Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Delta Terminology
Delta Terminology
Uploaded by
LOCNGUYENVAN1004Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Delta Terminology
Delta Terminology
Uploaded by
LOCNGUYENVAN1004Copyright:
Available Formats
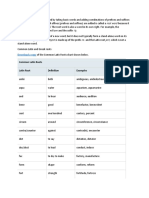
Delta terminology
Delta Module One is not a test of terminology. You do not have to memorise all of
these terms, and you should not aim to put as much terminology into your answers as
possible, just for the sake of it. However, these terms are worth knowing – or, more
importantly – understanding. As well as choosing some words from this list for Block B
Paper 1 Tasks 1 and 2, it’s worth researching the terms you’re not familiar with before
the exam. Note that this is not an exhaustive list!
Lexis
Morphology
Morphemes: freestanding & bound
Compound words
Delexicalised verbs
Lexical verbs
Content words
Function words
Chunks
Collocation
Fixed expressions
Semi-fixed expressions
Affixation: prefixes, suffixes & infixes
Semantic field
Lexical field
Lexical set
Lexical item
Synonyms
Antonyms
Meronyms
© 2022 Apollo Education & Training Vietnam
Metonyms
Superordinate
Hypernym
(Co) Hyponyms
Homographs
Homophones
Homonyms
Polysemy
Denotive meaning
Pragmatic meaning
Connotation
Reading
Skimming
Scanning
Extensive reading
Intensive reading
Reading for gist
Reading for specific information
Reading for detailed comprehension
Reading to deduce meaning from context
Reading to infer mood/opinion
Top-down processing
Bottom-up processing
© 2022 Apollo Education & Training Vietnam
Listening
Listening sub-skills (gist, specific information, etc. as above)
Intensive listening
Extensive listening
Writing skills
Product writing
Process writing
Drafting
Editing
Publishing
Genre
Audience
Register
Speaking
Ellipsis
Fillers
Back channelling
Turn-taking
Adjacency pairs
Paralinguistic features
Approaches to teaching new language
Inductive
Deductive
PPP
© 2022 Apollo Education & Training Vietnam
T-T-T
Guided Discovery
The Lexical Approach
Communicative Language Teaching
Task Based Learning
Grammar Translation
Audiolingualism
Direct Method
Behaviourism and Skinner
Mentalism and Chomsky
Total Physical Response (TPR)
The Silent Way
Suggestopaedia
Community Language Learning (CLL)
The Natural Approach
• The Acquisition/Learning Hypothesis
• The Monitor Hypothesis
• The Natural Order Hypothesis
• The Input Hypothesis
• I plus 1
• Roughly-tuned input & Finely-tuned input
• The Affective Filter Hypothesis
Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP)
Content and Language Integrated Learning (CLIL)
Dogme ELT
Demand High
© 2022 Apollo Education & Training Vietnam
Phonology
Segmentals:
Place of articulation
Manner of articulation
Consonant clusters
Minimal pairs
Glottal stop
Suprasegmentals:
Word stress
Connected speech
• Weak/Strong Forms
• Assimilation
• Elision
• Contractions
• Liaison/Linking/Catenation
• Intrusive sounds
• Juncture
Sentence stress
Intonation
Prosody
Allophones
Received Pronunciation (RP)
Accent
Dialect
Syllable-timed languages
Stress-timed languages
Time, Tense and Aspect
Tense
© 2022 Apollo Education & Training Vietnam
Aspect
Simple
Continuous
Perfect
Discourse
Discourse analysis
Coherence
Cohesion
Grammatical cohesion
• Reference devices
• Substitution devices
• Ellipsis
• Logical linking devices
Endophoric reference: anaphoric and cataphoric
Exophoric reference
Given-New (Theme-Rheme) ordering of information
Lexical cohesion
• Lexical sets
• Lexical chains
• Consistent register
• Collocation
• Lexical repetition
• Lexical substitution
• Parallelism
Assessment, Testing and Examinations
Achievement test
Diagnostic test
Placement test
© 2022 Apollo Education & Training Vietnam
Proficiency test
Authenticity
Practicality
Reliability
Validity
