Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ek Ah YG EIA: Albumin
Uploaded by
Rebekah EquizOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ek Ah YG EIA: Albumin
Uploaded by
Rebekah EquizCopyright:
Available Formats
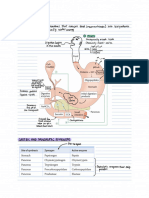
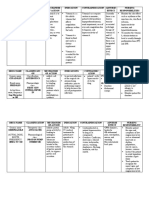
ALBUMIN Most abundant protein DECREASE
Produced in liver Hepatic cirrhosis
Syn in liver Burns
Soluble and monomeric Nephrotic syndrome
Responsible for osmotic pressure End-stage renal disease
REVERSIBLE Pregnancy
Elimination half life: 17-18 days
Ex. Salicylates, Phenylbutazone, Penicillin
A-ACID GLYCOPROTEIN/OROSOMUCOID Primarily basic (cationic) drugs INCREASE
MW: 44,000 Da Myocardial Infarction
Low plasma concentration: 0.4-1% Surgery
Ex. Propranolol, Imipramine, Lidocaine, Lidocaine, Crohn's Disease
Diazepam Trauma
Rheumatoid Arthritis
LIPOPROTEIN Macromolecular complexes
According to density and ultracentrifuge
Transport plasma liquids to liver
IA
Binding albumin is saturated
Ex. Diclofenac, Chlorpromazine, Cycloserine
ERYTHROCYTES Total volume: 45%
Endogenous and exogenous
Ex. Pentobarbital, Phenytoin, Flurazepam
GE
GLOBULINS ABY globulins
Certain endogenous
Distilled water and 50% saturated ammonium sulfate
Ex. Corticosteroid, Thyroxin, Vit. B12, Vit. ADEK
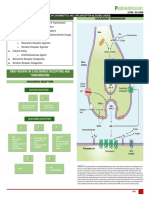
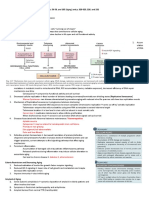
METABOLIC PROCESSES IN INFANT
Y
Age Metabolism Capacity Developed
Birth Sulfation
1st week
1st month
aH Reduction and Oxidation
Acetylation
2nd month Glucuronidation
3rd month Glycine Conjugation
Glutathione Conjugation
Cysteine Conjugation
k
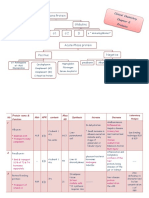
GFR MEASUREMENT
GROUP DESCRIPTION CREATININE CLEARANCE
1 Normal function >80 mL/min
be
2 Mild renal impairment 50-80 mL/min
3 Moderate renal impairment 30-50 mL/min
4 Severe renal impairment <30 mL/min
5 End-stage renal disease Dialysis
BIOPHARMACEUTICS CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM (BCS)
Re
CLASS SOLUBILITY PERMEABILITY
1 High High
2 Low High
3 High Low
4 Low Low
@
PAGE 2 OUT OF 11 PAGES
You might also like
- Metformin classification, indications, actions, contraindications and nursing responsibilitiesDocument7 pagesMetformin classification, indications, actions, contraindications and nursing responsibilitiesgateway1119No ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument15 pagesMetabolismnadila oktaviaNo ratings yet
- BCH369 StudentNotes7Document16 pagesBCH369 StudentNotes702chioka44785No ratings yet
- DRUGS2Document1 pageDRUGS2KaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Pharma Lecture With Dr. Maria Yña Eluisia T. Pereyra-Borlongan 1Document13 pagesPharma Lecture With Dr. Maria Yña Eluisia T. Pereyra-Borlongan 1Sammy GirlNo ratings yet
- AminoacidopathiesDocument2 pagesAminoacidopathiesbarbiegahibNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action, Indications, Contraindications, and Nursing Responsibilities for Magnesium SulfateDocument5 pagesMechanism of Action, Indications, Contraindications, and Nursing Responsibilities for Magnesium SulfateWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Overview of Established Antiepileptic DrugsDocument13 pagesOverview of Established Antiepileptic DrugsVasishta NadellaNo ratings yet
- Case Study-ChealeaDocument6 pagesCase Study-ChealeaAlaa GhazzawiNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeDocument5 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic PancreatitisDocument8 pagesAcute and Chronic PancreatitisIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities for Sodium Bicarbonate AdministrationDocument2 pagesNursing Responsibilities for Sodium Bicarbonate AdministrationKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- DR Dewi Farmakologi Pada Gangguan Neurologi - Maret 2021 DewiDocument81 pagesDR Dewi Farmakologi Pada Gangguan Neurologi - Maret 2021 DewiclarissaNo ratings yet
