Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hypothyroidism CTN
Uploaded by
Tanistha KhandelwalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hypothyroidism CTN
Uploaded by
Tanistha KhandelwalCopyright:
Available Formats
Hypothyroidism
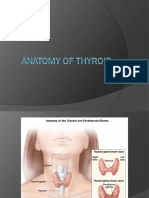
Hypothyroidism, also called underactive thyroid, is when the thyroid gland doesn’t make
enough thyroid hormones to meet your body’s needs.
Causes:
1. Hashimoto’s disease is an autoimmune disorder, The thyroid becomes inflamed and
can’t make enough thyroid hormones.
2. Thyroiditis An inflammation of your thyroid, that causes stored thyroid hormone to
leak out of your thyroid gland. This leakage increases your blood’s hormone levels,
leading to thyrotoxicosis.
3. Congenital hypothyroidism Some babies are born with a thyroid that is not fully
developed or does not work properly. If untreated, congenital hypothyroidism can
lead to intellectual disability and growth failure.
4. Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid When surgeons remove part of the
thyroid, the remaining part may produce normal amounts of thyroid hormone.
However, some people who have this surgery may develop hypothyroidism.
Removing the entire thyroid always results in hypothyroidism.
5. Radiation treatment of the thyroid Radioactive iodine, a common treatment for
hyperthyroidism, gradually destroys thyroid cells.
6. Medicines Some medicines can interfere with thyroid hormone production and lead to
hypothyroidism, including certain heart medicines, bipolar disorder, cancer
medicines, etc
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also called overactive thyroid, is when the thyroid gland makes more
thyroid hormones than your body needs.
Causes
1. Graves’ disease Graves’ disease, the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, is an
autoimmune disorder. With this disease, your immune system attacks the thyroid and
causes it to make too much thyroid hormone.
2. Overactive thyroid nodules Overactive thyroid nodules, or lumps in your thyroid, are
common and usually not cancerous. However, one or more nodules may become
overactive and produce too much thyroid hormone.
3. Thyroiditis Thyroiditis is inflammation of your thyroid gland. Some types of
thyroiditis can cause thyroid hormone to leak out of your thyroid gland into your
bloodstream. As a result, you may develop symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
4. Too much iodine Thyroid uses iodine to make thyroid hormone. How much iodine
one consumes affects how much thyroid hormone their thyroid makes. In some
people, consuming large amounts of iodine may cause the thyroid to make too much
thyroid hormone.
5. Too much thyroid hormone medicine Some people who take thyroid hormone
medicine for hypothyroidism may take too much.
6. Noncancerous tumor In some rare cases, a noncancerous tumor of the pituitary gland,
located at the base of the brain, can cause hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid nodule
A thyroid nodule is an unusual lump (growth) of cells on your thyroid gland. They’re common, almost
always noncancerous (benign) and usually don't cause symptoms.
Causes
1. Colloid nodules: These are one or more overgrowths of normal thyroid tissue. These growths
are not cancer (benign). They may grow large, but they don’t spread beyond your thyroid
gland. These are the most common type of thyroid nodules.
2. Thyroid cysts: These are growths that are filled with fluid or are partly solid and partly filled
with fluid. Cystic nodules pose a low risk for cancer (malignancy) and are either monitored or
biopsied if they’re larger than 2 centimeters.
3. Inflammatory nodules: These nodules develop as a result of long-term (chronic) swelling
(inflammation) of your thyroid gland. These growths may or may not cause pain.
4. Multinodular goiter: Sometimes an enlarged thyroid (goiter) is made up of many nodules
(which are usually benign).
5. Hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules: These nodules produce extra thyroid hormone, which may
lead to the development of hyperthyroidism. Hyperthyroidism requires treatment.
