersXyleene Jency Bien IINo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Metabolism Disorders Series 2Document5 pagesAmino Acid Metabolism Disorders Series 2kiedd_04No ratings yet
- ANTIPARASITICDocument5 pagesANTIPARASITICJahn MyrilleeNo ratings yet
- Aubf Lab Microscopic Examination Part 2Document3 pagesAubf Lab Microscopic Examination Part 2Hannah KateNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument2 pagesEndocrine DisordersRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Proteins and Liver Function TestsDocument56 pagesProteins and Liver Function TestsjoanNo ratings yet
- 4 Protein ReviewDocument87 pages4 Protein Reviewmika de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Etiology Non Modifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsDocument2 pagesEtiology Non Modifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry: NPNsDocument1 pageClinical Chemistry: NPNsMeevie ToledoNo ratings yet
- Assignment#1Document13 pagesAssignment#1Mark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- Summary Nelsons Chapter 84Document2 pagesSummary Nelsons Chapter 84Michael John Yap Casipe100% (1)
- Enzymes in Clinical DiagnosisDocument2 pagesEnzymes in Clinical DiagnosisShobe ChuaNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Manganese: AstrocytesDocument2 pagesAmmonia Manganese: AstrocytesJULIUS ART VINCENT A. PADINITNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Malarial ComplicationsDocument9 pagesPathogenesis of Malarial ComplicationsErrold Joseph LahaganNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Aspects of Urogenital DiseasesDocument80 pagesNutritional Aspects of Urogenital DiseasesAmirah Jihan AfryNo ratings yet
- Vii Urine Screening For Metabolic Disorders PDFDocument4 pagesVii Urine Screening For Metabolic Disorders PDFMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nsg. ConsiderationDocument6 pagesDrug Name Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nsg. ConsiderationjeremyescaraNo ratings yet
- All PharmDocument288 pagesAll PharmoliviagbeckNo ratings yet
- Tropical SprueDocument3 pagesTropical SprueAVINASH PvkNo ratings yet
- Path o PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramJet Ray-Ann GaringanNo ratings yet
- Type 2 DM PathoDocument5 pagesType 2 DM PathoPearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGYMargaret ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Different Hyperglycemic State: Ryan I. DaetDocument12 pagesDifferent Hyperglycemic State: Ryan I. DaetRyan DaetNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument7 pagesPathophysiology of CVAsarzlasco0967% (3)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagramnursing concept maps100% (5)
- FinaDocument20 pagesFinaJahn MyrilleeNo ratings yet
- AminoacidopathiesDocument5 pagesAminoacidopathiesljabieraNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Acidosis - Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders - Merck Manuals Professional EditionDocument2 pagesMetabolic Acidosis - Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders - Merck Manuals Professional Editionmaulidanabilah5No ratings yet
- Drug Study Potassium ChlorideDocument5 pagesDrug Study Potassium ChlorideKenneth Mark B. TevesNo ratings yet
- Urea Cycle DisordersDocument28 pagesUrea Cycle DisordersIndranil DuttaNo ratings yet
- Trans Hepatobiliary SystemDocument5 pagesTrans Hepatobiliary SystemJulie CatianNo ratings yet
- Esrd Diagram PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesEsrd Diagram PathophysiologySTEPHANIE JOSUE100% (1)
- Antineoplastic AgentsDocument3 pagesAntineoplastic AgentsJan Patrick ArrietaNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi Tumor KolonDocument2 pagesPatofisiologi Tumor Kolonnur hijriahNo ratings yet
- Metastatic Carcinoma of Prostate: AlkalineDocument2 pagesMetastatic Carcinoma of Prostate: AlkalineDjdjjd SiisusNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument46 pagesAmino AcidsdNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic PancreatitisDocument8 pagesAcute and Chronic PancreatitisIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Metabolic MRCPCHDocument11 pagesMetabolic MRCPCHJawwad Masood AhmadNo ratings yet