- Pcol Finals CompreDocument17 pagesPcol Finals CompreAbby LumanglasNo ratings yet
- Amylase, Lipase, LDH, Trop I (Tabulated)Document9 pagesAmylase, Lipase, LDH, Trop I (Tabulated)maja.amora.swuNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry: NPNsDocument1 pageClinical Chemistry: NPNsMeevie ToledoNo ratings yet
- Class: History:: Pharm-07A1 Pharm-04B6 Pharm-97A12Document3 pagesClass: History:: Pharm-07A1 Pharm-04B6 Pharm-97A12Ben PiperNo ratings yet
- 1.inhibit Synergistic EffectDocument8 pages1.inhibit Synergistic EffectSITTIE JOBAISAH TOMINAMAN ALINo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting on UterusDocument19 pagesDrugs Acting on Uterus101 102No ratings yet
- เอกหทัย แซ่เตีย MS.C, CDT: Excretory functionDocument29 pagesเอกหทัย แซ่เตีย MS.C, CDT: Excretory functionPakornTongsukNo ratings yet
- 3 s2.0 B9780123864543007053 MainDocument3 pages3 s2.0 B9780123864543007053 MainPeem PrinNo ratings yet
- Local Anaesthetics: Essential Guide to Properties and MechanismsDocument17 pagesLocal Anaesthetics: Essential Guide to Properties and MechanismsaliNo ratings yet
- Liver - Lecture 2 by Dr. Rehma Dar (16!03!2020)Document20 pagesLiver - Lecture 2 by Dr. Rehma Dar (16!03!2020)khadhiNo ratings yet
- Harmacology: Brief Review On Cholinergic Receptors and TransmissionDocument10 pagesHarmacology: Brief Review On Cholinergic Receptors and TransmissionMa. Mil Adrianne PamaNo ratings yet
- Ninja On Fleek - Fern Charts MT1Document42 pagesNinja On Fleek - Fern Charts MT1pp100% (1)
- Pharmacology of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and GlucocorticoidsDocument56 pagesPharmacology of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and GlucocorticoidsRidhaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - DrugsDocument4 pagesCase Study - DrugsYza DizaNo ratings yet
- All PharmDocument288 pagesAll PharmoliviagbeckNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal symptoms guideDocument1 pageGastrointestinal symptoms guideCHIEF DOCTOR MUTHUNo ratings yet
- 05 05 NOTES-HormonalDocument3 pages05 05 NOTES-HormonalSidney TyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry GuideDocument22 pagesClinical Chemistry GuideIsah SittiNo ratings yet
- Drugs GCDocument6 pagesDrugs GCDesiree MaylasNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi Tumor KolonDocument2 pagesPatofisiologi Tumor Kolonnur hijriahNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyAysaaa DCNo ratings yet
- Anti - Diarrheal DrugsDocument5 pagesAnti - Diarrheal DrugsFitri NurullahNo ratings yet
- CC2 Lab Week 6 EndocrineDocument8 pagesCC2 Lab Week 6 EndocrineReyn CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument13 pagesAcute PancreatitisJacob BorongNo ratings yet
- Drug Food/Drugs EffectDocument3 pagesDrug Food/Drugs Effectsadfg asdfgNo ratings yet
- LA GeneralDocument2 pagesLA GeneralNicole CardenasNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Malarial ComplicationsDocument9 pagesPathogenesis of Malarial ComplicationsErrold Joseph LahaganNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of DM - Oral Antidiabetic DrugsDocument3 pagesDrug Therapy of DM - Oral Antidiabetic DrugsSurria Suguna15No ratings yet
- Plasma Protein Albumins Globulins α 1 α 2 β: Prealbumin Albumin γ " immunoglobines"Document7 pagesPlasma Protein Albumins Globulins α 1 α 2 β: Prealbumin Albumin γ " immunoglobines"Lara MasriNo ratings yet
- 4.drug Metabolism (Biotransformation)Document33 pages4.drug Metabolism (Biotransformation)Osama KhanNo ratings yet
