Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(Xii) Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Uploaded by
sitaramroyalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(Xii) Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Uploaded by
sitaramroyalCopyright:
Available Formats
ELEGANT STUDY FORUM
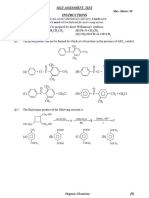
ASSIGNMENT CLASS - XII HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
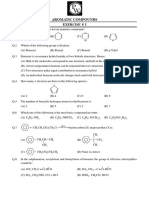
Q1. Which is not a good reagent to convert alcohols into alkyl chloride?
(a) NaCl (b) HCl + ZnCl2 (c) PCl3 (d) SOCl2
Q2. Which is best method to prepare 2-bromobutane?
𝐻𝐵𝑟 𝐻𝐵𝑟
(a) CH3 – CH = CH –CH2 – CH3 → (b) CH3 – CH2 – CH = CH2 →
𝐵𝑟2 𝐻𝐵𝑟
(c) CH3 – CH = CH – CH3 → (d) CH3 – CH2 – CH = CH2 →
Peroxide
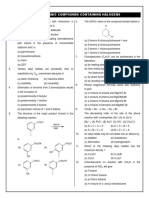
Q3. Among the following, which yields chloroform?
(a) Methanol (b) Hexanone-2 (c) Propanol-1 (d) Propanol-2
Q4. Product obtained when C2H5Br reacts with AgNO2(alc.) is:
(a) ethane (b) ethane (c) nitroethane (d) ethyl alcohol
Q5. Among the following, which pair gives butanenitrile on heating?
(a) Propyl alcohol and KCN (b) Butyl alcohol and KCN
(c) Butyl chloride and KCN (d) Propyl chloride and KCN
Q6. 1-Chlorobutane reacts with KOH(alc.) to give:
(a) 1-butene (b) 1-butanol (c) 2-butene (d) 2-butanol
𝑅𝑒𝑎𝑔𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑋
Q7. 𝑅 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐶𝑙2 − 𝑅 → 𝑅 − 𝐶 ≡ 𝐶 − 𝑅 Reagent X is:
(a) Na (b) HCl(aq.) (c) KOH(alc.) (d) Zn
Q8. Slow oxidation of chloroform by air in presence of light gives:
(a) formyl chloride (b) phosgene (c) trichloroacetic acid (d) formic acid
Q9. Phosgene is:
(a) PH3 (b) POCl3 (c) CS2 (d) COCl2
Q10. The product obtained when chloroform is boiled with caustic soda is:
(a) sodium acetate (b) sodium formate (c) sodium oxalate (d) methyl alcohol
Q11. Which acts as refrigerant?
(a) CH2F2 (b) CCl4 (c) CF4 (d) CF2Cl2
Q12. Which of the following reaction gives best yield of C 2H5Cl?
𝑈𝑉 𝑟𝑎𝑦𝑠 𝑅𝑇
(a) C2H6 (Excess) + Cl2 → (b) C2H6 + Cl2 →
Dark
𝑈𝑉 𝑈𝑉
(c) C2H6 + Cl2(Excess) → (d) C2H6 + Cl2 →
Q13. C2H5Cl reacts with …………. to form C2H5OH:
(a) KOH(alc.) (b) KOH(aq.) (c) H2O (d) H2O2
Q14. Alkyl halides on heating with dry Ag2O yields:
(a) Esters (b) Ethers (c) Ketones (d) AgCl + hydrocarbons
Q15. Chloroform is used as:
(a) insecticide (b) fungicide (c) industrial solvent (d) absorbent
ESF CHEMISTRY BY KUSHWAHA SIR CONTACT NO: 9450019247
Q16. Chloroform is manufactured by reaction between acetone and ………….
(a) phosgene (b) CaOCl2 (c) Cl2 (d) NaCl
Q17. Which of the following yields bromoethane in Wurtz reaction?
(a) 2, 3 – dimethyl butane (b) 2, 3-methyl propane (c) n-butane (d) n- propane
Q18. Formation of alkanes by action of Na/dry ether or alkyl halides is called:
(a) Frankland reaction (b) Sandmeyer’s reaction (c) Wurtz reaction (d) Kolbe reaction
Q19. Which of the following is gem-dihalide?
(a) CH3CHBr2 (b) BrCH2CH2Br (c) CH3CH(Br)CH2Br (d) CH3CH(Br)CH2CH2Br
𝑍𝑛𝑋2
Q20. C2H5OH + HX → C2H5X. Reactivity order of HX is:
(a) HBr > HI > HCl (b) HI > HCl > HBr (c) HI > HBr > HCl (d) HCl > HBr > HI
Q21. What is the product obtained when chloroform reacts with conc. HNO3?
(a) CHCl3 . NO2 (b) C(NO2)Cl3 (c) CHCl3.HNO3 (d) CHCl2.NO2
Q22. On oxidation, CHCl3 gives
(a) phosgene (b) formic acid (c) carbon tetrachloride (d) chloropicrin
Q23. When chloroform is exposed to air and sunlight, it is slowly oxidized and gives:
(a) phosgene (b) formic acid (c) formyl chloride (d) methyl chloride
Q24. Haloforms are trihalogen derivatives of:
(a) methane (b) ethane (c) propane (d) benzene
Q25. In the presence of light, chloroform oxidizes to produce:
(a) Carbon tetrachloride (b) Carbonyl chloride (c) Dichloromethane (d) None of these
Q26. In nucleophilic substitution reactions aryl halides are less reactive than alkyl halides is due to:
(a) formation of less stable carbonium ion (b) resonance stabilization
(c) longer C –H bond length (d) Inductive effect
Q27. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their dipole moments. Toluene (I), m-dichlorobenzene (II),
o-dichlorobenzene (III), p-dichlorobenzene (IV):
(a) I < IV < II < IIII (b) IV < I < II < III (c) IV < I < III < II (d) IV < II < I < III
Q28. Hydrogenation of benzyl chloride in the presence of Pd/BaSO4 gives:
(a) benzyl alcohol (b) benzaldehyde (c) benzoic acid (d) phenol
Q29. Which of the following process is used for industrial preparation of chlorobenzene?
