Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6 B)
6 B)
Uploaded by
edwinhunt2560 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesWhen deciding on public expenditure levels and allocations, governments must consider various opportunity costs. These include trade-offs between funding one area over others due to limited resources, such as whether to invest in education or healthcare. Other trade-offs involve balancing current versus future needs, economic growth versus social services, short-term versus long-term benefits, and public versus private sector investment. Proper consideration of all these opportunity costs is crucial for public expenditure decisions that maximize economic and social welfare over the long run.
Original Description:
Original Title
6 b)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWhen deciding on public expenditure levels and allocations, governments must consider various opportunity costs. These include trade-offs between funding one area over others due to limited resources, such as whether to invest in education or healthcare. Other trade-offs involve balancing current versus future needs, economic growth versus social services, short-term versus long-term benefits, and public versus private sector investment. Proper consideration of all these opportunity costs is crucial for public expenditure decisions that maximize economic and social welfare over the long run.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pages6 B)
6 B)
Uploaded by
edwinhunt256When deciding on public expenditure levels and allocations, governments must consider various opportunity costs. These include trade-offs between funding one area over others due to limited resources, such as whether to invest in education or healthcare. Other trade-offs involve balancing current versus future needs, economic growth versus social services, short-term versus long-term benefits, and public versus private sector investment. Proper consideration of all these opportunity costs is crucial for public expenditure decisions that maximize economic and social welfare over the long run.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
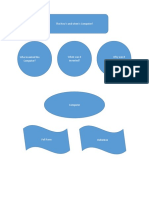
b) Discuss the various ways in which opportunity costs must be considered in
deciding the level and opportunity costs must be considered in deciding the level and
allocation of public expenditure
Opportunity cost is a fundamental economic concept that should be considered when
deciding the level and allocation of public expenditure. It refers to the value of the
next best alternative foregone when a choice is made. These are explaining how
opportunity costs should be factored into public expenditure decisions;
Trade-offs in Resource Allocation: Governments have limited resources, and
allocating funds to one area implies forgoing opportunities in others.
Choosing Between Public Services: When deciding on spending priorities,
governments must evaluate the potential benefits of investing in education, healthcare,
infrastructure, and other public services.
Balancing Current and Future Needs: Allocating too much to current expenditures
might limit future investment in critical areas.
Economic Growth vs. Social Services: Decisions often involve trade-offs between
promoting economic growth and providing essential social services.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Benefits: Prioritizing short-term gains may lead to
missed opportunities for long-term economic development.
Public vs. Private Investment: Governments must weigh the benefits of public
investments against those of private sector initiatives.
Effect on Different Groups: Consideration must be given to how spending decisions
impact various segments of the population.
Sacrificing Education and Health: Underinvestment in education and healthcare
might result in a less skilled and healthy workforce, impacting long-term economic
growth.
Infrastructure vs. Social Programs: Funding infrastructure projects might require
diverting resources from social programs, potentially affecting vulnerable
populations.
Defensive vs. Productive Spending: Some expenditures are primarily defensive,
such as national defense, while others, like education, are productive investments.
Opportunity for Innovation: Investing in research and development can foster
innovation, leading to new opportunities and economic growth.
Foreign Aid vs. Domestic Programs: Allocating funds to foreign aid implies an
opportunity cost of not addressing domestic needs.
Environmental Costs: Ignoring environmental protection might lead to long-term
environmental and health issues, incurring higher costs in the future.
Stimulus vs. Austerity: During economic downturns, decisions on public
expenditure often involve the trade-off between stimulating the economy and
practicing fiscal austerity.
Technology Investment: Public investments in technology can enhance productivity,
but there's an opportunity cost in terms of other potential investments.
Inequality: Spending decisions should consider the potential impact on income
inequality, which can have economic and social consequences.
Geographic Allocation: Opportunity costs differ across regions, and governments
must consider regional disparities when allocating resources.
Political Priorities: Public expenditure decisions can be influenced by political
priorities, which may not always align with economic efficiency.
