Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hemepath 10 19 17
Uploaded by
Phoebe AjeroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hemepath 10 19 17
Uploaded by
Phoebe AjeroCopyright:
Available Formats
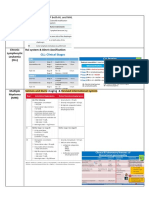
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Good Prognosis Intermediate Prognosis Poor Prognosis
Molecular in • Core Binding Factor (CBF) AML • t(9;11)(p22;q23); MLLT3-KMT2A • t(6;9)(p23;q34); DEK-NUP214
My Pocket… o t(8;21)(q22;q22); RUNX1-RUNX1T1 o Blasts with monocytic o Basophilia, multilineage dysplasia
Blasts with salmon/pink differentiation and fine • inv(3)(q21q26.2) or t(3;3)(q21;q26.2);
granules azurophilic granules RPN1-EVI1
Hematopathology o inv(16)(p13.1q22) or o Associated with gingival myeloid o Abnormal megakaryocytes
Revised September, 2017 t(16;16)(p13.1;q22); CBFB-MYH11 sarcoma o Multilineage dysplasia
Abnormal eosinophils • Normal Karyotype, mutation status • AML with myelodysplasia related
Prepared by the Association for o Worse prognosis in CBF AMLs unknown (or rarely negative) changes (AML-MRC)
Molecular Pathology when KIT is mutated o ≥50% dysplasia in ≥2 lineages
Training and Education Committee • Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL) o History of MDS
o t(15;17)(q22;q12); PML-RARA o MDS defining cytogenetic
For More Educational Resources: Bilobed blasts with granules abnormality (see MDS section)
www.amp.org/education +/- Auer rods • 11q23 (non t(9;11), many partners)
• t(1;22)(p13;q13); RBM15-MKL1 • t(9;22) (q34;q11.2 ); BCR-ABL1
o Megakaryoblastic • FLT3-ITD mutation
• NPM1 mutation • ASXL1, TP53, RUNX1, DNMT3A, WT1
• Biallelic mutations of CEBPA mutation
Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPN) and Mastocytosis
Cytogenetics Mutations Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) Chronic Neutrophilic Leukemia (CNL)
Very Good Prognosis Good Prognosis • t(9;22)(q34;q11.2 );BCR-ABL1 • CSF3R mutation, especially T618I
• del(11q)* or -Y • SF3B1 mutation (strongly correlated o Usually M-BCR (p210) breakpoint
Good Prognosis with ring sideroblasts) o Rarely m-BCR (p190) or -BCR Mastocytosis
• Normal o With SF3B1 mutation can (p230) breakpoints KIT D816V (~95% of cases)
• del(5q)*, del(12p)*, del(20q) diagnosis MDS with ring o ABL1 kinase mutations confer TKI
Intermediate Prognosis sideroblasts (MDS-RS) with only resistance
• del(7q) 5% ring sideroblasts rather than Particularly T315I
• Monosomy 5* 15% without the mutation
• Trisomy 8, trisomy 19 Polycythemia Vera (PV)
• i(17q)* Poor Prognosis • JAK2 V617F (~95% of cases)
• Monosomy 13* or del(13q)* • ASXL1, SRSF2, STAG2, EZH2, DNMT3A, • JAK2 exon 12 mutation (~5% of cases)
Poor Prognosis TET2, TP53 mutation
• Monosomy 7* Essential Thrombocythemia (ET) and
• inv(3), t(3;3), del(3q) Progression mutations Primary Myelofibrosis (PMF)
Very Poor Prognosis • RAS, FLT3, JAK2, NF1, RUNX1, ETV6, • JAK2 V617F (~50% of cases)
• Complex (≥3 abnormalities)* SETBP1 • CALR exon 9 indel mutations (~30% of
*MDS defining abnormality cases)
• MPL W515K/L (~5% of cases)
Other Entities T-cell Neoplasms
Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia Myeloid Neoplasms with Germline T Lymphoblastic Leukemia (T-ALL) T-cell Large Granular Lymphocyte
(CMML) Predisposition • NOTCH1, CDKN1/2 mutations Leukemia (T-LGL)
• Frequent TET2, SRSF2, ASXL1 mutation • AML with germline CEBPA mutation • STAT3 mutation
• Myeloid neoplasm with germline Early T-precursor Acute Lymphoblastic • STAT5B mutation - poor prognosis
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia DDX41 mutation Leukemia (ETP ALL)
(JMML) • Associated with platelet disorders • FLT3, NRAS/KRAS, DNMT3A, IDH1/2 Peripheral T cell lymphoma, NOS (PTCL)
• Somatic PTPN11, KRAS, NRAS mutation o RUNX1, ANKRD26, ETV6 mutation • TET2, DNMT3A, VAV1
• Clinical NF1 disease or NF1 mutation • Associated with other organ Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma, ALK-
Germline CBL mutation dysfunction negative (ALCL, ALK-) Follicular T cell lymphomas (inc.
