Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nikita Project 1-1
Uploaded by
swatitankasaliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nikita Project 1-1
Uploaded by
swatitankasaliCopyright:
Available Formats
B.V.V.
SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
JYOTHI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT.,MUDHOL.
A co-operative society is often a voluntary association of individuals who come together with the
intention to work together and to promote their economic interest. These societies work on the principle
of self-help as well as mutual help. The primary goal is to provide support to the members.
Cooperative banking refers to a small financial institution started by a group of individuals to address the
capital needs of their specific community. Such financial institutions are owned and controlled by their
members, and the board members are democratically selected to oversee the operations
The supervisory committee is charged with the responsibility of supervising or over sighting all the
operations of the society at all levels. This is a responsibility accorded to them by the members. The
supervisory committee being briefed of their roles and trained by the sub county cooperative officer in
addition an internal auditor is attached to them. They have express authority to access all sections of the
society. The Management committee BOD, directs the affairs of the cooperative. The fourth organ is the
management team that is hired as a team of professionals to run the affairs of the cooperative on a day to
day basis and on behalf of the board of directors.
An Organizational Profile Is a framework for understanding the internal and external factors that shape
the operating environment of a business and affect the business decisions made.
It aims to evaluate whether the national legislation in place supports or hampers the development of
cooperatives, and is, therefore “cooperative friendly” or not, and the degree to which it may be considered
so, also in comparison to the legislation in force in other countries of the ICA region, or at the
supranational level.
In addition, the research aims to provide recommendations for eventual renewal of the legal frameworks
in place in order to understand what changes in the current legislation would be necessary to improve its
degree of “cooperative friendliness”, which is to say, to make the legislation more favourable to
cooperatives, also in consideration of their specific identity. This webpage presents a snapshot of the legal
framework analysis results for India.
SOCIETY PROFILE:
Name : Jyothi co-operative credit society nyt., mudhol
TQ : Mudhol.
Dist : Bagalkot.
Establishment: December 14, 1990
Status of Society: Credit can have a legal status either as a Co-operative.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 1 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
Society with limited or unlimited liability. As an economic
interest grouping or as a joint-stock company.
Specialities. : providing loans.
Helping the small business holders like provide loans.
HISTORY :
HISTORY OF JYOTHI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL
The banking system is an integral part of the financial sector of our country. Therefore, the role
of banking in our economy must be seen in the context of its fundamental role in the entire
financial sector. The financial sector plays a major role in mobilization and allocation of savings.
Financial institutions, instrument and markets which constitutes the financial sector act as
aconduit for the transfer of financial resources from net savers to the net borrowers, i.e.
From those who spend less than they earn more than they spend. The financial sector performs
the basic economic function of intermediation essentially through four transformation
mechanisms.
Liability asset transformation: It means that accepting deposits as a liability and converting them
in to assets such as loans
Size transformation: i.e. providing large loans on the basis of assorted large medium and small
deposits.
Maturity transformation: i.e. offering savers deposits according to their liability preferences
while providing borrowers with loans of required maturities.
SPECIALITIES :
According to Calvert, “Co-operation is a specialized form of economic organization in which
people voluntarily associate together on a basis of equality for the promotion of their common
economic interests”.
A Co-operative Society is an enterprise formed and directed by an association of users, applying
within itself, the rules of democracy, and directly intended to serve both its own members and
the community as a whole – Lambert.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 2 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
A co-operative society is a special type of business organization different from other forms of
organization.
Specialities:
• To promote economic interests of the members in accordance with the co-operative
principles;
• To provide short and medium term loans;
• To promote savings habit among members;
• To supply agricultural inputs like fertilizers, seeds, insecticides and implements; • To
provide marketing facilities for the sale of agricultural produces; and
• To supply domestic products requirements such as sugar, kerosene, etc.
All agriculturists, agricultural labourers, artisans and small traders in the villages can become
members of the society.
1. Minimum short-term loan of Rs.2 lakhs for a society to become a viable unit.
2. Coverage of villages with a gross cropped area of 2000 ha to achieve this level of
business.
3. Appointment of a suitably trained full – time paid secretary to manage its affairs.
The National Bank has formulated a scheme known as instant fresh finance scheme during
1988-89 to issue timely fresh credit to those members of PACS who have repaid their early dues.
This policy improvement should go a long way to build confidence of the members in their
cooperative society as no member was allowed fresh loan irrespective of whether he has paid or
not repaid the loan when the society as such was declared ineligible for fresh financing.
The major functions of CCB / DCCBs are:
To meet the credit requirements of member societies;
To perform banking business; to act as balancing centres for the PACS by diverting the surplus
funds of some societies to those which face shortage of funds;
• To guide and supervise the PACS; and
• To undertake non-credit activities.
• The area of operation is generally a district.
BOARD OF DIRECTORS OF CREDIT CO-OPERATIVE SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL
Cooperative boards of directors can be made up of representatives from each member entity,
creating a situation almost resembling a congressional body. Having a representative from each
organization on the board of directors of a cooperative ensures that each company has a voice in
strategic decision-making. This can ease relations between members of a co-op, which may have
been direct competitors before entering into the partnership. Because of this, nonprofit board
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 3 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
members almost have to play the role of politicians as well as business leaders, keeping relations
smooth between all of the member entities.