6. Thyroid cancer: Cancer is the biggest concern when thyroid nodules form. Fortunately,
thyroid cancer is very rare — it’s found in less than 6.5% of all thyroid nodules.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/13121-thyroid-nodule
You might also like
- HypothyroidismDocument7 pagesHypothyroidismNader Smadi100% (2)
- Hypothyroidism, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypothyroidism, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- WHO Insider Blows Whistle On Gates and GAVI - LewRockwellDocument9 pagesWHO Insider Blows Whistle On Gates and GAVI - LewRockwellZsi GaNo ratings yet
- GoiterDocument4 pagesGoiterNader Smadi100% (1)
- Graves DiseaseDocument8 pagesGraves Diseasenini07No ratings yet
- Goiter: Prepared By: Felix Kevin M. Villa Iv, RNDocument47 pagesGoiter: Prepared By: Felix Kevin M. Villa Iv, RNFelix Kevin VillaNo ratings yet
- Safety and Infection Control: Archer NCLEX Review Crash CourseDocument75 pagesSafety and Infection Control: Archer NCLEX Review Crash CourseDanica Chiara Motia100% (1)
- HyperthyroidismDocument6 pagesHyperthyroidismNader Smadi100% (2)
- Drug Study For PneumoniaDocument15 pagesDrug Study For PneumoniaPrincess Pauline Abrasaldo100% (1)
- CRQs For The Final FRCA (Oxford Speciality Training Revision Texts) (Mar 21, 2021) - (0198850301) - (Oxford University Press)Document286 pagesCRQs For The Final FRCA (Oxford Speciality Training Revision Texts) (Mar 21, 2021) - (0198850301) - (Oxford University Press)AE100% (2)
- Thyroid Diet: How to Improve Thyroid Disorders, Manage Thyroid Symptoms, Lose Weight, and Improve Your Metabolism through Diet!From EverandThyroid Diet: How to Improve Thyroid Disorders, Manage Thyroid Symptoms, Lose Weight, and Improve Your Metabolism through Diet!No ratings yet
- Hypo Thyroids MDocument26 pagesHypo Thyroids MBridget NjambiNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and Adrenal MedullaDocument32 pagesThyroid and Adrenal MedullaDipika RawatNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYofDocument3 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYofRose Si CheeksNo ratings yet
- What Is Hyperthyroidism?: HighlightsDocument15 pagesWhat Is Hyperthyroidism?: Highlightsmateto_2014No ratings yet
- Understanding Thyroid ProblemsDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Thyroid ProblemsChellaMarieNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism Overview: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument13 pagesHyperthyroidism Overview: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentEahrielle Andhrew PlataNo ratings yet
- HYPERTHYROIDISMDocument8 pagesHYPERTHYROIDISMfortuneholiness11No ratings yet
- GoiterDocument22 pagesGoitermohamedkallon1996No ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism: What Is The Thyroid Gland?Document8 pagesHyperthyroidism: What Is The Thyroid Gland?scremo_xtremeNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument7 pagesPathophysiologyAko Si Vern ÖNo ratings yet
- De La Salle University - Dasmariñas: Genetics Final ElgaDocument8 pagesDe La Salle University - Dasmariñas: Genetics Final ElgaRocel LomedaNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid) - NIDDKDocument9 pagesHypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid) - NIDDKHannah Denise BatallangNo ratings yet
- Understanding Hyperthyroidism Causes and SymptomsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Hyperthyroidism Causes and SymptomsPutri LoongNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument11 pagesHypothyroidism Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentFarhat KhanNo ratings yet
- Endemic and Sporadic GoiterDocument13 pagesEndemic and Sporadic GoiterBtwo SoelNo ratings yet
- 4 Common Thyroid Disorders ExplainedDocument5 pages4 Common Thyroid Disorders ExplainedAnggunNMNo ratings yet
- Underactivity of Thyroid Gland (Hypothyroidism)Document5 pagesUnderactivity of Thyroid Gland (Hypothyroidism)Mohamed Omar SamatarNo ratings yet