- ANTHELMINTICSDocument2 pagesANTHELMINTICSMarie PaclebNo ratings yet
- Pharm - Endocrine - Anti-DiabeticsDocument1 pagePharm - Endocrine - Anti-DiabeticsAbhineeth BhatNo ratings yet
- Drug Receptor Types: Cut Here Cut HereDocument60 pagesDrug Receptor Types: Cut Here Cut Heredlneisha61100% (13)
- Kelainan Metabolisme BawaanDocument19 pagesKelainan Metabolisme BawaannurmultazamNo ratings yet
- Drugsto HAFALDocument3 pagesDrugsto HAFALThanyun YunNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Expected: IncreasedDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Expected: IncreasedMichaella MalimitNo ratings yet
- Renal PharmacologyDocument7 pagesRenal PharmacologywanichysonlyNo ratings yet
- Different Hyperglycemic State: Ryan I. DaetDocument12 pagesDifferent Hyperglycemic State: Ryan I. DaetRyan DaetNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone and Methotrexate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDexamethasone and Methotrexate Drug StudyJunel Paolo SilvioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyLA GomezNo ratings yet
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE5 With AnsDocument6 pagesEXERCISE5 With Ansesther samonteNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Romeo Rivera Jr.Document1 pagePathology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Romeo Rivera Jr.romeo riveraNo ratings yet
- Final ColistinDocument3 pagesFinal ColistinGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry and Biochemistry of Plant Hormones: Recent Advances in PhytochemistryFrom EverandThe Chemistry and Biochemistry of Plant Hormones: Recent Advances in PhytochemistryV. C. RunecklesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Rizl211 Midterm2Document1 pageRizl211 Midterm2Rebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Psma Q1Document5 pagesPsma Q1Rebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Rizl211 Midterm1Document1 pageRizl211 Midterm1Rebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Phos311-Midterm Reviewer7Document1 pagePhos311-Midterm Reviewer7Rebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Phos311-Midterm Reviewer9Document1 pagePhos311-Midterm Reviewer9Rebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Phos311-Midterm Reviewer5Document1 pagePhos311-Midterm Reviewer5Rebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Phos311-Midterm Reviewer6Document1 pagePhos311-Midterm Reviewer6Rebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Phos311-Midterm Reviewer10Document2 pagesPhos311-Midterm Reviewer10Rebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Phos311 Midterm1Document2 pagesPhos311 Midterm1Rebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Phos311-Midterm Reviewer3Document1 pagePhos311-Midterm Reviewer3Rebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Purchase thru repeat orders inventory controlDocument2 pagesPurchase thru repeat orders inventory controlRebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Psma411 Biochemistry StructuresDocument6 pagesPsma411 Biochemistry StructuresRebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Psma411-Prelim ReviewerDocument82 pagesPsma411-Prelim ReviewerRebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Arta211 Prelim HumanitiesDocument1 pageArta211 Prelim HumanitiesRebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Pubmed 1 & Ovid 2Document7 pagesPubmed 1 & Ovid 2Adam PrabataNo ratings yet