A board of directors in a cooperative functions as a policy-making body when it comes to big
picture issues such as financial responsibility, equal employment opportunity issues, compliance
with applicable legal guidelines and the co-op’s business dealings with its own members. Board
members also create policies governing the appointment and duties of board officers, including
the board president, secretary and treasurer. The board may set specific guidelines for hiring
practices to ensure compliance with EEO laws, for example, or may set policies regarding
executive compensation.
Financial Functions
Cooperative boards of directors are actively involved in the budgeting and financial reporting
processes of the organizations they oversee. Board members function as intermediaries between
the organization and external stakeholders at annual meetings, press conferences and public
relations events, as well as setting financial goals for co-op managers to reach for. In this way,
board members function as the face of the cooperative when dealing with the public and
potential investors.
The Board Meeting Is convened once in a month. The Executive Committee Meeting is
convened once a month.
In addition, we are also having Sub Committees consisting of Board of Directors in each
Committee to monitor the functions of the Bank and District Central Cooperative society .
BOARD OF DIRECTORS OF JYOTHI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT.,
MUDHOL
1. Shri.Nigappa .H. Hallad-chairman.
2. Shri. Chandrashekar .S. Gaddi – Vice Chairman.
3. Shri. Hanamanth. L. Malligeri -Director.
4. Shri. Bhimappa. Basavantappa. Tolamatti – Director.
5. Shri. Bhimappa. Shivalingappa. Kavatagi – Director.
6. Shri. Basavaraj. Mallappa. Dollashetty – Director.
7. Shri. Shivappa. Girimallappa. Utagai – Director.
8. Shri. Basavaraj. Shadashiv. Gantanti – Director.
9. Shri. Satish. Dundappa. Iynapur – Director.
PROCEDURE OF THE INTERNAL CHECK:
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 4 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
Meaning: An internal check is a continuous process of the accounting system to check for errors
or fraud in bookkeeping operations for early detection and prevention. The internal check is an
arrangement of the duties of the staff members of the accounting functions in such a way that
another automatically checks the work performed by a person.
In the opinion of Spicer and Pegler, “A system of internal check is an arrangement of staff duties,
whereby no one person is allowed to carry through and to record every aspect of a transaction so
that without collusion between two or more persons, fraud is activated and at the same time the
possibilities of errors are reduced to the minimum”.
L.R. Dicksee defines an internal check as “an arrangement of book-keeping routine that errors
and frauds are likely to be prevented or discovered by the very operation of the book-keeping
itself.”
Internal check means a continuous internal audit carried on by the staff, using which other staff
members independently check each individual’s work.
Characteristics of internal check:
8 qualities make an internal check system more effective and efficient.
1. Division of Work
2. Provision of Check
3. Use of Devices
4. Self-balancing System
5. Job Rotation
6. Specialization
7. Control
Division of Work
No one should be allowed to have the right to perform the work from origin to end.
For example – a transaction of sale may have to be split into a display of article by staff, the
preparation of invoice by another, the receipt of cash against the invoice by a third clerk, the
delivery of article against the proof of receipted invoice by another clerk, checking of outward
movement of an article against delivery order by a clerk and so on.
In big business houses, such specialized tasks increase work speed and automatically introduce
internal checks.
Provision of Check
An organization should set up such provisions so that work can be checked by other staff. An
officer can check the work of one staff by transferring to the staff and again.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 5 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
Use of Devices In this modem world, various devices can perform various functions like time
record machines, wage determination machines, etc. An organization should use machines that
help to make the work of internal checks easier.
Self-balancing System
An organization can use self-balancing ledger accounts, which help to make the work of internal
checks easier. Its effectiveness depends on its management.
Job Rotation
No individual clerk should be allowed to occupy a particular area of operation for long.
Familiarity with and exclusiveness in a position offer a person greater flexibility to attempt
manipulation with the system.
Specialization
Every staff may not have such specialized knowledge to maintain accounts properly. So, an
organization should give training to increase their skills so that internal checks can be made
more effective.
Control
There is more chance of fraud where there is direct contact between consumers or the public. So,
a manager can keep an eye on those works so that the internal check system can be more
effective.
Authority Level
There must be clear-cut authority levels according to sanctions for various transactions.
Commensurate to the authority vested, responsibility must be extracted. The existence of
authority levels results in a review of the operations of subordinates.
Objectives of Internal Check:
There are several objectives of the internal check. They are given below:
• To minimize the possibility of error, fraud, and irregularity.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 6 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
• To prevent the misappropriation of cash and goods.
• To allocate duties and responsibilities to every clerk in the organization.
• To ensure an accurate recording of all business transactions.
• To enhance the efficiency of the clerk in the organization.
• To exercise moral influence over the staff member.
• To prepare a final account with ease and efficiency.
Principles of Internal Check:
1. An internal check is based on some specific principles. Without which, an internal check
is of no use. These principles are given below:
2. The business staff should allocate the process according to the duties, responsibilities,
and rights. There is no room for interference.
3. No single person should have independent control over the all-important aspects of the
business.
4. The duties among the business staff should be changed from time to time so that no staff
should be engaged in a particular job for a long time.