In conclusion, opportunity cost is an essential consideration in public expenditure
decisions. Governments must carefully weigh the trade-offs between different
spending options, considering their short-term and long-term impacts on economic
growth, social welfare, and overall national well-being.
You might also like
- Types of Economic PlanningDocument8 pagesTypes of Economic PlanningPlatonic100% (14)
- Velocity TrianglesDocument33 pagesVelocity TrianglesAbubakarNo ratings yet
- NC1 - Principles - Multiple Choice Questions PDFDocument6 pagesNC1 - Principles - Multiple Choice Questions PDFsuparthakarchowdhuryNo ratings yet
- MDS 529 - Handout 1Document7 pagesMDS 529 - Handout 1faruque.ddsNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 SCBADocument7 pagesUnit-3 SCBAPrà ShâñtNo ratings yet
- Public Finance JKDocument6 pagesPublic Finance JKShawon Moshiur RahamanNo ratings yet
- 2022-23-3. POE AssignmentDocument14 pages2022-23-3. POE Assignmentpaman8497No ratings yet
- Lesson 03 - Public Expenditure PolicyDocument18 pagesLesson 03 - Public Expenditure PolicyMetoo ChyNo ratings yet
- PUBLIC EXPENDITURES NotesDocument13 pagesPUBLIC EXPENDITURES NotesemeraldNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-03-21 at 02.37.35Document48 pagesScreenshot 2024-03-21 at 02.37.35Darsh JainNo ratings yet
- Scba PMDocument12 pagesScba PMAli KhanNo ratings yet
- Govt Spending Economic GrowthDocument20 pagesGovt Spending Economic GrowthsalimNo ratings yet
- Economic PlanningDocument13 pagesEconomic PlanningQamar Ali100% (2)
- Economic PlanningDocument141 pagesEconomic PlanningAyaan Ansary50% (2)
- Chapter 2Document25 pagesChapter 2Abas Mohamed SidowNo ratings yet
- English AssignmentDocument4 pagesEnglish AssignmentSadia AwanNo ratings yet
- Social Cost Benefit Analysis (SCBA) : By: Narayan GaonkarDocument24 pagesSocial Cost Benefit Analysis (SCBA) : By: Narayan GaonkarusmanNo ratings yet
- Home Work - 1Document8 pagesHome Work - 1EmranNo ratings yet
- Term Paper ReportDocument5 pagesTerm Paper ReportPriyal SaraffNo ratings yet
- Dfi 341 - Lecture II RDocument28 pagesDfi 341 - Lecture II RElizabeth MulukiNo ratings yet
- Benefit Cost Analysis and Public Sector EconomicsDocument52 pagesBenefit Cost Analysis and Public Sector EconomicsHaery SihombingNo ratings yet
- PF Notes Chapter 7Document8 pagesPF Notes Chapter 7uah346No ratings yet
- Growth of Public ExpendicharDocument13 pagesGrowth of Public ExpendicharAbhilashAbiNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Fiscal DecentralizationDocument17 pagesLecture - Fiscal DecentralizationSanam KhanNo ratings yet
- Government Consumption - Government: Income DistributionDocument1 pageGovernment Consumption - Government: Income DistributionSemih EminiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 GursameDocument47 pagesUnit 2 Gursamedemeketeme2013No ratings yet
- Cost Efficiencies Work Group: Summary of Final Report October 30, 2015Document23 pagesCost Efficiencies Work Group: Summary of Final Report October 30, 2015Jackie Z. RaquelNo ratings yet
- Cost-Benefit Analysis in Public Project Appraisal: Krystyna BrzozowskaDocument6 pagesCost-Benefit Analysis in Public Project Appraisal: Krystyna BrzozowskaGanesh ShindeNo ratings yet
- Redo IilDocument11 pagesRedo IilParul NayakNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Public Expenditures Question: CompareDocument14 pagesChapter Three Public Expenditures Question: CompareWalid Mohamed AnwarNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Regional Planning StudioDocument19 pagesGroup 2 Regional Planning StudioTerna HonNo ratings yet