(a) Grignard reaction (b) Raschig process (c) Wurtz-Fittig reaction (d) Friedel-Craft reaction
Q30. In the presence of which of the following, toluene reacts with Cl2 to give benzyl chloride?
(a) Light (b) Absence of light (c) AlCl3 (d) As2S3
Q31. Chlorobenzene gives DDT when reacts with:
(a) CCl3CHO (b) C6H5NO2 (c) C6H5N2Cl (d) none of these
Q32. Chlorobenzene reacts with LiAlH4 to give:
(a) C6H6 (b) C6H5 – C6H5 (c) (C6H5)2CO (d) none of these
ESF CHEMISTRY BY KUSHWAHA SIR CONTACT NO: 9450019247
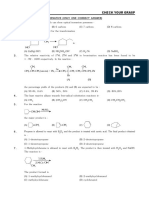
Q33.
Q34.
Q35. Product obtained by reaction of NH3 on chlorobenzene in the presence of cuprous oxide is:
(a) phenol (b) aniline (c) benzene (d) benzoic acid
ℎ𝑣
Q36. C6H6 + Cl2 → product is:
(a) C6H5Cl (b) o−C6H4Cl2 (c) C6H6Cl2 (d) p−C6H4Cl2
Q37. The reaction ; CH2 = CH2 + Br2 ⟶ CH2Br –CH2Br provides an example of a /an:
(a) Electrophilic addition (b) Electrophilic substitution
(c) Nucleophilic addition (d) Nucleophilic substitution
Q38. The reaction; C2H5Br + KCN ⟶ C2H5CN + KBr is an example of:
(a) Elimination (b) Nucleophilic substitution
(c) Electrophilic substitution (d) Free radical substitution
Q39. Best reagent for preparing a chloroalkane from an alcohol is:
(a) SOCl2 / C5H5N (b) HCl / ZnCl2 (c) PCl3 (d) Cl2 / CCl4
Q40. Addition of HBr to 2-methylpropene in the presence of hydrogen peroxide mainly forms:
(a) 1-bromo-2-methylpropane (b) 2-bromo-2-methylpropane
(c) 1-bromobutane (d) 2-bromopropane
Q41. Which is an optically active compound?
(a) 2-chloropropane (b) 2-chlorobutane (c) 3-chloropentane (d) None of these
Q42. Chlorobenzene on fusing with solid NaOH gives:
(a) Benzene (b) Benzoic acid (c) Phenol (d) Chlorophenol
Q43. Which of the following is a gem-dihalide?
(a) CH3CHBr2 (b) BrCH2CH2Br (c) CH3CHBrCH2Br (d) None of the above
ESF CHEMISTRY BY KUSHWAHA SIR CONTACT NO: 9450019247
Q44. Chlorine is least reactive in:
(a) Methyl chloride (b) Ethyl chloride (c) Vinyl chloride (d) Allyl chloride
Q45. When chloroform is heated with conc. Nitric acid, we get chloropicrin. It is used as:
(a) Fertilizer (b) Explosive (c) Antibiotic (d) Insecticide
Q46. Which one of the following is likely to give a precipitate with AgNO 3 solution?
(a) CCl4 (b) CHCl3 (c) CH2 = CHCl (d) (CH3)3CCl
Q47. Which of the following compounds would not give a precipitate with alcoholic solution of AgNO 3?
(a) Bromobenzene (b) 2-bromopropane (c) Allyl bromide (d) 1-bromopropane
Q48. Only two isomeric monochloro derivatives are possible for:
(a) Neopentane (b) Benzene (c) 2, 4-dimethylpentane (d) 2-methylpropane
Q49. Which of the following would exhibit Kharasch effect?
𝑃𝑒𝑟𝑜𝑥𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑠 𝑃𝑒𝑟𝑜𝑥𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑠
(a) CH3CH = CH2 + HCl → (b) CH2 = CH2 + HBr →
𝑃𝑒𝑟𝑜𝑥𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑠
(c) CH3CH = CH2 + HBr → (d) CH2 = CH2 + HCl ⟶
Q50. Which one of the following compounds will be most readily attacked by an electrophile?
(a) Chlorobenzene (b) Benzene (c) Phenol (d) Toluene
Q51. Reaction of CH2 − CH2 with RMgX followed with hydrolysis produces:
O
(a) RCHOHR (b) RCH2CH2OH (c) RCHOHCH3 (d) RCH = CHOH
Q52. A yellow precipitate is obtained when aqueous AgNO 3 is added to a solution of the compound:
(a) CCl3CHO (b) CHI3 (c) CHCl3 (d) C6H5CH2Cl
Q53. The bad smelling substance formed by the action of alcoholic caustic potash on chloroform and aniline is:
(a) Phenyl isocyanide (b) Nitrobenzene (c) Acetylene (d) Chlorobenzene
Q54. Which would be obtained by boiling CHCl3 with caustic soda?
(a) CH3COONa (b) HCOONa (c) Na2C2O4 (d) CH3OH
Q55. PCl5 reacts with propanone, to give:
(a) Gem-dichloride (b) Vic-dichloride (c) Propanal (d) Propane chloride
Q56. A salt solution is treated with chloroform drops and is shaken with chlorine water. Chloroform layer becomes
violet, solution contains:
(a) 𝑁𝑂2− (b) 𝑁𝑂3− (c) 𝐵𝑟 − (d) 𝐼 −
𝐴𝑐𝑒𝑡𝑜𝑛𝑒
Q57. The reaction, 𝑅𝐶𝑙 + 𝑁𝑎𝐼 → 𝑅 − 𝐼 + 𝑁𝑎𝐶𝑙 is known as:
(a) Wurtz’s reaction (b) Fittig reaction (c) Frankland’s reaction (d) Finkelstein’s reaction
Q58. The compound that will not give iodoform on treatment with alkali and iodine is:
(a) Acetone (b) Ethanol (c) Diethyl ketone (d) Isopropyl alcohol
Q59. A compound containing two – 𝑂𝐻 groups attached with one carbon atom is unstable but which one of the following
is stable? OH
OH OH
(a) CH3CH (b) CH3 −C − OH (c) Cl3C – CH (d) None of these
OH OH
OH
ESF CHEMISTRY BY KUSHWAHA SIR CONTACT NO: 9450019247
Q60. Carbon tetrachloride on treatment with Fe/H2O gives:
(a) Chloromethane (b) Methane (c) Chloroform (d) Methylene chloride
Q61. Iodoform test is not given by:
(a) Ethanol (b) Benzophenone (c) Ethanol (d) Acetophenone
Q62. Which one is liquid at room temperature?