5. Every staff member should be encouraged to go on leave at least once a year. This will
help in detecting concealed fraud.
Advantages of internal check;
• Moral Influence on Employees
• Determination of Employees’ Liability
• Less Possibility of Frauds
• Increase in Efficiency
• Auditing Made Easy
• Final Accounts Can Be Prepared
• Correct and Complete Records of all the Transactions
• Detection of Dishonesty or Irregularity
• Test Checking Possible
Less Possibility of Frauds:
There is less possibility of fraud under the system of the internal check because errors and frauds
can be detected early.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 7 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
Increase in Efficiency:
The internal checks ensure greater .efficiency and speed because the arrangement of internal
checks is based on a division of labour.
Auditing Made Easy :
The internal checks system facilitates auditors’ work to a great extent by enabling them to rely
on test checking.
Final Accounts Can Be Prepared :
In an internal check system, the ‘Profit and Loss Account’ and Balance Sheet is prepared without
any loss of time.
Correct and Complete Records of all the Transactions :
The system of an internal check may also result in correct and complete records of all the
transactions on each balancing of the books of accounts.
Detection of Dishonesty or Irregularity :
Any dishonesty or irregularity in the concern by the staff members can be detected before they
assume any complication.
Test Checking Possible :
Suppose the auditor finds the system of internal cheek satisfactory. Then by considering defects
or weak points, he can take the help of test checking.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 8 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
Disadvantages of Internal Check:
• Expensive
• Slackness in the Work
• Not Suitable for Small Concerns
• Grouping among Employees
• Expensive
• The system of Internal checks is more expensive and time-consuming.
Slackness in the Work
The auditor may show slackness at work. He may rely on the system of internal check
blindfolds, which may adversely affect the quality of audit work. This is also a serious defect of
the system of internal checks.
Not Suitable for Small Concerns
The system of internal checks is not suitable for small concerns as it may be uneconomical in
small concerns.
Grouping among Employees
If the concerned employees join hands, they may keep the employer in the dark and may cause
many irregularities defying any detection thereof. This grouping amongst the employees may not
be healthy.
Despite these four disadvantages, performing internal checks is crucial for all types of
organizations. Internal auditors are responsible for conducting internal checks and audits.
With a clear understanding of internal check; for more learning use our complete guideline on
fundamentals of management, auditing and strategic management.
Objectives Of Internal Check
Following are the main objectives of Internal Check –
To protect business from carelessness, inefficiency and fraud.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 9 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
• To ensure and produce adequate and reliable accounting information.
• To keep moral pressure over staff.
• To minimize the chances of errors and frauds and to detect them easily on early stage if it
is committed.
• To divide the work in such a way that no business transaction should be left unrecorded.
• To fix the responsibility of every clerk according to the division of work.
Internal Check as regards certain transactions
A. Cash Receipts
1. The correspondence like inward mails and remittances should be handled by some
responsible official.
2. There should be a separate clerk, known as cashier, to deal with cash receipts.
3. The cashier should not have access to the books of account.
4. Pre-numbered and pre-printed receipt book should be used for all cash collections.
5. All cash receipts should be deposited in the bank on daily basis through pay-in slips.
B. Cash Sales: Sales at the Counter
• The salesman, authorized to sell the goods at the counter, should be specifically named. A
specific number should be allocated to every salesman.
• Cash memos shall be printed in numerical sequence.
• The salesman sells goods to the customer and prepares four copies of cash memo, three
of them handed over to customer and one is retained by him.
• The customer will carry all the three copies to the cashier. After collecting the cash, the
cashier will return two copies to the customer, duly stamp marked as cash paid.
• Goods are handed over to the customer by gatekeeper and one copy of cash memo is
retained by the gatekeeper and the other one will remain with the customer.
• At the end of the day, salesman – cashier – gatekeeper prepares the summaries of cash,
sales separately and then they reconcile it, for any difference.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 10 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
The amount received from the cash sales should be deposited daily in the bank.
C. Cash Sales: Sales by Travelling Salesman/Agents
In some of the organizations, travelling salesman is appointed for direct sales promotion
and collection. In such a case, the internal check system should be:
• The salesman should be authorized to issue money receipts.
• They should deposit the entire cash collection daily to the cashier or to the bank account
of the company.
• The salesman should submit the daily report of sales and collection.
• The salesman should not keep any cash with him.
• No cash collection should remain outstanding.
• If possible, the salesman should be transferred from one area to another to avoid the
frauds.
Credit Sales
• The sales department receives a purchase order from the customer. On receipt of the
order, it should be numbered and preserved in the order received book.
• Before the sales orders are processed, credit department should determine the credit
worthiness of the customers.
• The dispatch department should be given a copy of order.
• The storekeeper who maintains custody over the inventory should issues goods to the
dispatch department.
• The statement of goods prepared by dispatch department should be checked with
customers’ order and then invoice should be prepared. The invoices are checked by a
responsible official.
• On dispatch of goods, outward note is prepared. Entries are made in the dispatch
register and sales book.
Purchases
• The department who is in need of material, should fill in the requisition slip duly signed
and shall send it to purchase department.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 11 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
• The purchase department should make an enquiry about the terms and conditions of
purchases from different suppliers on the basis of tenders and quotations.
