Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Example of Diagnostics and Laboratories
Uploaded by
kimmybapkidding0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesLaboratories Example Explanation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLaboratories Example Explanation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesExample of Diagnostics and Laboratories
Uploaded by
kimmybapkiddingLaboratories Example Explanation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
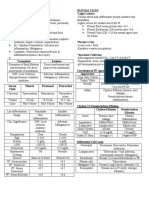
Diagnostic/Laboratories
URINALYSIS
A Urinalysis is a screening tool to check the overall health and to diagnose and manage a
medical condition. A urinalysis involves checking the appearance, concentration, and content of
urine.
Normal Findings Actual Findings Remarks Clinical Significance
Color Pale yellow to clear Yellow Normal Clear to yellow urine
like water color is normal and
indicates normal
kidney function.
Transparency Clarity/turbidity – Slightly Hazy Abnormal A hazy urine is a sign
Clear or Cloudy of a urinary tract
infection, which
caused by bacteria,
crystals, fat, white or
red blood cells, or
mucus in the urine
Specific Gravity 1.005 to 1.030 1.020 Normal Normal urine
concentration
indicates that the
kidneys are
functioning normally.
The higher the
number, it indicates
dehydration.
Albumin <150 mg/day Negative Normal This suggests normal
renal and glomerular
function.
Glucose 3.3-5.5 mmol/L Negative Normal This suggests normal
renal and glomerular
function. Glucose is
not usually found in
urine. Too much
glucose may indicate
high blood glucose.
RBC 0-3 / HPF 0-2 / HPF Normal High RBC in the urine
can indicate infection,
kidney disease, and
other health
conditions.
Bacteria <10,000 Few Abnormal The bacteria that grow
colonies/mL in the
urine may have
symptoms of an
infection or bladder
irritation.
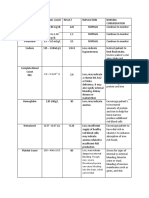
HEMATOLOGY
Complete blood count is a screening procedure that uses a blood sample as a specimen
to test for complication in a broader context, such as anemia, infections, and leukemia.
Normal Values Actual Findings Remarks Clinical Significance
Hemoglobin 139.0000- 71 Decrease Low hemoglobin levels
170.0000 g/L can be caused by a
diet low in iron,
gastrointestinal (GI)
bleeding and GI
surgery.
Hematocrit 0.4200-0.5100 0.21 Decrease This indicates
decrease RBC in the
body which can cause
Anemia.
RBC Count 5.0000-6.0000 2.27 Decrease Decrease RBC count
10^12/L may signify internal
bleeding or
malnutrition.
WBC Count 5.0000-10.0000 11.8 Increase Leukocytosis, or high
10^9/L white blood cell count,
can indicate a range of
conditions, including.
infections
Neutrophil 0.5500-0.6500 0.79 Increased Increase Neutrophil
often the result of a
bacterial infection.
Lymphocyte 0.2500-0.4000 0.17 Decreased Decrease lymphocyte
means a higher risk for
infection.
BLOOD CHEMISTERY RESULT
Blood Chemistry refers to the biochemical analysis of body fluids. It uses chemical
reactions to determine the levels of various chemical compounds in bodily fluids. These tests
are used to detect and quantify different compounds in blood and urine.
Normal Values Actual Findings Remarks Clinical Significance
Glucose 70.0000-140.0000 131 Normal An increase glucose
mg/dL level in the blood
means is it diabetic.
BUN 7.0000-30.0000 14 Normal Normal BUN levels can
mg/dL vary, but generally a
high level of blood
urea nitrogen is a sign
that your kidneys are
not working well.
Creatinine 0.6000-1.2000 1.6 Increase High creatinine levels
mg/dL usually indicate that
the kidneys are not
working. Possible
causes because of
dysfunction. (i.e.,
kidney infection.)
Uric Acid 3.5000-7.2000 5.1 Normal High levels can lead to
mg/dL gout, kidney disease,
and other health
issues.
Sodium 135.0000- 137.5 Normal Sodium is one of the
145.0000 mEq/L electrolytes that help
body function
normally by
maintaining fluid and
blood volume.
Potassium 3.5000-5.5000 4.05 Normal Potassium are one of
mEq/L the electrolytes that
helps body function
normally by
maintaining fluid and
blood volume.