o GATA2 mutation • Subset have rearrangement at 6p25 angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma,
Myeloid/Lymphoid Neoplasms o JMML type mutations (region with DUSP22 and IRF4) - good AILT)
associated with Eosinophilia prognosis • RHOA, CD28, TET2, DNMT3A, IDH2
• PDGFRA rearrangement (often Langerhans cell histiocytosis, histiocytic • TP63 rearrangement - poor prognosis
del(4)(q12q12); FIP1L1-PDGFRA) sarcoma, disseminated juvenile T Prolymphocytic leukemia (T-PLL; with
• PDGFRB rearangmeent (often xanthogranuloma, Erdheim-Chester Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma, ALK- inv(14) or t(14;14))
t(5;12)(q31~33;p12) ;ETV6-PDGFRB) disease, follicular dendritic cell sarcoma positive (ALCL, ALK+) • ATM, STAT5B, JAK3
• FGFR1 rearrangement (various • BRAF p.V600E mutation • Rearrangements t(2;5)(p23;q35); ALK-
partners) NPM1
• t(8;9)(p22;p24.1);PCM1-JAK2 • Other ALK rearrangements
B-cell Neoplasms
B Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-ALL) Follicular Lymphoma (FL) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma (LPL)
• Good prognosis • t(14;18)(q32;q21);IGH-BCL2 Lymphocytic Lymphoma (CLL/SLL) and IgM Monoclonal Gammopathy of
o Hyperdiploid o Less common in grade 3 • Good Prognosis Unknown Significance (MGUS)
o t(12;21)(p13;q22);ETV6-RUNX1 - • BCL6 rearrangements o del(13q14.3) • MYD88 p.L265P (~90% of cases)
good prognosis o Mutated VH • CXCR4 mutation (~30% of LPL, ~20%
• Interm. prognosis- t(5;14)(q31;q32); Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL) • Intermediate Prognosis of IgM MGUS)
IL3-IGH, associated with eosinophilia • t(11;14)(q13;q32);CCND1-IGH o Trisomy 12 (a/w NOTCH1)
• Poor Prognosis • Poor Prognosis Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
o t(9;22)(q34;q11.2 );BCR-ABL1 Burkitt Lymphoma (BL) o del(17p) • ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma
Usually m-BCR (p190) • MYC rearrangements o del(11q22-23) (a/w SF3B1) o t(2;17)(p23;q23);CLTC-ALK
o t(v;11q23);KMT2A rearranged o t(8;14)(q24;q32);MYC-IGH o del(6q) • Double/Triple-Hit Lymphoma
o Hypodiploid o t(2;8)(p12;q24);IGK-MYC Unmutated VH o MYC rearrangement with BCL2
o Intrachromosomal amplification o t(8;22)(q24;q11);MYC-IGL Extranodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma, and/or BCL6 rearrangement
of chromosome 21 (iAMP21) MALT type
o BCR-ABL1 like B-ALL Hairy Cell Leukemia (HCL) • t(11;18)(q21;q21) - gastric MALT
CRLF2 or EPOR rearrangement • BRAF p.V600E (~95% of cases) • t(14:18)(q32;q21) - orbital and salivary
JAK mutations • MAP2K1 mutations gland MALT
CDKN2A/B or IKZF1 deletion o Hairy Cell Leukemia variant (HCL- • t(3;14)(p14.1;q32) - thyroid, orbital,
Numerous other v) skin MALT
translocations involving o HCL expressing IGHV4-34
tyrosine kinases
You might also like
- Myeloproliferative DisordersDocument33 pagesMyeloproliferative DisordersDhera Charles100% (1)
- Haematology From The Image To The DiagnosisDocument300 pagesHaematology From The Image To The DiagnosismilkaNo ratings yet
- Role of Chemistry Lab in Diagnosis & TreatmentDocument34 pagesRole of Chemistry Lab in Diagnosis & TreatmentJacinta GachokiNo ratings yet
- Arber Da Orazi A Hasserjian R Et Al The 2016 Revision To The Wor 2016Document3 pagesArber Da Orazi A Hasserjian R Et Al The 2016 Revision To The Wor 2016Do Cam TunNo ratings yet
- Classification of AML SubtypesDocument4 pagesClassification of AML SubtypesANDREA FERNANDA MUÑOZ NARVAEZNo ratings yet
- Aml Patho Physiology & Classification - V RocchaDocument61 pagesAml Patho Physiology & Classification - V RocchaThuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Molecular Diagnosis in Oncology & GeneticsDocument119 pagesMolecular Diagnosis in Oncology & GeneticsErika ArnitasariNo ratings yet
- Molecular Diagnostics in Oncology & GeneticsDocument101 pagesMolecular Diagnostics in Oncology & GeneticsSorin LazarNo ratings yet
- What'S New in ?: PathologyDocument2 pagesWhat'S New in ?: PathologyRajnishNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia - AML: Clinical BackgroundDocument12 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia - AML: Clinical BackgroundNyxa AbdullaNo ratings yet
- 11-23-21 White Blood Cell DisordersDocument80 pages11-23-21 White Blood Cell DisordersdeNo ratings yet
- Medicine2 - Myeloproliferative, Lymphoproliferative WorkshopDocument118 pagesMedicine2 - Myeloproliferative, Lymphoproliferative Workshopapi-3762917100% (1)
- Chromosomal Abnormalities Provide Insights into Cancer GeneticsDocument48 pagesChromosomal Abnormalities Provide Insights into Cancer GeneticsDr.Santosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lo Coco FrancescoDocument61 pagesLo Coco FrancescoJess silvaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Acute LeukemiaDocument31 pagesMolecular Basis of Acute LeukemiaVivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Classification of Hematologic Malignancies On The Basis of GeneticsDocument16 pagesDiagnosis and Classification of Hematologic Malignancies On The Basis of GeneticsyunusaqNo ratings yet
- Review of Peripheral Blood and Bone Marrow Malignant DiseaseDocument112 pagesReview of Peripheral Blood and Bone Marrow Malignant DiseaseashjanbaslaibNo ratings yet
- Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument60 pagesAcute Promyelocytic Leukemia Diagnosis and TreatmentMUDASIR REHMANNo ratings yet
- MDS MPN2019 DR Rachel SalitDocument39 pagesMDS MPN2019 DR Rachel Salitluca.win92No ratings yet
- DD HematologyDocument43 pagesDD HematologyDemianaNo ratings yet
- MOLECULAR CYTOGENETICS IN ONCOLOGYDocument6 pagesMOLECULAR CYTOGENETICS IN ONCOLOGYClaudia DiţaNo ratings yet
- Molecular - Uniparental Disomy:: NPM1 Frequently Harbors A 4 BP Insertion in LeukemiaDocument16 pagesMolecular - Uniparental Disomy:: NPM1 Frequently Harbors A 4 BP Insertion in LeukemiaKHNo ratings yet
- 1 Acute LeukemiaDocument14 pages1 Acute Leukemiaسمير هزاعNo ratings yet
- Diseases Link To Chromosomal Abnormalities: Chromoso Me Abnormality DiseaseDocument7 pagesDiseases Link To Chromosomal Abnormalities: Chromoso Me Abnormality Diseasenreena aslamNo ratings yet
- Leucemias Agudas: Kenny Mauricio Galvez HematologiaDocument62 pagesLeucemias Agudas: Kenny Mauricio Galvez HematologiaMichelle Ocampo ValenciaNo ratings yet
- AML Pita DR MardiahDocument71 pagesAML Pita DR MardiahSarly Puspita AriesaNo ratings yet
- Fusion Gene in CancerDocument26 pagesFusion Gene in CancerSajjad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Clinical Significance of Cytogenetics in Acute Leukemias: Molecular DiagnosticsDocument7 pagesClinical Significance of Cytogenetics in Acute Leukemias: Molecular DiagnosticsblablalbablablablaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Myelomonocytic LeukemiaDocument17 pagesChronic Myelomonocytic LeukemiaaymenNo ratings yet
- Plasma Cell DisordersDocument67 pagesPlasma Cell DisordersAmbarsari Kusuma NingtyasNo ratings yet
- WhddidsorhkDocument50 pagesWhddidsorhkestherin909No ratings yet
- Acute Leukaemia-Update: DR Niranjan N. RathodDocument89 pagesAcute Leukaemia-Update: DR Niranjan N. RathodratanNo ratings yet
- 2016 NGS predictive of FIBROSISDocument12 pages2016 NGS predictive of FIBROSISmaomaochongNo ratings yet
- S2.2 Dimmy Prasetya - Trombositosis PKB 2019 PDFDocument20 pagesS2.2 Dimmy Prasetya - Trombositosis PKB 2019 PDFsiputleletNo ratings yet
- EAHP With Corrections (V2) - Changes by GCC (On 10-4-19)Document2 pagesEAHP With Corrections (V2) - Changes by GCC (On 10-4-19)Christopher JulienNo ratings yet
- - October 2008 -: C.Arion, M.D.,Phd; A.Colita,M.D.,Phd; L.Dumitrache M.D.,Phd; A.Sarsan M.D.,Phd; A.Glϋck, M.DDocument40 pages- October 2008 -: C.Arion, M.D.,Phd; A.Colita,M.D.,Phd; L.Dumitrache M.D.,Phd; A.Sarsan M.D.,Phd; A.Glϋck, M.DcalatorNo ratings yet
- Acute LeukemiasDocument79 pagesAcute LeukemiasSravani PeddagangannagariNo ratings yet
- WM ASH Hematology Review Series 6-2022Document64 pagesWM ASH Hematology Review Series 6-2022Иван НегарэNo ratings yet
- Multiple Myeloma A New Treatment ApproachDocument27 pagesMultiple Myeloma A New Treatment ApproachIndonesian Journal of Cancer100% (1)
- Sindrome MielodisplasicosDocument15 pagesSindrome MielodisplasicosMatias FlammNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics of Hematologic DisordersDocument85 pagesCytogenetics of Hematologic Disorderssarah3530_848531846100% (1)
- 105K OLIGO Array: Disorder ListDocument12 pages105K OLIGO Array: Disorder Listms5639No ratings yet
- Who 2016Document35 pagesWho 2016Herlina InaNo ratings yet
- NPM1 Gene Deletions in MDS Patients with 5q- Deletion and Complex KaryotypeDocument2 pagesNPM1 Gene Deletions in MDS Patients with 5q- Deletion and Complex KaryotypeglodovichiNo ratings yet
- Classification of Adult Acute Myeloid LeukemiaDocument24 pagesClassification of Adult Acute Myeloid LeukemiaSusianna RismandaNo ratings yet
- Leukemia TablesDocument2 pagesLeukemia TablesDevin BurrupNo ratings yet
- Microchip ALLDocument2 pagesMicrochip ALLyakanismNo ratings yet
- MPN GenomicsDocument1 pageMPN GenomicsTejus BehlNo ratings yet
- BHS training course in laboratory hematology cytogeneticsDocument35 pagesBHS training course in laboratory hematology cytogeneticsBai GraceNo ratings yet
- 2017 08 15 ConsensusGuidelinesHSCTinMDSandJMML v1-3Document19 pages2017 08 15 ConsensusGuidelinesHSCTinMDSandJMML v1-3cristina_zaharia865440No ratings yet
- #27 Myeloproliferative UpdateDocument31 pages#27 Myeloproliferative UpdateasclswisconsinNo ratings yet
- BoardReviewPart2B MalignantHemePathDocument207 pagesBoardReviewPart2B MalignantHemePathMaria Cristina Alarcon NietoNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow Microenvironment & HaematopoiesisDocument8 pagesBone Marrow Microenvironment & HaematopoiesisKe XuNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Classification and SubtypesDocument49 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Classification and SubtypesAnonymous Q2kXOfTOVENo ratings yet
- Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Lacking The Classic Translocation T (15 17)Document18 pagesAcute Promyelocytic Leukemia Lacking The Classic Translocation T (15 17)Josué Cristhian Del Valle HornaNo ratings yet
- Lymphoma SymposiumDocument161 pagesLymphoma SymposiummaomaochongNo ratings yet
- Plasma Cell NeoplasmsDocument36 pagesPlasma Cell Neoplasmsdrafq2000No ratings yet
- aCML Where Are We NowDocument17 pagesaCML Where Are We NowShayne Tee-MelegritoNo ratings yet
- CSF3R 4Document7 pagesCSF3R 4AndikhaNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Treatment-Free Remission in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: From concept to practice and beyondFrom EverandFast Facts: Treatment-Free Remission in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: From concept to practice and beyondNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Basis of Haematological CancersFrom EverandThe Genetic Basis of Haematological CancersSabrina TosiNo ratings yet
- Who Diagnostic Criteria MyelofibrosisDocument1 pageWho Diagnostic Criteria Myelofibrosispieterinpretoria391No ratings yet
- LMMC ManagementDocument44 pagesLMMC ManagementLuciano LaranjeiraNo ratings yet