• The purchase department should place the purchase order. Four copies of purchase order
are prepared. One is sent to the vendor, second to the stores department, third to the
accounting department and fourth is kept by the purchase department with itself.
On receipt of goods, they are properly inspected and entries are made in the goods inward
register.
• The purchase department should check the invoice and send the same to the accounting
department for payment.
• For the goods returned to the supplier entries should be made in the Purchase Return
Book and a debit note is issued to the supplier.
Cash Purchases
The purchase order should be prepared on the basis of purchase requisition duly authorized
by a competent official.
(i) The terms and conditions of purchase should be decided on the basis
of comparative tenders and quotations.
(ii) The materials purchased should be verified as regards quantity and
quality by the person independent of purchase department and store
department.
(iii) The purchase-invoice should be verified with purchase order and
goods received note.
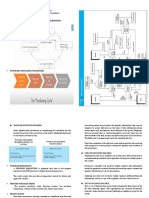
AUDIT PROCEDURE OF JYOTHI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT
SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL:
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 12 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
Meaning: Is review of operations and records undertaken within a business by internal staff
or outside agency specially deputed for this purpose. This review may be periodic or continuous.
It is an important tool in the hands of management. It is a type of control which functions by
evaluating the effectiveness of other types of controls.
Applicability of Internal Audit:
As per the Companies Act 2013, following class of companies shall have to mandatorily appoint
internal auditor.
• Every Listed Company
• Every Unlisted public company if during the preceding financial year, it satisfies any of
the below mentioned conditions:
1. Turnover of rupees two hundred crore or more.
2. Paid up share capital of rupees fifty crore or more.
3. Outstanding loans or borrowings from banks or PFI exceeding rupees one hundred crore
or more at any point of time.
4. Outstanding deposits of rupees twenty five crore or more at any point of time.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 13 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
Responsibilities of an Internal Auditor
• Always enjoy an independent status and shall not involve in the performance of executive
function.
Analyze the risk and bring them in the notice of management.
• Analyze the operations of the entity and maintain an adequate system of internal control,
also provide safeguard. Against misappropriation of assets.
• Evaluate the policies of organization and made necessary changes on it, if required.
• Keep an eye on all all important occurrences and events which may affect the business.
• Shall not take operation decision on those matters later which may be internal audit.
Skills Possessed by an Internal Auditor
• An internal auditor must possess an expertise necessary to evaluate the management
control system.
• An internal auditor must have a basic knowledge about the technology and commercial
practices followed by the entity. So, that he can evaluate the operational performance and
non-monetary, operational controls.
• An internal auditor must possess knowledge of commerce, laws, taxation, cost
accounting, economics, quantitative methods and ERP systems.
• He has an ability to deal with people and an understanding of management principles and
techniques.
• He should maintain the confidentiality of such information which he acquired during the
course of audit.
Report of Internal Auditor
• The Internal Auditor shall issue their report on the basis of his best professional
judgement, after consultation with the auditee, in a reasonable period of time from the
completion of audit. Key elements of internal audit report are as follows:
• Conclusion of internal audit report should be on the basis of audit procedures performed
during the audit and the analysis of the audit evidence obtained by performing these
procedures.
• If internal audit is performed as per Standards on Internal Audit then the auditor shall
specify the same in his report.
• Since the Standards on Auditing does not mandate the auditor to follow a particular
format. So, an auditor may frame his report by exercising professional judgement and
may be influenced by the preferences of the recipients.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 14 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
• After fulfillment of all the compliance procedure Copies of draft and final internal audit
reports to should be maintained in a proper manner.
Scope and Objectives
• To review the internal control system.
• To review the custodianship and safeguarding of assets.
• To review the compliance with plans, policies, procedures and regulations.
• To review the relevance and reliability of information.
• To review the utilization of resources.
• To review the accomplishment of goals and objectives.
Importance
Internal Audit is not compulsory under any statute; so, usually, only the large-scale organizations
used to get internal audit done. However, these days the concept of internal audit is gaining
significance because of the following reasons :
1. According to Companies Audit Report Order, 2003, in case of specified companies, the
statutory auditor is required to report whether internal audit system of the company
commensurate with the size and nature of the business. Specified company means a
company whose paid up capital and reserves exceed ` 50 lakhs or whose average annual
turnover for the last three financial years preceding the current financial year exceed ` 5
crores.
2. Internal audit as per section 138 of the Companies Act, 2013 is mandatory for every listed
public company and other public companies with a paid up share capital of ` 50 crores or
more. The Act also makes internal audit mandatory for all companies including private
companies with an annual turnover of ` 200 crores or more, or outstanding loans or
borrowings from banks or public financial institutions exceeding ` 100 crore.
Appointment of Auditor
The appointment of an Auditor is done by Registrar of Co-operative Societies. The Auditor
conducts his audit on behalf of the Registrar. The Audit fees is paid by co-operative society
according to the statutory scale of fees prescribed by the Registrar in this regard according to the
category of society. The Auditor is required to submit his audit report directly to the Registrar
and one copy of the audit report is submitted to the concerned society. Rights of an Auditor
• As per Section 17, an Auditor can access all the books, accounts, documents and
securities of the society.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 15 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
• He has to see that Balance-sheet of the society shows a true and fair view of a business
according to information and explanation given to him.
