0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views2 pagesTissues Class 9 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 6 (PDF)
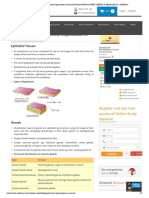
The document summarizes plant and animal tissues. It discusses how plants rely on tissues made of dead cells to provide structure and withstand environmental stresses since they cannot move. Animals consume more energy than plants and have specialized organs, while most plant tissues are meristematic or permanent. Meristematic tissue allows growth at tips and sides. Permanent tissues include parenchyma for support and food storage, collenchyma for flexibility, and sclerenchyma for strength.
Uploaded by
Dharya Pratap Singh RajpootCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views2 pagesTissues Class 9 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 6 (PDF)
The document summarizes plant and animal tissues. It discusses how plants rely on tissues made of dead cells to provide structure and withstand environmental stresses since they cannot move. Animals consume more energy than plants and have specialized organs, while most plant tissues are meristematic or permanent. Meristematic tissue allows growth at tips and sides. Permanent tissues include parenchyma for support and food storage, collenchyma for flexibility, and sclerenchyma for strength.
Uploaded by
Dharya Pratap Singh RajpootCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Tissues Overview
- Permanent Tissue