- Endocrine - L5 & 6Document26 pagesEndocrine - L5 & 6hussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- What is hypothyroidism? causes, symptoms, diagnosisDocument16 pagesWhat is hypothyroidism? causes, symptoms, diagnosisvinhannyNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism: Erbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical College MLT Department Third Stage Group: CDocument5 pagesHypothyroidism: Erbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical College MLT Department Third Stage Group: CRayan JabbarNo ratings yet
- Hyper BrochureDocument2 pagesHyper BrochureVksudhar SanamNo ratings yet
- THYROIDDocument17 pagesTHYROIDvinolashrimmishma.sNo ratings yet
- 35thyroid DisordersDocument21 pages35thyroid DisordersDurga VoraNo ratings yet
- Gabriel Chacón - ULA (VE) - Pharmacy - 1041 Physiopathology - Subject 4 - Endocrine DisordersDocument8 pagesGabriel Chacón - ULA (VE) - Pharmacy - 1041 Physiopathology - Subject 4 - Endocrine DisordersGabriel ChacónNo ratings yet
- Patient GDocument4 pagesPatient GDENNROSE DECLARONo ratings yet
- Anatomy of ThyroidDocument20 pagesAnatomy of ThyroidDaniel Gunawan SembiringNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland Dont Erase Ate KatDocument24 pagesThyroid Gland Dont Erase Ate KatThess Tecla Zerauc AzodnemNo ratings yet
- Hypertyroidism: Overview of The DiseaseDocument8 pagesHypertyroidism: Overview of The DiseaseCj UritaNo ratings yet
- Uninodular Goitre: One Thyroid Nodule Can Be Either Inactive, or Active (Toxic)Document6 pagesUninodular Goitre: One Thyroid Nodule Can Be Either Inactive, or Active (Toxic)Dimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Thyroid CancerDocument5 pagesThyroid CancerJulia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- GoiterDocument48 pagesGoiterRizki NurNo ratings yet
- Щитоподібна залоза ангDocument24 pagesЩитоподібна залоза ангdenysvorobchak-12No ratings yet
- What Is Goitre?: Thyroid GlandDocument3 pagesWhat Is Goitre?: Thyroid Glandflex gyNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorder Research PaperDocument5 pagesThyroid Disorder Research Paperapi-254922343No ratings yet
- Archivo en Ingles-Patologias TiroideasDocument4 pagesArchivo en Ingles-Patologias Tiroideasesther avilaNo ratings yet
- What Causes Hyperthyroidism and How Can It Be Treated - Aiden Adamson 4Document12 pagesWhat Causes Hyperthyroidism and How Can It Be Treated - Aiden Adamson 4api-549241785No ratings yet
- Ata Hyperthyroidism BrochureDocument3 pagesAta Hyperthyroidism BrochureSelvy Anriani GasperszNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism (Underactive)Document3 pagesHypothyroidism (Underactive)jhNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland AnaDocument1 pageThyroid Gland AnaManoj PakalapatiNo ratings yet
- English Espanol: GoiterDocument3 pagesEnglish Espanol: Goiterflex gyNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism Web BookletDocument25 pagesHypothyroidism Web BookletMujeer PashaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY PROJECT (Vasudeb) THYROIDDocument13 pagesBIOLOGY PROJECT (Vasudeb) THYROID38. Vasudeẞ Giri 10A2No ratings yet
- Emmy Harefa - Tiroid Diksar LIS, 5 Maret 2016Document81 pagesEmmy Harefa - Tiroid Diksar LIS, 5 Maret 2016jcyovelaNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism Vs Hypothyroidism: Ngmontecillo SSLC 1ST SEM 2021-2022Document76 pagesHyperthyroidism Vs Hypothyroidism: Ngmontecillo SSLC 1ST SEM 2021-2022Giovanne BuendiaNo ratings yet
- Ata Hypothyroidism BrochureDocument3 pagesAta Hypothyroidism BrochureThe Fitness CoachNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Heart Metabolism Hyperthyroidism Thyroid Hormone Thyroxine MetabolismDocument4 pagesThyroid Heart Metabolism Hyperthyroidism Thyroid Hormone Thyroxine MetabolismvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)_ Symptoms, Causes, Tests, TreatmentsDocument9 pagesHypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)_ Symptoms, Causes, Tests, TreatmentsHannah Denise BatallangNo ratings yet
- Group-1 SciDocument12 pagesGroup-1 SciJUNE NIEL CASIONo ratings yet
- Thyro I EctomyDocument9 pagesThyro I EctomySafwan SayedNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Thyroid ProblemsDocument4 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Thyroid ProblemsNicole Anne TungolNo ratings yet
- CVD & ThyroidDocument12 pagesCVD & ThyroidShang AllertseNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroid Is MDocument10 pagesHyperthyroid Is MBugMyNutsNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroid Is MDocument24 pagesHyperthyroid Is M70 Kirithic Roshan RKNo ratings yet