(a) CH3Cl (b) C2H5Cl (c) CH3Br (d) C2H5Br
Q63. Which of the following is a camphor substitute?
(a) CHCl3 (b) CF2Cl2 (c) CF3CHClBr (d) C2Cl6
Q64. Iodoform test is not given by:
(a) CH3COCH2COOC2H5 (b) CH3COCH3 (c) CH3CH2COCH3 (d) CH3CH2CHOHCH3
Q65. Which of the following represents Freon?
(a) Ethylene dichloride (b) Ethylidene dichloride
(c) Tetrafluoroethylene (d) Dichlorodifluoromethane
Q66. 20% aqueous solution of sodium chloride containing ethyl alcohol on electrolysis gives:
(a) Ethyl chloride (b) Chloral (c) Acetaldehyde (d) Chloroform
0
Q67. In the reaction of phenol with CHCl3 and aqueous NaOH at 70 C, the electrophile attacking the ring is:
(a) CHCl3 (b) CHCl2 (c) CCl2 (d) COCl2
Q68. Butane nitrile may be prepared by heating?
(a) Propyl alcohol with KCN (b) Butyl alcohol with KCN
(c) Butyl chloride with KCN (d) Propyl chloride with KCN
Q69. Isobutyl magnesium bromide with dry ether and absolute alcohol gives:
(a) CH3 . CH . CH2OH and CH3 . CH2MgBr (b) CH3.CH.CH2.CH2.CH3 and MgOHBr
CH3 CH3
(c) CH3 – CH − CH3 , CH2 = CH2 and Mg(OH)Br (d) CH3 – CH.CH3 and CH3CH2OMgBr
CH3 CH3
𝐻2 𝑆𝑂4
𝐶𝐻3 − 𝐶𝐻 = 𝐶𝐻 − 𝐶𝐻3
Q70. For the reaction, CH3 CH.CH2CH3 →
475 𝐾 𝐶𝐻2 = 𝐶𝐻. 𝐶𝐻2 . 𝐶𝐻3
X
(a) CH3 – CH = CH – CH3 predominates (b) CH2 = CH – CH2 – CH3 predominates
(c) Both are formed in equal amounts (d) The product ratio is dependent on the halogen X
Q71. A compound (A) of formula C3H6Cl2 on reaction with alkali can give (B) of formula C 3H6O or (C) of formula C3H4.
(B) on oxidation gave a compound of the formula C 3H6O2. (C) with dilute H2SO4 containing Hg2+ ion gave (D) of
formula C3H6O, which with bromine and NaOH gave the sodium salt of C 2H4O2. Then (A) is:
(a) CH3CH2CHCl2 (b) CH3CCl2CH3 (c) CH2ClCH2CH2Cl (d) CH3CHClCH2Cl
Q72. The reaction conditions leading to the best yields of C 2H5Cl are:
𝑈𝑉 𝑙𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡 Dark
(a) 𝐶2 𝐻6 (𝑒𝑥𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠) + 𝐶𝑙2 → (b) C2H6 + Cl2 →
Room temperature
UV light UV light
(c) C2H6 + Cl2(excess) → (d) C2H6 + Cl2 →
ESF CHEMISTRY BY KUSHWAHA SIR CONTACT NO: 9450019247
Q73. A mixture of 1-chloropropane and 2-chloropropane when treated with alcoholic KOH, it gives:
(a) 1-propene (b) 2-propene (c) Isopropylene
(d) A mixture of 1-propene and 2-propene
Q74. Vicinal and germinal dihalides can be distinguished by:
(a) KOH(aq.) (b) KOH(alc.) (c) Zn dust (d) None of these
𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻(𝑎𝑞.) 𝐴𝑙2𝑂3 𝐻𝑂𝐶𝑙
Q75. Identify ‘Z’ in the following reaction series, 𝐶𝐻3 . 𝐶𝐻2 𝐵𝑟 → (𝑋 ) → (𝑌) → (𝑍):
𝐻𝑒𝑎𝑡
(a) Mixture of CH3 − CH − CH2 and CH3 − CH− CH2
Cl Cl OH Cl
(b) CH3 − CH − CH2 (b) CH3 − CH − CH2 (d) CH3 − CH − CH2
OH Cl Cl OH Cl Cl
Q76. 𝑆𝑁1 reaction is favoured by:
(a) Non-polar solvents (b) More no. of alkyl group on the carbon atom attached to the halogen atom
(c) Small groups on the carbon attached to the halogen atom (d) None of these
Q77. Which compound on reaction with ethyl magnesium bromide and water will form 2-methyl-2-butanol?
(a) CH3COCH3 (b) CH3COOCH3 (c) CH3CH2CHO (d) C2H5COCH3
Q78. 1, 2-dibromoethane is added to prevent deposition of lead metal in:
(a) Water pipes (b) Petrol engines (c) Electric heaters
(d) Metal working lathe machines
Q79. The reaction, 𝐶𝐻3 𝐵𝑟 + 𝑂𝐻− ⟶ 𝐶𝐻3 𝑂𝐻 + 𝐵𝑟 − obeys the mechanism predominantly:
(a) 𝑆𝑁1 (b) 𝑆𝑁2 (c) 𝑆𝐹1 (d) 𝑆𝐹2
Q80. The reaction described below is:
(a) 𝑆𝐸1 (b) 𝑆𝑁2 (c) 𝑆𝐹1 (d) 𝑆𝐹 2
Q81. In 𝑆𝑁1 reaction, the first step involves the formation of:
(a) Free radical (b) Carbanion (c) Carbocation (d) Final product
Q82. (CH3)3CMgCl on reaction with D2O gives:
(a) (CH3)3CD (b) (CH3)3OD (c) (CD3)3CD (d) (CD3)3OD
𝑁𝑎𝑁𝐻2
Q83. In the given reaction, 𝐵𝑟𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝐻 = 𝐶𝐻2 → [𝑋]; the product ‘X’ is:
∆
(a) CH2 = C = CH2 (b) CH3C ≡ CH (c) CH3 − C ≡ 𝐶 − 𝑁𝑎 + (d) CH2 = C = 𝐶 − 𝑁𝑎 +
Q84. In the given reaction, Br
𝐾𝑂𝐻 (𝑎𝑙𝑐.)