• Every officer of the society is bound to give all information regarding working and
transactions of the society.
Duties of An Auditor
• An Auditor needs to consider the following points to be able to perform his duties in an
efficient way –
• An Auditor should be well-versed with the Co-operative Society Act, 1912 and the
bylaws of the society.
• If there is any type of irregularities and improprieties found by an Auditor during his
audit regarding Co-operative Societies Act, 1912 and by-laws, he should immediately
point out the same.
• An Auditor should ascertain that how many shares are held by each member of the
society; for this, he should check the member ship registers.
• An Auditor should be well aware of power of officers regarding loan, investment,
borrowings, advancing of the funds.
• He should thoroughly check and vouch the cash book and bank book.
• An Auditor should check all the receipts and payments of the society according to
standard auditing practice.
• An Auditor should physically examine and verify the assets of a society.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 16 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
• He should adopt different methods for different kind of societies.
• Balance-sheet, profit and loss account and Auditor report should be according to the
proforma given by the Chief Auditor of the Co-operative Society of the State.
• Accounts should be according to the Co-operative Society Act and also with the
provision of Income Tax Act.
(JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL.)
(Some specialities of Jyothi co-operative credit society nyt., Mudhol)
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 17 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
1. Providing the agriculture loan.
2. Providing the loans in the least rate of interest
3. Loans for animal husbandry.
4. Providing the firtilizers to the handicapped persons.
5. Death compensation.
6. Financial support to handicapped persons.
7. Employment opportunities for women.
8. Pigmy loans.
9. Helps through the yashaswini cards.
10. Providing the financial support to the window women.
11. It helps to overcome the constraints of agricultural development.
12. Provides agricultural credits and funds where state and private sectors
have not been able to do very much.
13. Providing the agriculture loan
14. To spread light of education among the children belong to destitute
families.
15. Advocacy programme on social issues.
Features of Credit Co-op Society:
• As it is voluntary association, the membership is also voluntary.
• It is compulsory for the co-operative society to get registration.
• It does not get affected by the entry or exit of it’s members.
• There is limited liability of the members of co-operative society Benefits of Farmers:
• Ownership and democratic control
• Increased farm income
• Improved service
• Quality of supplies and products
• Assured sources of supplies
• Enhanced competition
• Expanded market’s
• Improved farm management
Farmers who are efficiently organized can from a collection voice to advocate for their needs and
access services at more affordable prices that can help them increase yields, sales and
profits.producer organizations could achieve competitiveness for smallholder farmers.
Auditing process of credit co-operative society, mudhol :
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 18 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
4 stages as followed this society.
1. Planning
2. Field work
3. Audit report
4. Audit follow up
Planning: announcement letter, meeting, preliminary survey, internal control review, audit
programme.
Filed work: Transaction testing, Advice & Informal communication. Audit summary. Working
papers.
Audit report: Discussion, Formal draft, final report, client response, client comments,
Audit follow up: Follow -up review, Report, Audit annual report to the board.
Procedure of the internal check of credit co-operative society, mudhol :
Internal check as such an arrangement of book keeping routine that errors & frouds are likely to
be prevented or discovered by the very operation of the book keeping itself.
Objectives of internal check:
• To eliminate the acts of frouds & error.
• To fix up responsibility of each person.
• To prevent misappropriation of goods & cash.
• To detect frouds & errors immediately.
• To exercise moral influence on the auditor.
• To expenditure to work of employees.
• To simplify the work of the auditor.
• To increase the efficiency of employees.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 19 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
(Discussion to the audit process)
Cash Receipts:
1. The correspondence like inward mails and remittances should be handled by some
responsible official.
2. There should be a separate clerk, known as cashier, to deal with cash receipts.
3. The cashier should not have access to the books of account.
4. Pre-numbered and pre-printed receipt book should be used for all cash collections.
5. All cash receipts should be deposited in the bank on daily basis through pay-in slips.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 20 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
6. Bank pay-in slips should not be prepared by the same person who is in charge of making
actual deposits in bank.
7. Counterfoils of receipts issued should be preserved.
8. Cancellation of spoiled receipts (not to be torn off).
9. Safe custody of unused receipts.
10. If some alteration is made in the receipt already issued, it should be properly initialled.
Cash sales: sales at the counter:
1. The salesman, authorized to sell the goods at the counter, should be specifically named. A
specific number should be allocated to every salesman.
2. Cash memos shall be printed in numerical sequence.
3. The salesman sells goods to the customer and prepares four copies of cash memo, three
of them handed over to customer and one is retained by him.
4. The customer will carry all the three copies to the cashier. After collecting the cash, the
cashier will return two copies to the customer, duly stamp marked as cash paid.
5. Goods are handed over to the customer by gatekeeper and one copy of cash memo is
retained by the gatekeeper and the other one will remain with the customer.
6. At the end of the day, salesman – cashier – gatekeeper prepares the summaries of cash,
sales separately and then they reconcile it, for any difference.
