Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handwritten Lympathic - Functions & Structures The Lymphatic System Transports Fluids To Blood - Studocu
Uploaded by
Allyssa MarieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Handwritten Lympathic - Functions & Structures The Lymphatic System Transports Fluids To Blood - Studocu
Uploaded by
Allyssa MarieCopyright:
Available Formats
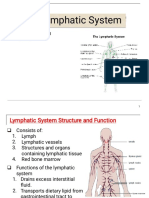
lymphatic
Functions & Structures
The lymphatic system transports ßuids to blood and acts as the bodies defence mechanism and
Þght against disease. It soaks up extra tissue ßuid and returns it back into the bloodstream. Fat-
glycerol and fatty acids are absorbed by lymphatic system maintains, creates and dispense
lymphocytes (T + B cells) which help protect the body against pathogens.
What are the structures?
1. Lymph nodes & vessels: Protect the body from foreign objects by removing pathogen like
bacteria
2. Lymph: It is made up of hormones, carbon dioxide, lymphocytes, metabolic waste, water,
nutrients and salts
3. Spleen: Its job is to Þlter the blood of viruses and bacteria, while destroying worn out red
blood cells, create blood in gestation and provide storage for blood
4. Tonsils: Catch and get rid of waste and foreign substances near the pharynx
5. Thymus: It highly functions only during childhood and site of maturing T-cells
Each lymph has 3 regions: Lymphatic Vessels
1. Cortical zone: lies at the periphery below the capsule Endothelial cells form overlapping
2. Medullary zone: lies in the central part of the lymph node one-way valves that allow entry of
3. Paracortical or juxtamedullary or deep cortex : lies ßuids and solutes but proven their
between the outer cortex & inner medulla return to the inner cellular spaces
formed from merging capillaries.
Lymphatic Ducts & Drainage Lymphatic capillaries are tiny, thin
The two main types of lymphocytes are T and B cells. The walled very permeable micro-
main purpose in the body is to Þght infections. There are vessels which is located in spaces
many lymphatic ducts in the body. The thoracic duct is between cells .
MBÖ
located near the cisterna chyli and drains the rest of the
body. The right lymphatic duct drains the upper right
:
arm and the right side of the cephalic and thorax. Adenoids
Meanwhile, both the thoracic duct and the right Tonsils
lymphatic duct empties lymph drainage into the venous
amMF¥ a wm¥
circulation by the jugular and subclavian veins on each
side of the body. Contractions of smooth muscles in the
walls of the lymphatics is how the body drains itself.
MkBmH¥
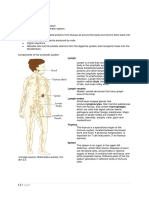
How does the body protect itself? Thymus
www.
Axillary
The lymphatic system protects our body through lymph
immunity! Bronchus nodes
Adaptive Immunity: It is the bodyÕs 3rd line of defence. associated
There are 2 types of adaptive immunity, these are cell- lymphoid
mediated and antibody-mediated (humoral) Spleen
tissues
1. Antibody-mediated Immunity: Involves the activation
of B cells and secretion of antibodies when in contact
with a pathogen. When exposed to the chemicals Intestine
released by activated helper T cells, a sensitized B cell Peters
divides, producing daughter cells that differentiate into patches
memory B cells and plasma cells. Appendix
2. Cell-mediated immunity: It allows adoption and Bone morrow Inguinal
formation of cytotoxic T cells which Þght against cancer lymph node
cells, foreign object transplant and pathogens.