• Content validity
• Face validity
• Construct validity
Backwash
Direct/Indirect testing
Objective/Subjective testing
Discrete point testing
Integrative testing
Criterion-referenced testing
Norm-referenced testing
Formative assessment
Summative assessment
Error and Correction
L1 Interference
Intralingual errors
© 2022 Apollo Education & Training Vietnam
You might also like
- InfinitivesDocument19 pagesInfinitivesTri Hadiati NurmeilasariNo ratings yet
- InterjectionDocument17 pagesInterjectionhidayah mohamedNo ratings yet
- Xhosa DictionaryDocument16 pagesXhosa DictionaryMr Reeds50% (2)
- Sentence Diagramming Adjectives Adverbs ArticlesDocument2 pagesSentence Diagramming Adjectives Adverbs ArticlesrowenimaryNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - Resub - MiguelLaricoCondoriDocument8 pagesAssignment 2 - Resub - MiguelLaricoCondoriMIGUEL ANGEL LARICO CONDORINo ratings yet
- PG Cert ELT and Professional Practice/ Delta Lesson Plan: Commented (A1) : Please Refer To The File Named Syllabus'Document8 pagesPG Cert ELT and Professional Practice/ Delta Lesson Plan: Commented (A1) : Please Refer To The File Named Syllabus'Nguyễn Hoài Anh ThưNo ratings yet
- Grammar BackgroundDocument10 pagesGrammar Backgroundpandreop100% (1)
- Advanced Grammar + Grammar For IELTSDocument45 pagesAdvanced Grammar + Grammar For IELTSBhavanandhan RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Lsa 2 Skills (Speaking) : TitleDocument13 pagesLesson Plan Lsa 2 Skills (Speaking) : TitleZeynep BeydeşNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Listening + CommentaryDocument7 pagesLesson Plan - Listening + CommentaryZeynep BeydeşNo ratings yet
- Conditionals LSA ExampleDocument5 pagesConditionals LSA ExampleMikeNo ratings yet
- Bang - November 2020 QPDocument20 pagesBang - November 2020 QPAdeeba iqbal100% (1)
- Blank LRT Grid (Advice)Document2 pagesBlank LRT Grid (Advice)Clara Maria Quispe CéspedesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Candidate: Olga Date: 20.08.2021 Level: Intermediate Tutor: Anna Muzafarova TP No.: 6 Length: 45 MinsDocument9 pagesLesson Plan: Candidate: Olga Date: 20.08.2021 Level: Intermediate Tutor: Anna Muzafarova TP No.: 6 Length: 45 MinsOlga SlaschovaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Rinto Gramar 2Document16 pagesTugas Rinto Gramar 2Rinto Suoth86% (7)
- RitsIILCS 8.1pp.183 193peatyDocument13 pagesRitsIILCS 8.1pp.183 193peatyMartha Peraki100% (1)
- Testing ReceptiveSkillsReadandLIstenDocument48 pagesTesting ReceptiveSkillsReadandLIstenRoy Lustre Agbon100% (1)
- CELTA Course Assignments (2022)Document4 pagesCELTA Course Assignments (2022)Evelyne Rodriguez HilarioNo ratings yet
- Exam Thread: Further Work On Paper 1 Tasks 1, 2 & 3 and Paper 2 Tasks 1 & 4Document42 pagesExam Thread: Further Work On Paper 1 Tasks 1, 2 & 3 and Paper 2 Tasks 1 & 4AlexNo ratings yet
- Text-Based Guided Discovery (Grammar) Lesson Plan - CELTADocument11 pagesText-Based Guided Discovery (Grammar) Lesson Plan - CELTAmgomezNo ratings yet
- Exam Thread: Paper 1 Tasks 1 & 2 and Paper 2 Tasks 2 & 3: The Distance Delta Module OneDocument28 pagesExam Thread: Paper 1 Tasks 1 & 2 and Paper 2 Tasks 2 & 3: The Distance Delta Module OneAlexNo ratings yet
- Teaching Speaking & Listening Through Communicative ActivitiesDocument29 pagesTeaching Speaking & Listening Through Communicative ActivitiesNor Faa'iza Binti Taib100% (2)
- Language Systems Assignment: Raise Awareness of Delexicalised Verbs and Their Collocates To Intermediate Level StudentsDocument9 pagesLanguage Systems Assignment: Raise Awareness of Delexicalised Verbs and Their Collocates To Intermediate Level StudentsEleni Vrontou100% (1)
- DELTA Module II LSA 2 Developing PlanninDocument11 pagesDELTA Module II LSA 2 Developing PlanninSam SmithNo ratings yet