You might also like
- Diagnostic Exam Date 8-24-19 Urinalysis Resul T Norma L Interpretatio N Clinical Significance NormalDocument7 pagesDiagnostic Exam Date 8-24-19 Urinalysis Resul T Norma L Interpretatio N Clinical Significance Normalハリコ ノビNo ratings yet
- Ezra M. Darubday NCP Sample Surgical WardDocument9 pagesEzra M. Darubday NCP Sample Surgical WardEzra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Iii. Medical Management A. Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresDocument11 pagesIii. Medical Management A. Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresNickaela CalalangNo ratings yet
- Examinations Patient's Result Normal Value Indication Blood ExamDocument3 pagesExaminations Patient's Result Normal Value Indication Blood ExamPatricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Procedure Description of The Procedure Purpose of The Procedure Date of The Procedure Reference Findings ImplicationsDocument7 pagesDiagnostic Procedure Description of The Procedure Purpose of The Procedure Date of The Procedure Reference Findings ImplicationsDizah Faye OsboroNo ratings yet
- Interpretation: Slightly Turbid in Urine Analysis: Normal Urine Is TransparentDocument7 pagesInterpretation: Slightly Turbid in Urine Analysis: Normal Urine Is Transparentclare_gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Result Urinalysis January 27, 2012 Test Result Normal Values ImplicationDocument11 pagesLaboratory Result Urinalysis January 27, 2012 Test Result Normal Values ImplicationAl-Mujib TanogNo ratings yet
- UrinalysisDocument5 pagesUrinalysisRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- TAHBSO Lab ResultDocument3 pagesTAHBSO Lab ResultGacutan JonathanNo ratings yet
- Lab ResultsDocument2 pagesLab ResultsBonji AdonaNo ratings yet
- Medical Management FINALDocument11 pagesMedical Management FINALjannaelemento11No ratings yet
- Case 4 Final Lab Diagnosis 2Document4 pagesCase 4 Final Lab Diagnosis 2Mary Jane TiangsonNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Diagnostic ProceduresDocument12 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostic ProceduresKrishcel Canlapan InsoNo ratings yet
- Examination Done Date Results Normal Values Significance or Relevance To Patient's Condition UrinalysisDocument10 pagesExamination Done Date Results Normal Values Significance or Relevance To Patient's Condition UrinalysisStephanie Libo-onNo ratings yet
- URINALYSISDocument4 pagesURINALYSISsheila_01No ratings yet
- February 28,2011Document3 pagesFebruary 28,2011Beth PascuaNo ratings yet
- Laboratories and Results: Physical PropertiesDocument5 pagesLaboratories and Results: Physical PropertiesBeverly DatuNo ratings yet
- AUBFDocument30 pagesAUBFSkylarNo ratings yet
- Vi. Laboratory Examinations Findings and InterpretationDocument14 pagesVi. Laboratory Examinations Findings and InterpretationStephanie Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Liver and Biliary DiseaseDocument4 pagesInvestigation of Liver and Biliary DiseaseNeil Patrick AngelesNo ratings yet
- Ladja, Irish V. BSN 3-C Laboratory ResultsDocument13 pagesLadja, Irish V. BSN 3-C Laboratory ResultsEzra LambarteNo ratings yet
- Date/Time Order RationaleDocument4 pagesDate/Time Order RationaleJes Cristy LindonganNo ratings yet
- Chapter XI FinalDocument12 pagesChapter XI FinalFadNo ratings yet
- Serous Physiology Pleural FluidDocument3 pagesSerous Physiology Pleural FluidGhina Ü MaderaNo ratings yet
- Initial Observations: Normal Values SignificanceDocument3 pagesInitial Observations: Normal Values SignificanceRhea JessicaNo ratings yet
- Group F DXDocument2 pagesGroup F DXmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- IDA PPT FinalDocument26 pagesIDA PPT FinalYen-yen FaveNo ratings yet
- 1.010 - 1.025 With A Normal Fluid IntakeDocument3 pages1.010 - 1.025 With A Normal Fluid Intakeelvie21No ratings yet
- NCP ProperDocument9 pagesNCP Properstephanie eduarteNo ratings yet
- Study NotesDocument4 pagesStudy NotesErika Joille PatayonNo ratings yet