You might also like
- IT ParksDocument12 pagesIT ParksDivam Goyal0% (1)
- John Stossel - Myths, Lies and Downright Stupidity - Get Out The Shovel - Why Everything You Know Is Wrong-Hyperion (2007) PDFDocument321 pagesJohn Stossel - Myths, Lies and Downright Stupidity - Get Out The Shovel - Why Everything You Know Is Wrong-Hyperion (2007) PDFdiegohrey239No ratings yet
- Immune System Docs 2019Document13 pagesImmune System Docs 2019David DavidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010Document85 pagesChapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010TofikNo ratings yet
- Unit-IXLymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology.Document9 pagesUnit-IXLymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology.Rao Asad MubeenNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Immune SystemDocument19 pagesOrgans of The Immune SystemprabuNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 pagesLymphatic SystemBasant karn100% (6)
- Basic Immunology PDFDocument6 pagesBasic Immunology PDFAnastasia ENo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Function of Lymphoid Tissues: Wesam Mohammed EmharibDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Function of Lymphoid Tissues: Wesam Mohammed Emharibنسيم حامدNo ratings yet
- Lymphatics - Immunity Lec Notes - With PicsDocument14 pagesLymphatics - Immunity Lec Notes - With PicsEdgar MartínezNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: Jeezreel M. Orquina, RN, LPTDocument18 pagesLymphatic System: Jeezreel M. Orquina, RN, LPTJezreel OrquinaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument17 pagesLymphatic SystemxoxoNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and Immunity: Student Learning OutcomesDocument8 pagesLymphatic System and Immunity: Student Learning Outcomeslily1liang-1No ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument18 pagesLymphatic SystemAlliyah SalindoNo ratings yet
- Lymph NodeDocument13 pagesLymph NodeNurul Ilma AllauwNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument28 pagesLymphatic Systemdeepika kushwahNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesLymphatic System Anatomy and PhysiologyElyka Alivan Valdez Polonio100% (1)
- WEEK 1 - Chapter 16 - Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocument59 pagesWEEK 1 - Chapter 16 - Lymphatic System and ImmunityOliver Namyalo100% (1)
- Lymphatic System For Medical StudentsDocument18 pagesLymphatic System For Medical StudentsTriza JeremiahNo ratings yet
- 12SUMMARYLYMPHATICSYSTEMDocument20 pages12SUMMARYLYMPHATICSYSTEMArvenBitasNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 pagesLymphatic SystemAlyssa Mae AzarconNo ratings yet
- Lymphoid and Immune Systems: Department of Histology FK UNSRIDocument59 pagesLymphoid and Immune Systems: Department of Histology FK UNSRIMuhammad Ali Ridho ShahabNo ratings yet
- Immuno Notes LectureDocument30 pagesImmuno Notes LectureSteph TabasaNo ratings yet
- 08 - Lymphatic SystemDocument19 pages08 - Lymphatic SystemDanielSenpai69No ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System Notes StudentDocument7 pagesThe Lymphatic System Notes Studentapi-655732711No ratings yet
- Powerlecture: ImmunityDocument107 pagesPowerlecture: Immunitymr. nicartNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic and Immune SystemDocument12 pagesThe Lymphatic and Immune SystemAthena Huynh100% (1)
- 08 - Lymphatic SystemDocument19 pages08 - Lymphatic SystemKonstantinos KosmidisNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Lymphatic SystemDocument7 pagesModule 7 Lymphatic SystemWai KikiNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: Prof. Shekhar TeliDocument19 pagesLymphatic System: Prof. Shekhar TeliShekhar TeliNo ratings yet
- Limfatic Sistem - TortoraDocument17 pagesLimfatic Sistem - TortoraAghata ZahraNo ratings yet
- LymphDocument11 pagesLymphDeshmukh KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic - StudentDocument9 pagesLymphatic - StudentLeslie CuevasNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System and Immunity by Navarro and Orjalo BS Psy 3 1Document27 pagesThe Lymphatic System and Immunity by Navarro and Orjalo BS Psy 3 1markNo ratings yet
- Functions of Immune SystemDocument6 pagesFunctions of Immune Systemanna jean oliquianoNo ratings yet
- BIOL25441 Class 5 and 6 Winter 2013Document58 pagesBIOL25441 Class 5 and 6 Winter 2013raunak .comNo ratings yet
- VIIII Lymphatic SystemDocument23 pagesVIIII Lymphatic SystemHannah DiñosoNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsDocument35 pagesLymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsAlyssum MarieNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic & Body DefensesDocument11 pagesLymphatic & Body DefensesJeah LourraineNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System NotesDocument7 pagesLymphatic System NotesNahid ParveenNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument20 pagesLymphatic SystemROSE ANN JAWADNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Immune System and Lymphatic SystemDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Immune System and Lymphatic SystemSnehjyoti JhaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocument4 pagesLymphatic System and ImmunityBlessed May PastranaNo ratings yet