7. The amount received from the cash sales should be deposited daily in the bank.
Cash Sales: Sales by Travelling Salesman/Agents
In some of the organizations, travelling salesman is appointed for direct sales promotion and
collection. In such a case, the internal check system should be:
1. The salesman should be authorized to issue money receipts.
2. They should deposit the entire cash collection daily to the cashier or to the bank account
of the company.
3. The salesman should submit the daily report of sales and collection.
4. The salesman should not keep any cash with him.
5. No cash collection should remain outstanding.
6. If possible, the salesman should be transferred from one area to another to avoid the
frauds.
Cash Payments
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 21 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
1. The official responsible for making cash payments should have no connection with the
receipt of cash.
2. All payments, as far as possible, should be through cheques or NEFT/RTGS/IMPS.
3. The cheques should be signed by the authorized official only.
4. All payments exceeding some specified limit should be duly authorized.
5. Safe custody of unused cheques.
Payment of Wages and Salaries.
• To avoid incorrect time records or piecework records.
• To avoid the inclusion of dummy workers.
• To avoid the fraudulent manipulation of wage sheet.
• To avoid misappropriation of money, etc.
Proper Maintenance of Wage Records: The workers are paid wages either on the basis of time
spent by them or number of pieces produced by them. Therefore, there should be proper time
records or piecework records. The overtime records should also be kept in the organization.
Cash Purchases
• The purchase order should be prepared on the basis of purchase requisition duly
authorized by a competent official.
• The terms and conditions of purchase should be decided on the basis of comparative
tenders and quotations.
• The materials purchased should be verified as regards quantity and quality by the person
independent of purchase department and store department.
• The purchase-invoice should be verified with purchase order and goods received note.
Credit Sales
• The sales department receives a purchase order from the customer. On receipt of the
order, it should be numbered and preserved in the order received book.
• Before the sales orders are processed, credit department should determine the credit
worthiness of the customers.
• The dispatch department should be given a copy of order.
• The storekeeper who maintains custody over the inventory should issues goods to the
dispatch department.
This is the complete process of credit co-operative society, mudhol.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 22 of 23
B.V.V.SANGHA’S
S.R.KANTHI ARTS, COMMERCE & SCIENCE COLLEGE MUDHOL-587313.
CONCLUSION:
Verifies that all accounts and transactions are posted correctly and that the
trial balance is in balance. Segregation of Duties: This internal check ensures that no single
individual has control over a transaction from start to finish.
A system through which the accounting procedures of an organisation are so laid out that
the accounts procedures are not under the absolute and independent control of any person.
Internal auditing is a professional activity involved in helping organizations to achieve their
stated objectives. It does this by utilizing a systematic methodology for analysing business
processes, procedures and activities with the goal of highlighting organizational problems
and recommending solutions.
If the controls are found to be effective, the auditor may rely on them to reduce the extent
of substantive testing. If the controls are found to be ineffective or have material
weaknesses, the auditor will need to plan and perform additional audit procedures to obtain
sufficient appropriate audit evidence.
Generally today a step forward in banks' perception of necessity in forming efficient
management system and internal control system has been made. But still there're many
questions remaining which are important to work out (like providing integration of banking
community and supervision authority approaches in different aspects).
All in all, control system is an important part of banking activity, maintaining its reputation.
And at any time any financial institution can't do without it.
The internal audit function of corporate governance provides objective and independent
assurance and consulting services designed to add value and improve the company's
sustainable performance in the areas of operations, risk management, internal controls,
financial reporting, and government processes.
Internal auditors are well trained and positioned to provide numerous assurance services
to their organization. The emerging trend toward more emphasis on MBL of governance,
economic, ethical, social, and environmental performance requires organizations to provide
assurance on a variety of their performance measures and achievements. SOX does not
directly address internal auditor responsibilities or internal audit function.