- Lab and Diagnostic Test (Liver Cancer) 1Document3 pagesLab and Diagnostic Test (Liver Cancer) 1Ericka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Diagnostic Exams: Test Result Normal Value SignficanceDocument3 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostic Exams: Test Result Normal Value SignficanceAlfrien Ivanovich LarchsonNo ratings yet
- CASE-SCENARIO 4 QuestionsDocument16 pagesCASE-SCENARIO 4 QuestionsEduard GarchitorenaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test PrefaceDocument9 pagesDiagnostic Test PrefaceEula Angelica OcoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study UTI (Domo-Os, Belenda)Document6 pagesDrug Study UTI (Domo-Os, Belenda)Irene BungalsoNo ratings yet
- Renal FailureDocument19 pagesRenal FailuredianaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Result Final Na JudDocument11 pagesLaboratory Result Final Na JudMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- Final Laboratory ProceduresDocument14 pagesFinal Laboratory ProceduresJosh BlasNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Result: Normal AbnormalDocument3 pagesLaboratory Result: Normal AbnormalMartin T ManuelNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis LABS&DXDocument4 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis LABS&DXganda akoNo ratings yet
- Invest and Medication 1Document9 pagesInvest and Medication 1RajaNo ratings yet
- LaboratoryDocument3 pagesLaboratoryKate Leysa MamonNo ratings yet
- Organ Function Test: Assessment of Functions of The OrgansDocument39 pagesOrgan Function Test: Assessment of Functions of The OrgansSri Abinash MishraNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention-Rationale Evaluation Fluid Volume Excess Related ToDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention-Rationale Evaluation Fluid Volume Excess Related ToJen BallesterosNo ratings yet
- 7-Renal Function TestsDocument4 pages7-Renal Function TestsAhmed ImranNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco80% (5)
- Laboratory Normal Range Result Significance A (+)Document1 pageLaboratory Normal Range Result Significance A (+)kimberly dedaseNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Case Pres 2Document8 pagesLaboratory Test Case Pres 2Angel HernandezNo ratings yet
- 2 0 1 0 Color Light Straw To Dark AmberDocument3 pages2 0 1 0 Color Light Straw To Dark Amberelvie21No ratings yet
- LabsDocument3 pagesLabsKate Leysa MamonNo ratings yet
- Darunday, Ezra M. Rot II (Final)Document16 pagesDarunday, Ezra M. Rot II (Final)Ezra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Findings: Laboratory Examination Result Normal Value Nursing Implication/ SignificanceDocument5 pagesLaboratory Findings: Laboratory Examination Result Normal Value Nursing Implication/ SignificanceNader AbdurasadNo ratings yet
- University of Tabuk Faculty of Medicine: Laboratory Medicine Module CLC 436Document26 pagesUniversity of Tabuk Faculty of Medicine: Laboratory Medicine Module CLC 436kholoud220No ratings yet
- Urine AnalysisDocument9 pagesUrine AnalysisAnn Justine OrbetaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ResultsDocument4 pagesLaboratory Resultsjackie funtanillaNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Jaundice Group 6Document33 pagesObstructive Jaundice Group 6Qurbon AliNo ratings yet
- 9.0 Blood AnalysisDocument11 pages9.0 Blood Analysiskibitokstephen1No ratings yet
- Git Case 3 Kunwor, BishalDocument15 pagesGit Case 3 Kunwor, BishalBishal JB KunworNo ratings yet
- Lab ResultsDocument3 pagesLab ResultsKristal Cyril PolzNo ratings yet
- Jaundice, (Hyperbilirubinemia) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandJaundice, (Hyperbilirubinemia) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing - LaborDocument12 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing - LaborkimmybapkiddingNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing - Postpartum PeriodDocument3 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing - Postpartum PeriodkimmybapkiddingNo ratings yet
- Volleyball TermsDocument2 pagesVolleyball TermskimmybapkiddingNo ratings yet
- MCN - Maternal and Child Health Nursing ReviewerDocument6 pagesMCN - Maternal and Child Health Nursing ReviewerkimmybapkiddingNo ratings yet