- Functions:: Four Functions of SpleenDocument5 pagesFunctions:: Four Functions of SpleenRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Reticuloendothelial SystemDocument26 pagesReticuloendothelial SystemNashreen QtqtNo ratings yet
- Primary or Central 33Document23 pagesPrimary or Central 33Mahesh DevarintiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 14 Lymphatic SystemDivinefavourNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument12 pagesLymphatic SystemMyat NyanNo ratings yet
- HSP2 Topic 5 (Anatomy & Physiology of Immune System)Document52 pagesHSP2 Topic 5 (Anatomy & Physiology of Immune System)gilliansong17No ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument10 pagesLymphatic SystemPasipanodya MuzendaNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument21 pagesImmune SystemAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument24 pagesLymphatic SystemjabirNo ratings yet
- What Is/are The Most Abundant Connective Tissue Cells Present in The Stroma?Document3 pagesWhat Is/are The Most Abundant Connective Tissue Cells Present in The Stroma?yumie dimaculanganNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocument5 pagesLymphatic System and ImmunityMaria Teresita NuescaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument3 pagesLymphatic Systempierre TritzNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument17 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemIzza Javaid100% (1)
- Chapter 22 Summary Chapter 22 SummaryDocument13 pagesChapter 22 Summary Chapter 22 SummarytinecastilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Immune SystemDocument37 pagesLesson Plan - Immune Systemsonyblank0% (1)
- Immune Response and The Role of Lymphatic SystemDocument6 pagesImmune Response and The Role of Lymphatic SystemchiomasingsNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Lymphatic and Immune SystemDocument27 pagesHistology of The Lymphatic and Immune Systemirakozehugue14No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Empson Peacock AngelDocument274 pagesEmpson Peacock AngelV.F.No ratings yet
- Courtney Loper-ResumeDocument2 pagesCourtney Loper-Resumeapi-354618234No ratings yet
- Gender Inequality in Bangladesh PDFDocument20 pagesGender Inequality in Bangladesh PDFshakilnaimaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science & Sustainability Unit-2 ISO 14001 & Environmental Management System (EMS)Document47 pagesEnvironmental Science & Sustainability Unit-2 ISO 14001 & Environmental Management System (EMS)Vani SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Foundations of American DemocracyDocument9 pagesUnit 1 - Foundations of American DemocracybanaffiferNo ratings yet
- Jewish Standard, December 18, 2015Document64 pagesJewish Standard, December 18, 2015New Jersey Jewish StandardNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management (Pertemuan V)Document85 pagesInventory Management (Pertemuan V)Asep RahmatullahNo ratings yet
- Action Plan in Edukasyong Pantahanan at Pangkabuhayan School Year 2017-2018Document3 pagesAction Plan in Edukasyong Pantahanan at Pangkabuhayan School Year 2017-2018MERLINDA PACQUIAONo ratings yet
- PGL-Lesson 76-80Document18 pagesPGL-Lesson 76-80Jomabelle UbaldoNo ratings yet
- SlumsDocument6 pagesSlumsRidhima Ganotra100% (1)
- Resolution No. 1433Document2 pagesResolution No. 1433MA. DIVINA LAPURANo ratings yet
- Mindset Development Organisation Annual Report 2012Document29 pagesMindset Development Organisation Annual Report 2012chenyi55253779No ratings yet
- BYD Case StudyDocument12 pagesBYD Case StudyELIZANo ratings yet
- BankingDocument50 pagesBankingKishore MallarapuNo ratings yet
- How To Write SpecificationsDocument9 pagesHow To Write SpecificationsLeilani ManalaysayNo ratings yet
- Sample Activity ReportDocument2 pagesSample Activity ReportKatrina CalacatNo ratings yet
- Outcomes of Democracy: How Do We Assess Democracy?Document7 pagesOutcomes of Democracy: How Do We Assess Democracy?Ankita MondalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Chapter 2Document20 pagesUnit 2 - Chapter 2Dennise Kate CabiedesNo ratings yet
- Kitty GenoveseDocument2 pagesKitty GenoveseRachael BartlettNo ratings yet
- Stop TB Text Only 2012Document30 pagesStop TB Text Only 2012Ga B B OrlonganNo ratings yet
- Appellate BriefDocument3 pagesAppellate Briefelan de noir100% (1)
- Sustainable Development - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument22 pagesSustainable Development - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaŚáńtőśh Mőkáśhí100% (1)
- 01-14 STP RSTP ConfigurationDocument67 pages01-14 STP RSTP ConfigurationKiKi MaNo ratings yet
- Abhimanshree SampleDocument4 pagesAbhimanshree SampleMandar KurkureNo ratings yet
- Answers To Workbook Exercises: Cambridge University Press 2014Document3 pagesAnswers To Workbook Exercises: Cambridge University Press 2014M BNo ratings yet
- Induction and Training Road-Map: GenpactDocument27 pagesInduction and Training Road-Map: GenpactShrey KanungoNo ratings yet
- HarshadDocument61 pagesHarshadsaurabh deshmukhNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Mathematics (Honours and Regular) : Submitted ToDocument19 pagesSyllabus Mathematics (Honours and Regular) : Submitted ToDebasish SharmaNo ratings yet