CH3CH2CHCH = CH2 → [𝑋]; the product ‘X’ is:
(a) CH3CH2 – CH = C = CH2 (b) CH2 = CH − CH2 − CH = CH2
(c) CH3 − CH = CH – CH = CH2 (d) CH3 – CH2CH2C ≡CH
ESF CHEMISTRY BY KUSHWAHA SIR CONTACT NO: 9450019247
𝐶𝐻 𝑁
2 2
𝑅 𝐻 →
Q85. In the given reaction, 𝐶=𝐶 ′𝑋′; then product ‘X’ is:
𝐻 𝑅 ether, hv
𝑅 𝐻
(a) Trans dialkyl cyclo propane (b) 𝐶 −𝐶
𝐻 𝑅
CH2
(b) Formed due to stero specific syn. addition by singlet carbine on alkene
(d) All of these
Q86. The rate law for the reaction, 𝑅𝐶𝑙 + 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻(𝑎𝑞.) ⟶ 𝑅𝑂𝐻 + 𝑁𝑎𝐶𝑙 is given by, rate = 𝐾1 [𝑅𝐶l]. The rate of the
reaction will be:
(a) Doubled on doubling the concentration of sodium hydroxide
(b) Halved on reducing the concentration of alkyl halide to half
(c) Decreased on increasing the temperature of the reaction
(d) Unaffected by increasing the temperature of the reaction
Q87. Which compound shows fastest 𝑆𝑁1 reaction mechanism?
(a) (CH3)2CHI (b) CH3CH2I (c) (CH3)3Cl (d) CH3CH2CH2I
Q88. Which of the following compounds shows greater reactivity towards 𝑆𝑁1 reaction?
(a) CH3Cl (b) C2H5Cl (c) CH3 = CHCl (d) CH2 = CHCH2Cl
𝐻𝐵𝑟
Q89. The product formed in the reaction is: 𝑀𝑒3 𝐶𝐶𝐻2 𝑂𝐻 → Product
(a) CH3Cl (b) C2H5Cl (c) CH3 = CHCl (d) CH2 = CHCH2Cl
Q90. 2-Phenyl ethyl chloride undergoes alkaline hydrolysis to give 2-phenyl ethanol with:
(a) Me3CCH2Br (b) Me2CHCH = CH2 (c) Me3C − CH3 (d) Me2C(Br)CH2CH3
Q91. Reaction of methylene chloride with excess of benzene in presence of anhydrous AlCl 3 gives:
(a) C6H5CH2Cl (b) C6H5CH2C6H5 (c) C6H5CHCl2 (d) None of these
Q92. Trimethyl ethyl ammonium iodide is treated with AgOH and the product formed on heating upto 140 0C gives:
(a) Methyl amine (b) Dimethyl amine (c) Trimethyl amine
(d) Tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide
Q93. The product X in the reaction:
CH3
CH3 − C −I + NaOEt ⟶X + NaI + EtOH is:
CH3
Q94. 𝑅3 𝐶 − 𝐵𝑟 + 𝑂𝐻 ⟶ 𝑅3 𝐶 − 𝑂𝐻 + 𝐵𝑟 − . Which of the following mechanism is followed by above reaction?
−
(a) 𝑆𝑁2 (b) 𝑆𝑁1 (c) 𝑆𝑁1 (d) ipso substitution
Q95. The compound ‘X’ of molecular formula C3H6Cl2 gives acetone when treated with aq. alkali, X is:
(a) 1, 1- dichloropropane (b) 2, 2- dichloropropane (c) 1, 2- dichloropropane (d) 1, 3- dichloropropane
Q96. Which of the following will not give haloderivative by addition of HBr?
(a) Cyclohexane (b) Styrene (c) Benzene (d) Butene
Q97. The prodect obtained when n-propyl bromide reacts with KOH(alc.) is:
(a) propane (b) propyne (c) propene (d) propanol
Q98. t-butyl bromide reacts with sodium methoxide to yield:
(a) t-butyl methyl ether (b) iso-butane (c) sodium-t-butoxide (d) iso-butylene
ESF CHEMISTRY BY KUSHWAHA SIR CONTACT NO: 9450019247
Q99. Chloropicrin is:
(a) CCl2HNO2 (b) CClH2NO2 (c) CCl3NO2 (d) CCl2(NO2)2
Q100. With conc. HNO3, chloroform yields:
(a) chloropicrin (b) nitromethane (c) picric acid (d) acetylene
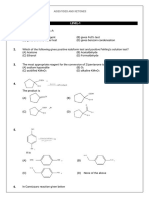
Q101. Case Study
(1) This reaction is an example of:
(a) 𝐸 + subs (b) 𝑁𝑢− subs (c) 𝐸1 reaction (d) either of these
(2) In comparision to benzene, this reaction takes place:
(a) easily (b) difficulty (c) does not occur (d) can’t predict
Q102. Which of the following compounds is likely to show both Frenkel and Schottky defects in its crystalline form?
(a) AgBr (b) CsCl (c) KBr (d) ZnS
Q103. The ratio of number of atoms present in a simple cubic, body centered cubic and face centered cubic structure are, respectively.
(a) 8 : 1 : 6 (b) 1 : 2 : 4 (c) 4 : 2 : 1 (d) 4 : 2 : 3
Q104. Percentage of free space in cubic close packed structure and in body centred packed structure are respectively.
(a) 30% and 26% (b) 26% and 32% (c) 32% and 48% (d) 48% and 26%
Q105. Copper crystallizes in fcc with a unit cell length of 361 pm. What is the radius of copper atom?
(a) 108 pm (b) 127 pm (c) 157 pm (d) 181 pm
Q106. Total volume of atoms present in a face-centred cubic unit cell of a metal is (r is atomic radius)
20 24 12 16
(a) 𝜋𝑟 3 (b) 𝜋𝑟 3 (c) 𝜋𝑟 3 (d) 𝜋𝑟 3
3 3 3 3
Q107. In a compound, atoms of element Y form ccp lattice and those of element X occupy 2/3 rd of tetrahedral voids. The formula of
the compound will be:
(a) X4Y3 (b) X2Y3 (c) X2Y (d) X3Y4
Q108. How many unit cells are present in a cube shaped ideal crystal of NaCl of mass 1.00 g? [Atomic mass: Na = 23, Cl = 35.5]
(a) 2.57 × 1021 (b) 5.14 × 1021 (c) 1.28 × 1021 (d) 1.71 × 1021
Q109. In a face centred cubic lattice, atom (A) occupies the corner positions and atom (B) occupies the face centre positions. If one
atom of (B) is missing from one of the face centred points, the formula of the compound is:
(a) A2B5 (b) A2B3 (c) AB2 (d) A2B
Q110. In Frenkal defect:
(a) Density decreases (b) Density increases (c) Density changes (d) Density does not change
Q111. NaCl crystal is:
(a) Face centred cubic (b) Monoclinic (c) Orthorhombic (d) Tetragonal
Q112. Packing efficiency for simple cubic structure, body centred cubic structure and fcc structure is respectively:
(a) 50% , 60%, 70% (b) 68% , 74%, 52.4% (c) 30%, 40%, 50% (d) 52%, 68%, 74%
Q113. The density of the crystal is lowered in:
(a) Frenkel defect (b) Schottky defect (c) both (d) metal excess defect
Q114. In carbyl amine reaction, the main product is:
(a) cyanide (b) isocyanide (c) acid (d) alcohol
Q115. Which process does not occur during the formation of chloroform from ethanol and bleaching powder?
(a) Oxidation (b) Elimination (c) Chlorination (d) Hydrolysis
Q116. 1-chlorobutane on reaction with alcoholic potash gives:
(a) 1-butanol (b) but-1-ene (c) but-2-ene (d) butan-2-ol
ESF CHEMISTRY BY KUSHWAHA SIR CONTACT NO: 9450019247
Q117. In addition of HBr to propene in the absence of peroxides, the first step involves the addition of:
(a) 𝐻. (b) 𝐻 + (c) 𝐵𝑟 − (d) 𝐵𝑟 .
Q118. The intermediate during the addition of HCl to propene in presence of peroxide is:
(a) CH3CHCH2Cl (b) CH3CHCH3 (c) CH3CH2ĊH2 (d) CH3CH2CH2
Q119. Which of the following reaction is most suitable for the preparation of n-propyl benzene?
(a) Friedel-Crafts alkylation (b) Wurtz reaction (c) Wurtz-Fittig reaction (d) Swarts reaction
Q120. Haloform reaction does not take place with:
(a) propan-2-one (b) propan-2-ol (c) ethanol (d) 2-chloropropane
Q121. During halogenation of an alkane, the ease of replacement of hydrogen atoms follows the order?
(a) 30 H-atom > 20 H-atom > 10 H-atom (b) 20 H-atom > 30 H-atom > 10 H-atom
(c) 10 H-atom > 20 H-atom > 30 H-atom (d) 10 H-atom > 30 H-atom > 20 H-atom
Q122. Which of the following is likely to decompose on standing in presence of sunlight?
(a) CH3CH2Cl (b) CH3CH2l (c) CH3CH2Br (d) CH3CH2F
− −
Q123. The reaction, (𝐶𝐻3 )3 𝐶 − 𝐵𝑟 + 𝑂𝐻 ⟶ (𝐶𝐻3 )3 𝐶 − 𝑂𝐻 + 𝐵𝑟 occurs through:
(a) SN1 mechanism (b) SN2 mechanism (c) E1 mechanism (d) E2 mechanism
Q124. The reactivity of 10 alkyl halides follows the order:
(a) CH3CH2X < CH3X < CH3CH2CH2X (b) CH3X < CH3CH2X < CH3CH2CH2X
(c) CH3CH2X < CH3CH2CH2X < CH3X (d) CH3CH2CH2X < CH3CH2X < CH3X
Q125. Elimination of bromine from 2-bromobutane results in the formation of:
(a) predominantly but-1-yne (b) predominantly but-1-ene
(c) predominantly but-2-ene (d) equimolar mixture of but-1-ene and but-2-ene
Q126. The reactivity order of halides for dehydrohalogenation is:
(a) 𝑅 − 𝐹 > 𝑅 − 𝐶𝑙 > 𝑅 − 𝐵𝑟 > 𝑅 − 𝐼 (b) 𝑅 − 𝐼 > 𝑅 − 𝐵𝑟 > 𝑅 − 𝐶𝑙 > 𝑅 − 𝐹
(c) 𝑅 − 𝐼 > 𝑅 − 𝐶𝑙 > 𝑅 − 𝐵𝑟 > 𝑅 − 𝐹 (d) 𝑅 − 𝐹 > 𝑅 − 𝐼 > 𝑅 − 𝐵𝑟 > 𝑅 − 𝐶𝑙
Q127. In the presence of peroxide, hydrogen chloride and hydrogen iodide do not give anti-Markownikoff’s addition to
alkene because:
(a) both are highly ionic (b) one is oxidising and the other is reducing
(c) one of the steps is endothermic in both the case (d) all the steps are exothermic in both the reaction
Q128. In order to prevent the formation of phosgene from chloroform, the substance added to chloroform is:
(a) CH3COCH3 (b) C2H5OH (c) CH3COOH (d) CH3CHO
Q129. Tertiary alkyl halides are practically inert to substitution by S N2 mechanism because of:
(a) insolubility (b) instability (c) inductive effect (d) steric hindrance
Q130. KCN reacts readily to form cyanide with:
(a) ethanol (b) ethyl bromide (c) bromobenzene (d) chlorobenzene
Q131. Which of the following compounds has the highest boiling point?