- 3M DP 810 MSDSDocument25 pages3M DP 810 MSDSvivek jayswalNo ratings yet
- Kieni - Factors Influencing Influx of Street Children in Urban Areas - A Case of Street Children Projects in Meru Town - KenyaDocument73 pagesKieni - Factors Influencing Influx of Street Children in Urban Areas - A Case of Street Children Projects in Meru Town - KenyaMary Ann Yongco CalalinNo ratings yet
- Kode Icd 10Document38 pagesKode Icd 10interna squardNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Adult With Nausea and Vomiting - UpToDateDocument20 pagesApproach To The Adult With Nausea and Vomiting - UpToDateJolien JobsNo ratings yet
- Community MedicineDocument17 pagesCommunity Medicineapi-1986354850% (4)
- AOAC Rapid Method ValidationDocument60 pagesAOAC Rapid Method ValidationPiruzi MaghlakelidzeNo ratings yet
- Learning More About Personal and Mental HealthDocument4 pagesLearning More About Personal and Mental HealthJoan VecillaNo ratings yet
- Exam #2 Pediatric Blueprint 2019Document2 pagesExam #2 Pediatric Blueprint 2019Stephanie DeeNo ratings yet
- Early Adulthood: Stages in The Life SpanDocument6 pagesEarly Adulthood: Stages in The Life SpanAngelica Mae DanaoNo ratings yet
- Mo Sobhy Academy Procedures 2022 NoteDocument37 pagesMo Sobhy Academy Procedures 2022 NoteisraaobaidyNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Group 2Document30 pagesResearch Proposal Group 2Anthony PelayoNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Skeletal SystemDocument65 pagesPathology of Skeletal SystemFirda S SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Chayote Juice (Sechium Edule) To Reduce Blood Pressure in Elderly With HypertensionDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Chayote Juice (Sechium Edule) To Reduce Blood Pressure in Elderly With HypertensionBudi AtmikaNo ratings yet
- DR Fardowsa Mohamed Adam Last UpdateDocument71 pagesDR Fardowsa Mohamed Adam Last UpdateAbdulkadir KanaaleNo ratings yet
- INTEGRIS COVID19Interpreting COVID19 Test Results7720Document2 pagesINTEGRIS COVID19Interpreting COVID19 Test Results7720nellyNo ratings yet
- Group PresentationDocument26 pagesGroup PresentationA&H Printing ServicesNo ratings yet
- 22.MIPhystidine BiosensorsandBioelectrics GideonDocument10 pages22.MIPhystidine BiosensorsandBioelectrics GideonjuansanninNo ratings yet
- Shock Comparison ChartDocument2 pagesShock Comparison Chartlinnaete88% (8)
- O C A C, Republic of China (Taiwan) : Items Required For Health Certificate 3 Valid For Three MonthsDocument1 pageO C A C, Republic of China (Taiwan) : Items Required For Health Certificate 3 Valid For Three Months李倬伶No ratings yet
- 2019 EMOP Diagnóstico y ManejoDocument8 pages2019 EMOP Diagnóstico y ManejoJeff Daniel Landauro PanayNo ratings yet
- BUKU Acute Coronary Syndrome Update 2020Document16 pagesBUKU Acute Coronary Syndrome Update 2020Embun Suci LestariNo ratings yet
- BSP Treatment Flow Chart 16 For ScreenDocument2 pagesBSP Treatment Flow Chart 16 For ScreenshahadNo ratings yet
- Prometric Pharmacy MCQs (Solved)Document45 pagesPrometric Pharmacy MCQs (Solved)cuami84% (45)
- MCTD 3Document1 pageMCTD 3Laksmita Ayu Dewi TetanelNo ratings yet
- Chronic Pain SyndromeDocument1 pageChronic Pain SyndromeAdvance Pain CareNo ratings yet
- Subjective:: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventi ONS Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesSubjective:: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventi ONS Rationale EvaluationCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Rotter's Locus of Control Scale: Psychological Testing PresentationDocument13 pagesRotter's Locus of Control Scale: Psychological Testing PresentationApexa KeraiNo ratings yet
- Hygiene and Sanitary Practices of Street Vendors in Digos Night MarketDocument8 pagesHygiene and Sanitary Practices of Street Vendors in Digos Night MarketWen Delada Centino CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1. IdentificationDocument10 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Section 1. IdentificationAnto SaraNo ratings yet
- 106 FinalsDocument27 pages106 FinalsCreciabullecerNo ratings yet