JYOTI CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT SOCIETY NYT., MUDHOL Page 23 of 23
You might also like
- Neelam ReportDocument86 pagesNeelam Reportrjjain07100% (2)
- Co - Operative SocietyDocument40 pagesCo - Operative SocietyZubairia Khan100% (5)
- 1js16mba16 Main ProjectDocument69 pages1js16mba16 Main ProjectmanjunathNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument16 pagesThe Problem and Its BackgroundJolinaNo ratings yet
- 8 Microfinance Lending ModelsDocument12 pages8 Microfinance Lending Modelsanamikabhoumik100% (12)
- Rushikesh Kale Abmp 201738 1Document75 pagesRushikesh Kale Abmp 201738 1Yogesh VeerNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Urban Cooperative BanksDocument6 pagesThesis On Urban Cooperative Bankssararousesyracuse100% (2)
- Uscp (Week 1)Document36 pagesUscp (Week 1)Charies Nazareno Moreno AbingNo ratings yet
- A Comparitive Study of Cooperative BanksDocument10 pagesA Comparitive Study of Cooperative BanksSureshNo ratings yet
- Siddheswar Co-Operative Bank LTD, BijapurDocument63 pagesSiddheswar Co-Operative Bank LTD, Bijapurarunsavukar100% (2)
- Full DissertationDocument48 pagesFull DissertationSandip NaradNo ratings yet
- Adansi Baptist Credit UnionDocument12 pagesAdansi Baptist Credit Unionjules abrokwahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Co-Operative Banking: DefinationDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Co-Operative Banking: DefinationHelloprojectNo ratings yet
- Importance of SACCOS in TanzaniaDocument16 pagesImportance of SACCOS in TanzaniaMichael Nyaongo75% (4)
- 09 - Chapter 3 PDFDocument31 pages09 - Chapter 3 PDFPRASHANTAKUMARNo ratings yet
- SudhaDocument12 pagesSudhaRAJ GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- Sutex Co-Op Bank ProjectDocument49 pagesSutex Co-Op Bank ProjectHinal Prajapati100% (4)
- Non State InstitutionsDocument23 pagesNon State InstitutionsJenky PetateNo ratings yet
- Sustainability of MFI's in India After Y.H.Malegam CommitteeDocument18 pagesSustainability of MFI's in India After Y.H.Malegam CommitteeAnup BmNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Banking-1111Document63 pagesCooperative Banking-1111ch.nagarjunaNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis On Cooperative BanksDocument6 pagesPHD Thesis On Cooperative Bankssusanandersonannarbor100% (1)
- Resilience of The Cooperative Business ModelDocument16 pagesResilience of The Cooperative Business ModelFernandez MiaNo ratings yet
- Sahak AriDocument45 pagesSahak AriSaroj TharuNo ratings yet
- Summer Training ReportDocument36 pagesSummer Training Reportsimran LyricsNo ratings yet
- Priyankur SynopsisDocument26 pagesPriyankur SynopsisMukesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Spoorthi V Full Report Editing FinalDocument72 pagesSpoorthi V Full Report Editing Finalspoorthi venuNo ratings yet
- UCSP Q2 Week 6 1 2Document14 pagesUCSP Q2 Week 6 1 2Zhandra PascuaNo ratings yet
- Aeco136 - Final Term Report (Manatal Multipurpose Cooperatives)Document20 pagesAeco136 - Final Term Report (Manatal Multipurpose Cooperatives)JoyDianneGumatayNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Bank Whole InfoDocument9 pagesCooperative Bank Whole Infoyatin patilNo ratings yet
- Kasaba SocityDocument82 pagesKasaba SocitySubramanya DgNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study Between Two Co-Opertive BankDocument47 pagesComparative Study Between Two Co-Opertive BankParag More71% (7)
- Project On Co-Operative Banks and Rural DevelopmentDocument52 pagesProject On Co-Operative Banks and Rural DevelopmentDileep94% (17)
- An Evaluation of The Grameen Bank Project of BangladeshDocument26 pagesAn Evaluation of The Grameen Bank Project of Bangladeshamajaher0% (1)
- Research Paper On Cooperative BanksDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On Cooperative Banksefmf5mdh100% (1)
- A Microfinance Institution With A Difference: What We Mean by ShgsDocument5 pagesA Microfinance Institution With A Difference: What We Mean by ShgsnishaNo ratings yet
- Submitted in Partial Fulfillment For The Requirement For The Award ofDocument21 pagesSubmitted in Partial Fulfillment For The Requirement For The Award ofmahendhar reddyNo ratings yet
- Islamic Finance Pakistan: Governance in Islamic Financial InstitutionsDocument8 pagesIslamic Finance Pakistan: Governance in Islamic Financial InstitutionsnewsletterifpNo ratings yet
- Kasaba Co-Operative SocityDocument104 pagesKasaba Co-Operative SocitySubramanya Dg100% (1)
- Comparative Study of Sarswat Co POOJADocument9 pagesComparative Study of Sarswat Co POOJARavi harhareNo ratings yet
- 25 Co-Operative Banks in IndiaDocument20 pages25 Co-Operative Banks in IndiaAman SinghNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary 1. BackgroundDocument62 pagesExecutive Summary 1. BackgroundMehul AnandparaNo ratings yet
- Micro Finance in IndiaDocument8 pagesMicro Finance in IndiaHarjot SinghNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance in Urban Co-Operative Banks: An Indian PerspectiveDocument14 pagesCorporate Governance in Urban Co-Operative Banks: An Indian PerspectiveKrishna KamtheNo ratings yet
- Cooperatives Formation and Management GuidelinesDocument21 pagesCooperatives Formation and Management GuidelinesnambehelaNo ratings yet
- Cooperatives and Public Limited CompanyDocument18 pagesCooperatives and Public Limited CompanyPaul KamalaNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Citizens Urban Co-Op. Bnak: Submitted To: - Submitted ByDocument55 pagesProject Report On Citizens Urban Co-Op. Bnak: Submitted To: - Submitted ByAnkitNo ratings yet