(a) CH3CH2CH2Cl (b) CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl (c) CH3CH(CH3)CH2Cl (d) (CH3)3CCl
Q132. The raw materials for the commercial manufacturer of DDT are:
(a) chlorobenzene and chloroform (b) chlorobenzene and iodoform
(c) chlorobenzene and chloral (d) chlorobenzene and chloromethane
ESF CHEMISTRY BY KUSHWAHA SIR CONTACT NO: 9450019247
Q133. Amongst the following the most reactive nucleophile is:
(a) 𝐶𝐻3 𝑂− (b) 𝐶6 𝐻5 𝑂− (c) (𝐶𝐻3 )2 𝐶𝐻𝑂 (d) (𝐶𝐻3 )3 𝐶𝑂
Q134. The compound B is:
(a) chlorobenzene (b) bromobenzene (c) benzyl bromide (d) benzyl chloride
Q135. The correct increasing order of boiling points of the following compounds is:
(a) bromobenzene < 1-bromobutane < 1-bromopropane < 1-bromoethane
(b) bromobenzene < 1-bromo ethane < 1-bromopropane < 1-bromobutane
(c) 1-bromopropane < 1-bromobutane < 1-bromoethane < bromobenzene
(d) 1-bromoethane < 1-bromopropane < 1-bromobutane < bromobenzene
Q136. Ziegler – Natta catalyst is:
(a) mixture of titanium (IV) chloride and triethyl aluminium
(b) mixture of zirconium (III) chloride and triethyl aluminium
(c) mixture of zirconium (III) chloride and dimethyl aluminium
(d) mixture of titanium (III) chloride and dimethyl aluminium
Q137. Which of the following compounds forms as addition compound with CH 3MgBr, which on hydrolysis produces a
secondary alcohol?
(a) HCHO (b) CH3CHO (c) CH3COCH3 (d) CH3COOCH3
Q138. When phenyl magnesium bromide reacts with tertiary butanol, the product formed will be:
(a) phenol (b) benzene (c) tertiary acid on chlorobenzene
(d) chlorine on picric acid
Q139. Chloropicrin is obtained by the reaction of:
(a) nitric acid on chloroform (b) steam on carbontetrachloride
(c) nitric acid on chlorobenzene (d) chlorine on picric acid
Q140. An alkyl bromide produces a single alkene when it reacts with sodium ethoxide and ethanol. This alkene undergoes
hydrogenation and produces 2-methyl butane. What is the identity of the alkyl bromide?
(a) 1-bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane (b) 1-bromobutane
(c) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane (d) 2-bromopentane
Q141. An organic compound A(C 4H9Cl) on reaction with diethyl ether gives a hydrocarbon, which on monochlorination
gives only one chloro derivative ‘A’ is:
(a) t-butyl chloride (b) s-butyl chloride (c) iso-butyl chloride (d) n-butyl chloride
Q142. Which of the following compounds when heated with KOH and a primary amine gives carbylamine test?
(a) CHCl3 (b) CH3Cl (c) CH3OH (d) CH3CN
ESF CHEMISTRY BY KUSHWAHA SIR CONTACT NO: 9450019247
Q143. The reaction between 2-bromobutane and alc. KOH gives but – 2 – ene as major product along but-1-ene as minor
product according to:
(a) Markownikoff’s rule (b) Saytzeff’s rule (c) Kharasch effect (d) Hoffmann’s rule
Q144. Methyl ketone group is identified by:
(a) Iodoform test (b) Fehling solution (c) Tollen’s reagent (d) Schiff’s reagent
Q145. Which of the following is liquid at room temperature?
(a) CH3Br (b) C2H4Cl (c) CH3I (d) CH3F
Q146. The correct order of nucleophilicity would be:
(a) 𝐵𝑟 − < 𝐶𝑙 − < 𝐼 − (b) 𝐼 − < 𝐵𝑟 − < 𝐶𝑙 − (c) 𝐶𝑙 − < 𝐵𝑟 − < 𝐼 − (d) 𝐼 − < 𝐶𝑙 − < 𝐵𝑟 −
Q147. Which of the following is correct order of decreasing S N2 reactivity?
(a) R2CHX > R3CX > RCH2X (b) RCH2X > R3CX > R2CHX
(c) RCH2X > R2CHX > R3CX (d) R3CX > R2CHX > R3CH2X (X = halogen)
Q148. The correct increasing order of the reactivity of halides for S N1 reaction is?
(a) CH3 − CH2−X < (CH3)2CH –X < CH2 = CH – CH2X < PhCH2X
(b) (CH3)2CH –X <CH3−CH2−X < CH2 = CH−CH2X < PhCH2X
(c) PhCH2X < (CH3)2CH –X < CH3 –CH2−X <CH2 = CH –CH2X
(d) CH2 = CH –CH2X < PhCH2X < (CH3)2CH – X < CH3− CH2−X
Q149. Methyl bromide in converted into ethane by heating it in ether medium with:
(a) Al (b) Zn (c) Na (d) Cu
Q150. Which one of the following forms propane nitrile as the major product?
(a) Ethyl bromide + alc. KCN (b) Propyl bromide + alc. KCN
(c) Propyl bromide + alc. AgCN (d) Ethyl bromide + alc. AgCN
Q151. The decreasing order of boiling points of alkyl halides is:
(a) RF > RCl > RBr > RI (b) RBr > RCI > RI > RF
(c) RI > RBr > RCI > RF (d) RCI > RF > RI > RBr
Q152. Iodoform can be prepared from all except:
(a) isopropyl alcohol (b) 3-methyl-2-butanone
(c) isobutyl alcohol (d) ethyl methyl ketone
Q153. Upon treatment with I2 and aqueous NaOH, which of the following compounds will form iodoform?