- Social Cost-Benefit Analysis: Submitted To Doctor GetnetDocument15 pagesSocial Cost-Benefit Analysis: Submitted To Doctor GetnetSamuel DebebeNo ratings yet
- Economics Planning (MA in Economics)Document52 pagesEconomics Planning (MA in Economics)Karim Virani0% (1)
- Public ExpenditureDocument26 pagesPublic ExpenditureKd YdvNo ratings yet
- IPF - Classnote 8Document30 pagesIPF - Classnote 8Hope LessNo ratings yet
- Intro To Building EconomicsDocument28 pagesIntro To Building EconomicsRaymon PrakashNo ratings yet
- HSN-301 Tutorial 1Document12 pagesHSN-301 Tutorial 1sadsamosasNo ratings yet
- GD TopicsDocument11 pagesGD Topicsguptadisha241No ratings yet
- Ex 11Document4 pagesEx 11Іра КостюкNo ratings yet
- BF 434 Group1 PresentationDocument4 pagesBF 434 Group1 Presentationgoitsemodimoj31No ratings yet
- Pad 413-4Document163 pagesPad 413-4Business HomeNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Financial-Management-In-Psu-SDocument14 pagesUnit 11 Financial-Management-In-Psu-SGinu George VargheseNo ratings yet
- PrivatisationDocument19 pagesPrivatisationNishil MehraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Applied Economics: Slides Prepared by Leigh LimDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Applied Economics: Slides Prepared by Leigh LimJhun Ely Bhoy CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Offs Involved.: Chap 1: Basic Economic Ideas and Resource AllocationDocument2 pagesOffs Involved.: Chap 1: Basic Economic Ideas and Resource AllocationDương Ngọc HuyềnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1Jimmy LojaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 and 5 Project AbDocument77 pagesChapter 4 and 5 Project Abnigus gurmis1No ratings yet
- Public Support For Carbon Pricing Policies and DifDocument17 pagesPublic Support For Carbon Pricing Policies and DifKraft DinnerNo ratings yet
- State Budget and Its OrganizationsDocument7 pagesState Budget and Its Organizationsrotalfail0770No ratings yet
- Intro Fiscal Policy o-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesIntro Fiscal Policy o-WPS OfficeJohn NjorogeNo ratings yet
- Article On Effects of Public ExpenditureDocument11 pagesArticle On Effects of Public Expendituretanmoydebnath474No ratings yet
- Module 10 Expenditure Policy and ReformDocument43 pagesModule 10 Expenditure Policy and ReformDaisy LalasNo ratings yet
- Economic Policies 3Document4 pagesEconomic Policies 3malena muloniaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Applied Welfare Economics and Benefit Cost AnalysisDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Applied Welfare Economics and Benefit Cost AnalysisIRPSNo ratings yet
- Mohan Kumar G.: A Seminar byDocument39 pagesMohan Kumar G.: A Seminar byAnshul BhallaNo ratings yet
- A. Critically Analyze The Issue of Energy Subsidies and Their Impact On An Economy. Who Are The Ultimate Beneficiaries of Such Subsidies?Document3 pagesA. Critically Analyze The Issue of Energy Subsidies and Their Impact On An Economy. Who Are The Ultimate Beneficiaries of Such Subsidies?dasarup24123No ratings yet
- Cost Benefit Analysis1Document15 pagesCost Benefit Analysis1Neharika KatariaNo ratings yet
- SCBA Project Case Study PDFDocument22 pagesSCBA Project Case Study PDFrishipathNo ratings yet
- Project Mngt. UNIT 3Document2 pagesProject Mngt. UNIT 3Kŕiśhñą ŚińghNo ratings yet
- Definition of The Problem This Is A Statement of The Problems Which IdentifiesDocument11 pagesDefinition of The Problem This Is A Statement of The Problems Which IdentifiesesawunyamaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World ReportDocument5 pagesContemporary World Reportjohn mark tumbagaNo ratings yet