- 5 AA and ProteinDocument6 pages5 AA and ProteinArielle MarvicNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CushingDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of CushingAj MacotoNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Management On Kidney Disease: Prof DR DR Haerani Rasyid, Mkes, SPPD, KGH, SPGK 2018Document108 pagesNutritional Management On Kidney Disease: Prof DR DR Haerani Rasyid, Mkes, SPPD, KGH, SPGK 2018Rahmawati HamudiNo ratings yet
- Biologically Active Amines Found in Man: Their Biochemistry, Pharmacology, and Pathophysiological ImportanceFrom EverandBiologically Active Amines Found in Man: Their Biochemistry, Pharmacology, and Pathophysiological ImportanceNo ratings yet
- Front PageDocument5 pagesFront PageAnas AloyodanNo ratings yet
- Api-650 Storage Tank Design Calculations - DamasGate WikiDocument3 pagesApi-650 Storage Tank Design Calculations - DamasGate Wikipowder18No ratings yet
- Nike Marketing Plan PDFDocument1 pageNike Marketing Plan PDFSumaira Binte SaleemNo ratings yet
- Visualization BenchmarkingDocument15 pagesVisualization BenchmarkingRanjith S100% (1)
- Practical Mix Design of Concrete2Document3 pagesPractical Mix Design of Concrete2Jiabin LiNo ratings yet
- Activity 15 - Compass ErrorDocument3 pagesActivity 15 - Compass ErrorzeynNo ratings yet
- 1st PUC BLUE PRINT FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENTDocument1 page1st PUC BLUE PRINT FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENTthakursingh14367% (3)
- Study of Steam Generation Units With Their Accessories and MountingsDocument64 pagesStudy of Steam Generation Units With Their Accessories and MountingsMasudur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Full Report XeriaDocument11 pagesFull Report XeriaHamierul MohamadNo ratings yet
- Persentasi Luwak CoffeeDocument36 pagesPersentasi Luwak CoffeeMukti LestariNo ratings yet
- Generators Portable Supersilent DCA60SSI2 Rev 3 STD Manual DataId 19056 Version 1Document164 pagesGenerators Portable Supersilent DCA60SSI2 Rev 3 STD Manual DataId 19056 Version 1andrealunalogoNo ratings yet
- Holes by Louis Sachar: Guided Reading Questions, Vocabulary, and Task Sheets by Heather BlackburnDocument22 pagesHoles by Louis Sachar: Guided Reading Questions, Vocabulary, and Task Sheets by Heather BlackburnSonia ChowdhariNo ratings yet
- Best Freight Forwarding ERP Software - CargoNet PDFDocument19 pagesBest Freight Forwarding ERP Software - CargoNet PDFGo cargonetNo ratings yet
- SD 1.1.3 Design CriteriaDocument10 pagesSD 1.1.3 Design Criterianapoleonpt2No ratings yet
- Practical 9: Enthalpy Change of ReactionDocument4 pagesPractical 9: Enthalpy Change of ReactionJulia QistinaNo ratings yet
- Fermentación BatchDocument8 pagesFermentación BatchJennifer A. PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Financial Inclusion A Literature ReviewDocument7 pagesHealth Benefits of Financial Inclusion A Literature Reviewl1wot1j1fon3No ratings yet
- Wire Loops - PrecastDocument2 pagesWire Loops - PrecastkamakshiNo ratings yet
- Stochastic Epidemic ModellingDocument15 pagesStochastic Epidemic ModellingIRJMETS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Exercises For Functional AnalysisDocument10 pagesExercises For Functional AnalysisEDU CIPANANo ratings yet
- Offer and Acceptance:: Lapse of An OfferDocument12 pagesOffer and Acceptance:: Lapse of An OfferPriya AroraNo ratings yet
- 2022 Grade 10 Study GuideDocument85 pages2022 Grade 10 Study Guideeskaykhan11No ratings yet
- How Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Work TogetherDocument9 pagesHow Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Work TogetherjohnteecubeNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor NotesDocument20 pagesInduction Motor NotesMani SaiNo ratings yet
- Bimedtral Ing. 4 Y 3Document2 pagesBimedtral Ing. 4 Y 3Derly Garcia0% (1)
- ConclusionDocument1 pageConclusionArun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Defence10 BookDocument58 pagesDefence10 BookYash ChanneNo ratings yet
- Linux CommandDocument128 pagesLinux CommandZakNo ratings yet
- English Compulsory (1) PrintDocument15 pagesEnglish Compulsory (1) PrintZakir KhanNo ratings yet
- Protein MetabolismDocument78 pagesProtein MetabolismU2002862 STUDENTNo ratings yet