- Addressing Symptom Burden in Myeloproliferative NeoplasmsDocument10 pagesAddressing Symptom Burden in Myeloproliferative Neoplasmsshaza elkourashyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Polycythemia Vera: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Polycythemia Vera: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentSalam ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Vox Sanguin Juli 2021Document124 pagesVox Sanguin Juli 2021rsdarsono labNo ratings yet
- Portal Vein Thrombosis: ReviewDocument9 pagesPortal Vein Thrombosis: ReviewMahmoud AbouelsoudNo ratings yet
- Nonmalignant Leukocyte Disorder Chapter 26-35Document15 pagesNonmalignant Leukocyte Disorder Chapter 26-35Reizel GaasNo ratings yet
- American J Hematol - 2023 - Patnaik - Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Myeloproliferative NeoplasmDocument9 pagesAmerican J Hematol - 2023 - Patnaik - Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Myeloproliferative NeoplasmRana RaedNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR 3 Neoplastic, Myeloproliferative and Myelodysplastic DisordersDocument6 pagesSEMINAR 3 Neoplastic, Myeloproliferative and Myelodysplastic DisordersMICHELLE RAPELONo ratings yet
- Oncology PDFDocument55 pagesOncology PDFPolito SoytiNo ratings yet
- ML7111 September quiz answers rapid referenceDocument10 pagesML7111 September quiz answers rapid referenceCleo Salvador100% (2)
- Essential ThrombocytopeniaDocument6 pagesEssential ThrombocytopeniaAkbar DeyaHarsyaNo ratings yet
- Hematology MCQSDocument36 pagesHematology MCQSLorelie ChenNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Adult With Pancytopenia - UpToDateDocument32 pagesApproach To The Adult With Pancytopenia - UpToDatePatricio RamirezNo ratings yet
- Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument12 pagesChronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia Diagnosis and TreatmentFilzah Anisa MayariNo ratings yet
- Haematopathology 3:: Leucocytosis/LeucopeniaDocument113 pagesHaematopathology 3:: Leucocytosis/LeucopeniaarwaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Myeloproliferative DiseasesDocument84 pagesChronic Myeloproliferative DiseasesKayzee CruzNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Approach To The Patient With Polycythemia - UpToDateDocument17 pagesDiagnostic Approach To The Patient With Polycythemia - UpToDatePascácio Brasileiro100% (1)
- Myeloproliferative DisordersDocument2 pagesMyeloproliferative DisordersGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Focus On Myeloproliferative Diseases and Myelodysplastic SyndromesDocument6 pagesFocus On Myeloproliferative Diseases and Myelodysplastic SyndromesBopiyudha bopiyudhaNo ratings yet
- Hema Primary DisordersDocument13 pagesHema Primary DisordersMiki NishiharaNo ratings yet
- CP Hematologic Bonemarrow 19 4000 PDFDocument15 pagesCP Hematologic Bonemarrow 19 4000 PDFAlec MaquilingNo ratings yet
- Luekemia by Dr. WongelDocument63 pagesLuekemia by Dr. Wongelmogesie1995No ratings yet
- Post Polycythemia Vera Myelofibrosis PPV MF A Case Report of A Patient Transplanted After An Adverse Reaction To Covid VaccinationDocument5 pagesPost Polycythemia Vera Myelofibrosis PPV MF A Case Report of A Patient Transplanted After An Adverse Reaction To Covid VaccinationLord 11No ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Bone Marrow Biopsy PathologyDocument6 pagesRecent Advances in Bone Marrow Biopsy PathologypushkaradmaneNo ratings yet
- 2016 EdBookDocument931 pages2016 EdBookvarun7189100% (1)
- Polycythemia Vera ReportDocument31 pagesPolycythemia Vera ReportAdrianNo ratings yet
- Jack 2Document5 pagesJack 2Josue BarralNo ratings yet