- Robbins Notes: Aging, Radiation, and Inflammation Self StudyDocument44 pagesRobbins Notes: Aging, Radiation, and Inflammation Self StudyJustine HungNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (COPD) : Is An Obstructive Lung Diseases in Which Irreversible Lung Damage Has OccuredDocument25 pagesChronic Obstructive Lung Disease (COPD) : Is An Obstructive Lung Diseases in Which Irreversible Lung Damage Has OccuredOmar AbdillahiNo ratings yet
- RENR MOCK EXAMINATION 2 2018. Question SheetDocument24 pagesRENR MOCK EXAMINATION 2 2018. Question SheetSasha UterNo ratings yet
- Soal Dan Jawaban Uas English For NurseDocument4 pagesSoal Dan Jawaban Uas English For Nurseahsan fillahNo ratings yet
- 2022 University Question Paper Question PaperDocument8 pages2022 University Question Paper Question Papersonali swainNo ratings yet
- Principles of Seizure ManagementDocument119 pagesPrinciples of Seizure ManagementRenan Toledo SandaloNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing Ebook 8th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Ebook 8th Edition Ebook PDFcarey.sowder235100% (39)
- Soal Unbk Dan Usbn: Kerjakan Try Out UN Online Bahasa Inggris SMKDocument8 pagesSoal Unbk Dan Usbn: Kerjakan Try Out UN Online Bahasa Inggris SMKAtic JeNo ratings yet
- Forensic ToxicologyDocument10 pagesForensic ToxicologyArchie ToribioNo ratings yet
- Classification of Periodontal Diseases and ConditionsDocument4 pagesClassification of Periodontal Diseases and ConditionsDewi FNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration FormDocument1 pageHealth Declaration FormVeralynNo ratings yet
- Package leaflet for Drotaverine injection provides dosing and safety informationDocument1 pagePackage leaflet for Drotaverine injection provides dosing and safety informationZarbakht AliNo ratings yet
- Spine High Yield PDFDocument81 pagesSpine High Yield PDFBimnilson SinghNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Hep BDocument4 pagesDrug Study Hep BSawada TsunayoshiNo ratings yet
- NUTRITIONAL NEEDS OF CRITICALLY ILL CHILD SanthoshDocument21 pagesNUTRITIONAL NEEDS OF CRITICALLY ILL CHILD SanthoshSanthosh.S.U100% (1)
- Post Pandemic Architecture: Misha Khaliq and Najeeba RamazanDocument178 pagesPost Pandemic Architecture: Misha Khaliq and Najeeba RamazanDarshini manoharanNo ratings yet
- QuizbowlDocument23 pagesQuizbowlOlive NNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding Causes and ManagementDocument36 pagesGastrointestinal Bleeding Causes and ManagementMuwanga faizoNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Review (PREP) NotesDocument27 pagesExam 1 Review (PREP) Notesmarlen100% (1)
- Module 6 Student Activity SheetDocument7 pagesModule 6 Student Activity SheetJenny Agustin FabrosNo ratings yet
- Childhood Cancer Staging For Population RegistriesDocument64 pagesChildhood Cancer Staging For Population RegistriesMaria MihalachiNo ratings yet
- Eosinophils in Vasculitis Characteristics - Khoury-Nrrheum.2014.98Document11 pagesEosinophils in Vasculitis Characteristics - Khoury-Nrrheum.2014.98Francisco Baca DejoNo ratings yet
- Admission Form 2935Document6 pagesAdmission Form 2935Erica KatzNo ratings yet
- The Perceptions of The Students On The Effects of Street Foods To Their HealthDocument24 pagesThe Perceptions of The Students On The Effects of Street Foods To Their HealthEddie ViñasNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmias in ChildrenDocument50 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias in ChildrenNorhafizah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Immunisation ScheduleDocument3 pagesImmunisation SchedulejegathesmsjsNo ratings yet
- Learn Therapeutic Mudras: Secrets of AyurvedaDocument19 pagesLearn Therapeutic Mudras: Secrets of Ayurvedarraghunathan773488100% (1)
- JAH V BurneDocument28 pagesJAH V BurneZACHARIAH MANKIRNo ratings yet
- CCNDocument39 pagesCCNMann TSha100% (1)