(a) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CHO (b) CH3CH2COCH2CH3
(c) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH (d) CH3CH2CH2CH(OH)CH3
Q154. During the course of an SN1 reaction, the intermediate species formed is:
(a) a carbocation (b) a free radical
(c) a carbanion (d) an intermediate complex
ESF CHEMISTRY BY KUSHWAHA SIR CONTACT NO: 9450019247
You might also like
- HALOALKANES AND HALOARENESDocument5 pagesHALOALKANES AND HALOARENESkavitha2511977No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Questions 1Document3 pagesOrganic Questions 1SABARI SRINIVAS ANo ratings yet
- Hydrocar SHEET3Document4 pagesHydrocar SHEET3Aayush SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol and Ether Study GuideDocument10 pagesAlcohol, Phenol and Ether Study GuideAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument16 pagesAromatic CompoundsadityaNo ratings yet
- 13 DPP 09a-09d Halk & Harn EvolveDocument17 pages13 DPP 09a-09d Halk & Harn Evolvemangeshchavan980No ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds 12thDocument24 pagesCarbonyl Compounds 12thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Attempt Any 40) : So HCL CL H CDocument4 pagesAttempt Any 40) : So HCL CL H CJatin ChouhanNo ratings yet
- CH# 10 XII (Chem 12 Exam Task)Document3 pagesCH# 10 XII (Chem 12 Exam Task)daniyal.king55No ratings yet
- Aromatic Compounds (13th)Document24 pagesAromatic Compounds (13th)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes & KetonesDocument23 pagesAldehydes & KetonesManthan JhaNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivative of Alkanes & Arenes (Level - Iii & Iv) : Choh Socl CHCL So HCLDocument4 pagesHalogen Derivative of Alkanes & Arenes (Level - Iii & Iv) : Choh Socl CHCL So HCLAbhi WanwadeNo ratings yet
- Alkanes Alkenes Alkynes ObjectiveDocument7 pagesAlkanes Alkenes Alkynes ObjectiveVishal_93No ratings yet
- Class Test-1-Aldehydes & Ketones - PreparationDocument5 pagesClass Test-1-Aldehydes & Ketones - PreparationSarthak VermaNo ratings yet
- BB YASMt DVEvy ZZi PR NYRDocument8 pagesBB YASMt DVEvy ZZi PR NYRarindamNo ratings yet
- Iit Questions On Carbonyl Compounds & Carboxylic Acid and Its DerivativeDocument12 pagesIit Questions On Carbonyl Compounds & Carboxylic Acid and Its DerivativeRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons - Practice SheetDocument7 pagesHydrocarbons - Practice Sheetspthonti1No ratings yet
- ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDSDocument7 pagesALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDSkavitha2511977No ratings yet
- Alkanes - Alkenes - Alkynes - DPP 3Document3 pagesAlkanes - Alkenes - Alkynes - DPP 3Vishal_93100% (1)
- Waghs Chemistry: Chapter-Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pagesWaghs Chemistry: Chapter-Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic AcidsRiddhesh100% (1)
- Alkanes 24.12...........Document4 pagesAlkanes 24.12...........vengateshwaran kNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds SheetDocument133 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Sheetadityavaish739No ratings yet
- 3B-HYDROCARBON Assignment - FinalDocument49 pages3B-HYDROCARBON Assignment - Finalkraken monsterNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 10+11+12 B-II)Document2 pagesChemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 10+11+12 B-II)XXXNo ratings yet
- Topic: Organic Compounds Containing HalogensDocument5 pagesTopic: Organic Compounds Containing Halogensvictoria schoolNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2nd Year Eamcet Named Reaction Identification of Functional Group-1Document7 pagesChemistry 2nd Year Eamcet Named Reaction Identification of Functional Group-1Surya Charan Reddy100% (1)
- Carbonyl Compounds SheetDocument6 pagesCarbonyl Compounds SheetRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Alcohols & EthersDocument36 pagesAlcohols & EthersKaveesh KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Combine Alkyl Halide (2)Document18 pagesChemistry Combine Alkyl Halide (2)Vanshika LudhaniNo ratings yet
- KVS Bhopal Region Chemistry Pre-Board Exam ReviewDocument6 pagesKVS Bhopal Region Chemistry Pre-Board Exam ReviewDrk ZeusNo ratings yet
- 12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS QDocument20 pages12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS Q123No ratings yet
- Nsec 1999Document12 pagesNsec 1999CorneliaNo ratings yet
- PDF Alkanepdf DLDocument8 pagesPDF Alkanepdf DLGeraldineNo ratings yet
- Highest Selection in IIT-JEE since 2006Document13 pagesHighest Selection in IIT-JEE since 2006adityaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: CHO H CH CH C CHDocument8 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: CHO H CH CH C CHUjjwal TomarNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument18 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesBhavesh KNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Class Xii (Chemistry) Unit 5: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument21 pagesQuestion Bank Class Xii (Chemistry) Unit 5: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Multiple Choice QuestionsSahilNo ratings yet
- 34 Alcohols & Ethers - Problems For Practice - Level 1Document14 pages34 Alcohols & Ethers - Problems For Practice - Level 1Abuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes & Ketones (Booklet-2Document15 pagesAldehydes & Ketones (Booklet-2kraken monsterNo ratings yet
- 655f0ac18d579400185b427d_##_Aromatic Compounds Questions Notes Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024Document58 pages655f0ac18d579400185b427d_##_Aromatic Compounds Questions Notes Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024sontygaming001No ratings yet
- C10 - HALOALKANES & HALOARENES (1) .9bd6790Document4 pagesC10 - HALOALKANES & HALOARENES (1) .9bd6790akashkishore363No ratings yet
- Nitrogen CompoundsDocument11 pagesNitrogen CompoundsJatindra PatelNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Q.p.set-1Document6 pages12 Chemistry Q.p.set-1HpNo ratings yet
- Exercise-01 Check Your Grasp: O CH HO HODocument7 pagesExercise-01 Check Your Grasp: O CH HO HOChesta MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon and Isomerism TestDocument6 pagesHydrocarbon and Isomerism TestveerlocusNo ratings yet
- Alkyl HalideDocument8 pagesAlkyl HalideMegh Raj BhattNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: Time: 90 Minutes Max. Marks: 35Document9 pagesSample Paper: Time: 90 Minutes Max. Marks: 35Harsh PatelNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document11 pagesSheet 1Zooper lNo ratings yet