- CarbohydrateDocument3 pagesCarbohydrateTanistha KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- NHE (Foods To Eat & Avoid While Breastfeeding)Document16 pagesNHE (Foods To Eat & Avoid While Breastfeeding)Tanistha KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- To Eat Breast FeedingDocument7 pagesTo Eat Breast FeedingTanistha KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Final Report of Importance of WaterDocument5 pagesFinal Report of Importance of WaterTanistha KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Related To Vegan FspaDocument5 pagesFood Safety Related To Vegan FspaTanistha KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Incident Reporting SystemDocument5 pagesIncident Reporting SystemAhmed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Literature Review FinalDocument4 pagesLiterature Review Finalapi-549244735No ratings yet
- Emergencydepartment Managementofacute Kidneyinjury, Electrolyte Abnormalities, Andrenal Replacementtherapyinthe CriticallyillDocument13 pagesEmergencydepartment Managementofacute Kidneyinjury, Electrolyte Abnormalities, Andrenal Replacementtherapyinthe Criticallyilldogui0071No ratings yet
- Prime 18Document42 pagesPrime 18Mera LaptopNo ratings yet
- Fiscella and Sanders 2016Document24 pagesFiscella and Sanders 2016rceasaradudeNo ratings yet
- PT Health RisksDocument3 pagesPT Health Riskskathrine_fernandezNo ratings yet
- Prospects and Perspectives of Natural Plants Products in MedicineDocument12 pagesProspects and Perspectives of Natural Plants Products in Medicinecoolarun86No ratings yet
- Abdomen Macleod - S - Clinical - Examination - 15thDocument28 pagesAbdomen Macleod - S - Clinical - Examination - 15thwxyngtc4n9No ratings yet
- En VENTIlogic-LS Plus 67781i User ManualDocument125 pagesEn VENTIlogic-LS Plus 67781i User ManualMehmet Ali KaraNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics V16 The Prevention and Management of RH Disease Chapter Medical Management of Rhesus Disease 1696739347Document8 pagesObstetrics V16 The Prevention and Management of RH Disease Chapter Medical Management of Rhesus Disease 1696739347priyankafetalmedicineNo ratings yet
- All About Panchagavya For Human Usage - A Review: February 2021Document10 pagesAll About Panchagavya For Human Usage - A Review: February 2021DezyaNo ratings yet
- Migmar Tsering (Mike) S ResumeDocument3 pagesMigmar Tsering (Mike) S Resumeapi-284044370No ratings yet
- Duty Report 31 MeiDocument26 pagesDuty Report 31 Meidrkarina mukhtiNo ratings yet
- Applied Anatomy of Spinal CordDocument34 pagesApplied Anatomy of Spinal CordSuhana PathanNo ratings yet
- G1 Therapeutics - G1T28-207 - SIF Version 1 - 21apr2020Document6 pagesG1 Therapeutics - G1T28-207 - SIF Version 1 - 21apr2020Mohammad HojoujNo ratings yet
- Giant Dental Calculus: A Rare Case Report and ReviewDocument3 pagesGiant Dental Calculus: A Rare Case Report and ReviewKiyRizkikaNo ratings yet
- Adverse Drug ReactionDocument7 pagesAdverse Drug ReactionufahadNo ratings yet
- Use of Local Anesthesia For Pediatric Dental Patients: Latest RevisionDocument6 pagesUse of Local Anesthesia For Pediatric Dental Patients: Latest RevisionzainaNo ratings yet
- DesmopressinDocument3 pagesDesmopressinKim RuizNo ratings yet
- Concept of Prakriti in Ayurveda and Its Significance in Evading Lifestyle DisordersDocument8 pagesConcept of Prakriti in Ayurveda and Its Significance in Evading Lifestyle Disorderstherapeticka the-healing-tribeNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastrointestinal Bleeding - PPTX 2Document17 pagesAcute Gastrointestinal Bleeding - PPTX 2karen kate ablesNo ratings yet
- Philippine Drug Enforcement Agency: Republic of The Philippines Office of The PresidentDocument87 pagesPhilippine Drug Enforcement Agency: Republic of The Philippines Office of The PresidentMelvin YnionNo ratings yet
- Phlebotomy and Specimen ConsiderationsDocument21 pagesPhlebotomy and Specimen ConsiderationsLesly Marie LaxamanaNo ratings yet
- Biosafety Levels: WWW - Techef.InDocument21 pagesBiosafety Levels: WWW - Techef.InSmk Mahmud KoliNo ratings yet