- Name: Syed Shehryar Ali Zaid ID: 63850 Assignment # 3 SfadDocument4 pagesName: Syed Shehryar Ali Zaid ID: 63850 Assignment # 3 SfadAsad MemonNo ratings yet
- Revisiting Our Social GoalsDocument4 pagesRevisiting Our Social GoalsromyvilNo ratings yet
- Cooperation and HarmonyDocument27 pagesCooperation and Harmonyshreya1600No ratings yet
- Word 1695583048966Document32 pagesWord 1695583048966Anvesh Pulishetty -BNo ratings yet
- Yes Bank Corp Govn.Document24 pagesYes Bank Corp Govn.choco_pie_952No ratings yet
- Avinash ProjectDocument58 pagesAvinash ProjectSonali Pawar100% (1)
- Introducing: Pre-Registration Seminar (PRS)Document152 pagesIntroducing: Pre-Registration Seminar (PRS)XanderPerez100% (2)
- Ucsp Module4Document8 pagesUcsp Module4Brendan Lewis DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Financial AccountingDocument36 pagesFinancial Accountingkhanafsha100% (1)
- Research On CoopDocument4 pagesResearch On Coopma christineNo ratings yet
- Co-Operative Banks in IndiaDocument9 pagesCo-Operative Banks in Indiachaitali jadhavNo ratings yet
- Socio-Economic Impact of Cooperatives Among Members: An Input To Customized Program Development Framework For CooperativesDocument16 pagesSocio-Economic Impact of Cooperatives Among Members: An Input To Customized Program Development Framework For CooperativesPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary Journal100% (1)
- In The Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Degree of Bachelor of Business Studies (BBS) Siddhapaila Campus, Surkhet 2020Document16 pagesIn The Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Degree of Bachelor of Business Studies (BBS) Siddhapaila Campus, Surkhet 2020govindaNo ratings yet
- Banking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingFrom EverandBanking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingNo ratings yet
- Common Practices in Business OrganizationsDocument11 pagesCommon Practices in Business OrganizationsAurea Breanna PabloNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument6 pagesSwot Analysisbegaduhmetal100% (2)
- Business Proposal 1Document37 pagesBusiness Proposal 1ain_94No ratings yet
- TLE Home Economics Quarter 3: LAS (Week8)Document6 pagesTLE Home Economics Quarter 3: LAS (Week8)Ma Junnicca MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Panduan Slide Presentation Crew EnrichmentDocument23 pagesPanduan Slide Presentation Crew EnrichmentMaret JahanamNo ratings yet
- MKT101 - Group AssignmentDocument3 pagesMKT101 - Group AssignmentThảo PhươngNo ratings yet
- Exercises Short ProblemsDocument6 pagesExercises Short ProblemsKlaire SwswswsNo ratings yet
- Weighted Average Cost of CapitalDocument20 pagesWeighted Average Cost of CapitalSamuel NjengaNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance Services 15Th Edition Arens Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument44 pagesAuditing and Assurance Services 15Th Edition Arens Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFstephenthanh1huo100% (11)
- Do Industries Lead Stock Markets?: Harrison Hong, Walter Torous, Rossen ValkanovDocument3 pagesDo Industries Lead Stock Markets?: Harrison Hong, Walter Torous, Rossen ValkanovmnadiriNo ratings yet
- 2008 RMS Regional ExamDocument28 pages2008 RMS Regional ExamNitinNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance Services Louwers 6th Edition Solutions ManualDocument20 pagesAuditing and Assurance Services Louwers 6th Edition Solutions ManualRichardThomasrfizy100% (36)
- Customer-Based Brand EquityDocument22 pagesCustomer-Based Brand Equityspcam-mba marketingNo ratings yet
- Etisalat Group Financial Report q2 2022Document24 pagesEtisalat Group Financial Report q2 2022Raees KhanNo ratings yet
- Larsen and Toubro ReportDocument37 pagesLarsen and Toubro ReportKarthick MuraliNo ratings yet
- Financial Reporting by New Zealand Charities - Finding A Way ForwardDocument30 pagesFinancial Reporting by New Zealand Charities - Finding A Way ForwardRay BrooksNo ratings yet
- Keegan Global Marketing 7eDocument23 pagesKeegan Global Marketing 7eRalph Johnson100% (2)
- Reviewer 5Document14 pagesReviewer 5Cyrene CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - AnswerDocument14 pagesChapter 11 - Answerlooter198100% (1)
- Bonus QuizDocument13 pagesBonus QuizAshley Ann StocktonNo ratings yet
- Solution To Chapter 22Document13 pagesSolution To Chapter 22Sy Him80% (5)
- EconomyDocument12 pagesEconomyRayZa Y MiralNo ratings yet
- Cookie Ch2Document5 pagesCookie Ch2Charmaine Bernados Brucal100% (3)
- Industrial and System EngineeringDocument213 pagesIndustrial and System EngineeringAjaikrishnaNo ratings yet
- SAP ECC and BW Report MapingDocument6 pagesSAP ECC and BW Report Mapingskskumar4848No ratings yet
- ITB NotesDocument30 pagesITB NotesUmmi AniNo ratings yet
- Question: The Crimson Press Curriculum Center ... : SearchDocument3 pagesQuestion: The Crimson Press Curriculum Center ... : SearchSebastian StanNo ratings yet
- Case QuestionsDocument5 pagesCase Questionsaditi_sharma_65No ratings yet
- Marketing Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesMarketing Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersNicola DudanuNo ratings yet
- Agronomy (TLE 10) : Agricultural Crop ProductionDocument3 pagesAgronomy (TLE 10) : Agricultural Crop ProductionHelian Zoe Eloise YvetteNo ratings yet