- Helping Intermediate Learners Manage Interactive ConversationsDocument29 pagesHelping Intermediate Learners Manage Interactive ConversationsChris ReeseNo ratings yet
- KDC - Celta - TP8Document8 pagesKDC - Celta - TP8oanailieNo ratings yet
- Focus On The Learner - NHDocument15 pagesFocus On The Learner - NHRoger mandujano macedoNo ratings yet
- Task 5Document2 pagesTask 5Dale CoulterNo ratings yet
- Speakout Pre IntermediateDocument52 pagesSpeakout Pre IntermediateGuillermo RojasNo ratings yet
- DELTA Module Two Lesson Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesDELTA Module Two Lesson Plan TemplateAhmed NaeemNo ratings yet
- Task 5 BadnaswersDocument1 pageTask 5 BadnaswersDale CoulterNo ratings yet
- Teaching House - Candidate Handbook 2019Document132 pagesTeaching House - Candidate Handbook 2019ShayNo ratings yet
- Delta Module 1 Exam Report Dec 2008Document6 pagesDelta Module 1 Exam Report Dec 2008ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - TesolDocument12 pagesModule 4 - TesoldindoNo ratings yet
- English as a Foreign or Second Language: Selected Topics in the Areas of Language Learning, Teaching, and TestingFrom EverandEnglish as a Foreign or Second Language: Selected Topics in the Areas of Language Learning, Teaching, and TestingNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan PassiveDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Passivearina_diaNo ratings yet
- Module ThreeDocument57 pagesModule ThreeЮлия КумичеваNo ratings yet
- Angel Correa-Pedreros - LSA 1 Final Lesson Plan - DELTA Module 2Document19 pagesAngel Correa-Pedreros - LSA 1 Final Lesson Plan - DELTA Module 2ÁngelNo ratings yet
- A Corpus-Analysis of Chinese EFL Learners Employment of AlthoughDocument12 pagesA Corpus-Analysis of Chinese EFL Learners Employment of AlthoughJingwen ChenNo ratings yet
- Checklist For LSA 2Document2 pagesChecklist For LSA 2eddydasilvaNo ratings yet
- Delta M1 Task 1,2 TerminologyDocument27 pagesDelta M1 Task 1,2 TerminologyIoanna Jane Andreopoulou100% (1)
- DELTA - Grammar and VocabularyDocument5 pagesDELTA - Grammar and VocabularyEmily JamesNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Genre AnalysisDocument16 pagesPart 1 Genre AnalysisdanizaNo ratings yet
- Trinity Lesson Plan 2 Edcc 340Document8 pagesTrinity Lesson Plan 2 Edcc 340api-439472994No ratings yet
- CELTA Assignment 4Document7 pagesCELTA Assignment 4hninwutyeeoothestudentNo ratings yet
- Review of From Rules To Reasons by Danny Norrington-Davies (Pavilion 2016)Document3 pagesReview of From Rules To Reasons by Danny Norrington-Davies (Pavilion 2016)DeisyNo ratings yet
- Communicative CompetenceDocument18 pagesCommunicative CompetenceLara OñaralNo ratings yet
- Exercises of Job InterviewDocument5 pagesExercises of Job InterviewNaza lsNo ratings yet
- Celta Pre Interview Task Sep15Document4 pagesCelta Pre Interview Task Sep15scribd_cartiNo ratings yet
- Error Correction 1 - TeachingEnglish - British Council - BBCDocument5 pagesError Correction 1 - TeachingEnglish - British Council - BBCLamaCNo ratings yet
- Impactful Communication & Negotiations Lecture 4Document35 pagesImpactful Communication & Negotiations Lecture 4Mohammad BabarNo ratings yet
- The Long-Neglected Phrasal VerbDocument8 pagesThe Long-Neglected Phrasal VerbAzra Hadžić100% (1)
- HL Lsa4 PleDocument2 pagesHL Lsa4 PleEmily JamesNo ratings yet
- D1b DELTA Pre Course Directed Reading TaskDocument13 pagesD1b DELTA Pre Course Directed Reading TaskNaserElrmahNo ratings yet
- (ELT READING) How To Teach VocabularyDocument9 pages(ELT READING) How To Teach VocabularyKiều Dực LinhNo ratings yet
- Language AnalysisDocument13 pagesLanguage AnalysisMuhammad Iqbal100% (4)
- Speaking TBL 1 PDFDocument3 pagesSpeaking TBL 1 PDFEko Wahyu ApriliantoNo ratings yet