- Guha EPW 1985 4375015Document11 pagesGuha EPW 1985 4375015Madhurima GuhaNo ratings yet
- Stefan Molyneux - The - Handbook - of - Human - Ownership PDFDocument25 pagesStefan Molyneux - The - Handbook - of - Human - Ownership PDFSamuelNo ratings yet
- Toliss Airbus A319 V1.6 - Simulation ManualDocument57 pagesToliss Airbus A319 V1.6 - Simulation ManualAdrianoNo ratings yet
- T Codes FicoDocument42 pagesT Codes FicoArjun WaniNo ratings yet
- Flowcharts PPT CADocument14 pagesFlowcharts PPT CAHarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Institute Name: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University (IR-E-U-0017)Document2 pagesInstitute Name: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University (IR-E-U-0017)Shwetha MudireddyNo ratings yet
- SAT Refresher ManualDocument200 pagesSAT Refresher ManualJake Girman100% (1)
- Marungko FinalDocument73 pagesMarungko FinalJohn Steven Concepcion100% (4)
- Be InspiredDocument50 pagesBe InspiredBenMaddieNo ratings yet
- OceanofPDF - Com Learning To Love Myself - Alex AubreyDocument143 pagesOceanofPDF - Com Learning To Love Myself - Alex AubreyJeshvanthNo ratings yet
- Avinash Singh: Most Proud of ExperienceDocument2 pagesAvinash Singh: Most Proud of ExperienceAvinash SinghNo ratings yet
- Me3112 2 Lab Dynamic Balancing Amp Gyroscopic EffectsDocument12 pagesMe3112 2 Lab Dynamic Balancing Amp Gyroscopic EffectsDenise Isebella LeeNo ratings yet
- Indian Maritime University (Imu) : AY 2022-23 Onwards Affiliation Process HandbookDocument202 pagesIndian Maritime University (Imu) : AY 2022-23 Onwards Affiliation Process Handbookazaraero87No ratings yet
- Simha Mam Ukha 002Document3 pagesSimha Mam Ukha 002albertmelondiNo ratings yet
- About Sheepdog Church Security Equipment?Document2 pagesAbout Sheepdog Church Security Equipment?hmareidNo ratings yet
- Septone Brake Dust Cleaner SDSDocument15 pagesSeptone Brake Dust Cleaner SDSMarkSomniumNo ratings yet
- An Action Research ProposalDocument21 pagesAn Action Research ProposalRICHEL MANGMANGNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercises CAEDocument2 pagesPractice Exercises CAENiya PreldjichNo ratings yet
- Speech EvaluationDocument2 pagesSpeech EvaluationAndi AndersonNo ratings yet
- Ed Stone Theory of Writing EssayDocument3 pagesEd Stone Theory of Writing EssayNathan GehlNo ratings yet
- Wachter ReviewDocument71 pagesWachter ReviewkeajraNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of BIMDocument37 pagesThe Little Book of BIMlinuxp97No ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Oxygen ControlDocument6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Oxygen ControlJezrell JaravataNo ratings yet
- The Cell's Life Cycle: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualDocument6 pagesThe Cell's Life Cycle: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualJan Edward Abarientos MandaniNo ratings yet
- Presentation Anglais Ecovadis InfographiqueDocument2 pagesPresentation Anglais Ecovadis InfographiqueSteve TedomNo ratings yet
- The Acoustic Emission Monitoring System of Aboveground Storage TanksDocument8 pagesThe Acoustic Emission Monitoring System of Aboveground Storage TanksGonzalo TelleríaNo ratings yet
- Rdsopeskac0206-2019 Sheet 1 To 48 25-04-2019Document48 pagesRdsopeskac0206-2019 Sheet 1 To 48 25-04-2019Arshad AlamNo ratings yet
- Voices in Harmony ProgramDocument4 pagesVoices in Harmony ProgramagnesmalkNo ratings yet