- Alkanes - Alkenes - Alkynes - DPP 2Document3 pagesAlkanes - Alkenes - Alkynes - DPP 2Vishal_93No ratings yet
- MCQ Halo Alkanes and ArenesDocument27 pagesMCQ Halo Alkanes and ArenessarahNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Question Bank Class: Xii, Chemistry Unit 4: Haloalknaes & HaloarenesDocument27 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Question Bank Class: Xii, Chemistry Unit 4: Haloalknaes & HaloarenesAkshita BoroNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones - 3Document6 pagesAldehydes and Ketones - 3iitlectureNo ratings yet
- Quiz Organic 1Document6 pagesQuiz Organic 1ronakgupta332005No ratings yet
- Organic chemistry practice questionsDocument29 pagesOrganic chemistry practice questionsHet PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGENDocument6 pagesORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGENkavitha2511977No ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument22 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsBhavesh K100% (1)
- Aromatic Compound SheetDocument71 pagesAromatic Compound Sheetadityavaish739No ratings yet
- D Block Compounds12thDocument7 pagesD Block Compounds12thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- VampireRev4-Page Editable PDFDocument4 pagesVampireRev4-Page Editable PDFNicholas DoranNo ratings yet
- How To Write Field Notes Teaching Practice-I 8607 AIOU B.EdDocument2 pagesHow To Write Field Notes Teaching Practice-I 8607 AIOU B.EdMazhar ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Acros Organics Acta N°006Document20 pagesAcros Organics Acta N°006Atomer FormationNo ratings yet
- Shri Mata Vaishno Devi Shrine Board - Welcome To Online ServicesjjDocument2 pagesShri Mata Vaishno Devi Shrine Board - Welcome To Online Servicesjjeternal diagnosticsNo ratings yet
- Process Payments & ReceiptsDocument12 pagesProcess Payments & ReceiptsAnne FrondaNo ratings yet
- 342 Mechanical and Fluid Drive Maintenance Course DescriptionDocument2 pages342 Mechanical and Fluid Drive Maintenance Course Descriptionaa256850No ratings yet
- COPD medications and interventionsDocument34 pagesCOPD medications and interventionssaroberts2202100% (1)
- Weak Downlink Data for Multiple TRX Indices Over TimeDocument3,643 pagesWeak Downlink Data for Multiple TRX Indices Over TimeSK Basak BDNo ratings yet
- The Metacentric Height EX3Document3 pagesThe Metacentric Height EX3Edrees JamalNo ratings yet
- Master Gardener Home Vegetable Guide: Chapter 1 - Gardening BasicsDocument30 pagesMaster Gardener Home Vegetable Guide: Chapter 1 - Gardening BasicsAmr M. SaidNo ratings yet
- Duoc Dien Duoc Lieu Dai Loan - 3rd - 2019Document639 pagesDuoc Dien Duoc Lieu Dai Loan - 3rd - 2019Hương Nguyễn100% (1)
- Assessment of Fiber Optic Pressure Sensors: NUREG/CR-6312Document133 pagesAssessment of Fiber Optic Pressure Sensors: NUREG/CR-6312abhrajitsahaNo ratings yet
- Panjab University, Chandigarh: (Theory Examinations) TIME OF EXAMINATION: 9.30 A.M. To 12.30 P.MDocument3 pagesPanjab University, Chandigarh: (Theory Examinations) TIME OF EXAMINATION: 9.30 A.M. To 12.30 P.MManav ChhabraNo ratings yet
- 5 BFU 07406 Assessment of Credit ApplicationsDocument109 pages5 BFU 07406 Assessment of Credit ApplicationsDeogratias MsigalaNo ratings yet
- Dgca Da42 Exam PaperDocument7 pagesDgca Da42 Exam PaperDharmendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Selected Questions Revised 20200305 2HRDocument3 pagesSelected Questions Revised 20200305 2HRTimmy LeeNo ratings yet
- Barcelona Conferences Abstracts December 2016Document82 pagesBarcelona Conferences Abstracts December 2016Bahadır AkbalNo ratings yet
- Moral and Non Moral StandardsDocument6 pagesMoral and Non Moral StandardsGerry AbuanNo ratings yet
- 2018-03-23 Tier 25 Register of SponsorsDocument1,910 pages2018-03-23 Tier 25 Register of SponsorsAnonymous TjeiW5No ratings yet
- Virus Programming Basics 1 Hacking Virus Programming AsmDocument17 pagesVirus Programming Basics 1 Hacking Virus Programming AsmMegamozgNo ratings yet
- Zenith 19M20 Sams 259 16Document26 pagesZenith 19M20 Sams 259 16dds94No ratings yet
- Body in Movement - WorkshopDocument8 pagesBody in Movement - WorkshopAndrew CareyNo ratings yet
- Piping Colour Code Is 2379Document3 pagesPiping Colour Code Is 2379Yashpal Singh Ghaman100% (2)
- Jurnal SinusitisDocument49 pagesJurnal SinusitisAramanda Dian100% (1)
- Report On MinesDocument7 pagesReport On MinesYhaneNo ratings yet
- Chap3-2e SO2 Absorption ExampleDocument8 pagesChap3-2e SO2 Absorption Exampledarkelf_riderNo ratings yet
- Tracing Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Tsfunction Is Key To ME - CFS - B Day PDFDocument91 pagesTracing Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Tsfunction Is Key To ME - CFS - B Day PDFsanthigiNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument7 pagesReadmeLogan SilvaNo ratings yet
- Lippo Karawaci Review 30 September 2019 FINAL PDFDocument149 pagesLippo Karawaci Review 30 September 2019 FINAL PDFAndy AghastaNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and Student Relationship of Haydn and BeethovenDocument10 pagesThe Teacher and Student Relationship of Haydn and BeethovenVinny MuscarellaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Meltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalFrom EverandMeltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsFrom EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Gas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsFrom EverandGas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Chemistry: 1001 Practice Problems For Dummies (+ Free Online Practice)From EverandChemistry: 1001 Practice Problems For Dummies (+ Free Online Practice)No ratings yet
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Transformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathFrom EverandTransformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Guidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsFrom EverandGuidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- Stuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials That Shape Our Man-Made WorldFrom EverandStuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials That Shape Our Man-Made WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (289)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodFrom EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (20)