- ISE 1 (B1) Interview - Lesson Plan 6 - Using Trinity DVDs For Preparation (Final)Document4 pagesISE 1 (B1) Interview - Lesson Plan 6 - Using Trinity DVDs For Preparation (Final)iSVilaNo ratings yet
- Are Is Alves Process Writing LTMDocument24 pagesAre Is Alves Process Writing LTMM Nata DiwangsaNo ratings yet
- Emma Halliday LSA 2: Helping Learners Listen To Broadcast NewsDocument16 pagesEmma Halliday LSA 2: Helping Learners Listen To Broadcast NewsAhmed BelalNo ratings yet
- 490354the Oral Error Correction Techniques Used by Libyan Secondary School Teachers of English Muhsen Abobaker A. Ali ADocument315 pages490354the Oral Error Correction Techniques Used by Libyan Secondary School Teachers of English Muhsen Abobaker A. Ali ALouis WilliamNo ratings yet
- Celta Application Form and Language Awareness Task - British Council Bangladesh 1Document7 pagesCelta Application Form and Language Awareness Task - British Council Bangladesh 1rehan3038No ratings yet
- SAMPLE Language Analysis Sheet - GRAMMAR & VOCAB Cambridge CeltaDocument3 pagesSAMPLE Language Analysis Sheet - GRAMMAR & VOCAB Cambridge CeltaRoger mandujano macedoNo ratings yet
- Teaching English To Very Young LearnersDocument4 pagesTeaching English To Very Young LearnersnganNo ratings yet
- Teaching Register and Genre FeaturesDocument4 pagesTeaching Register and Genre FeaturesRubens RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Word Formation PDFDocument3 pagesWord Formation PDFŔįssįnģ MõõnNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Grammar Usage Sentence StructuringDocument180 pagesVocabulary Grammar Usage Sentence StructuringAASIM MUSTAFANo ratings yet
- Questions For Semantic Review (K22)Document4 pagesQuestions For Semantic Review (K22)CA Pham Khai80% (5)
- Phrase, Clause and SentenceDocument26 pagesPhrase, Clause and SentenceDikla Sasta WijaksaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in MorphologyDocument4 pagesWorksheet in MorphologyLiezel MaquilingNo ratings yet
- PrefixDocument8 pagesPrefixheerawm100% (1)
- Opposite Words ArabicDocument44 pagesOpposite Words ArabicSaeeda KhanNo ratings yet
- Analisis Hakim''Document3 pagesAnalisis Hakim''sasro simamoraNo ratings yet
- Word Formation ProcessesDocument4 pagesWord Formation ProcessesMacwin KiatNo ratings yet
- What Is A PrepositionDocument10 pagesWhat Is A PrepositionAngelica AclanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Sense Relations - Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesLecture 1 Sense Relations - Lecture NotesMihaela Codrina AntonNo ratings yet
- UNIT1Parts of SpeechPART 3Document68 pagesUNIT1Parts of SpeechPART 3David OpokuNo ratings yet
- Lexical Cohesion: Discourse Analysis - Lecture 4Document52 pagesLexical Cohesion: Discourse Analysis - Lecture 4Marina TanovićNo ratings yet
- What Is PhonologyDocument7 pagesWhat Is PhonologyMartin HopeNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Journal TemplatesDocument12 pagesVocabulary Journal TemplatesErika Schultz Matthews100% (1)
- Homonymy Is The Relation Between Words With Identical Forms ButDocument2 pagesHomonymy Is The Relation Between Words With Identical Forms ButWolf ClawsNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech and Word Classes: Old-Fashioned Latin GrammarDocument4 pagesParts of Speech and Word Classes: Old-Fashioned Latin GrammarAshraf KhanNo ratings yet
- SemanticDocument15 pagesSemanticHồng DungNo ratings yet
- A Copy: Common Latin RootsDocument7 pagesA Copy: Common Latin RootsAshleigh Jenson WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- AmbiguityDocument6 pagesAmbiguitygreen_tio100% (1)
- Session 2 - Unit 2 & 3-Level IvDocument12 pagesSession 2 - Unit 2 & 3-Level IvMARCO ANTONIO VALERIO VASQUEZNo ratings yet
- S LV CDocument37 pagesS LV CMariane T. ArellanoNo ratings yet