0% found this document useful (0 votes)
138 views14 pagesElectrical Measuring Instruments Guide
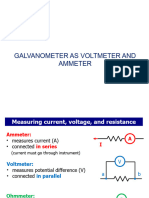
- An ammeter is used to measure current and must be connected in series with the component. Current is the same in series.
- A voltmeter is used to measure voltage and must be connected in parallel across the component. Voltage is the same in parallel.
- An ohmmeter can measure resistance by connecting its probes across a resistor. Resistors have color bands indicating their resistance value.
Uploaded by
lwitsfadontCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
138 views14 pagesElectrical Measuring Instruments Guide
- An ammeter is used to measure current and must be connected in series with the component. Current is the same in series.
- A voltmeter is used to measure voltage and must be connected in parallel across the component. Voltage is the same in parallel.
- An ohmmeter can measure resistance by connecting its probes across a resistor. Resistors have color bands indicating their resistance value.
Uploaded by
lwitsfadontCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd