Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Change in Gravitational Potential Energy Final Kinetic Energy 1750 1750 17 500 17 500 450 1750 16 200 17 500
Uploaded by
Ziauddin TaposhOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Change in Gravitational Potential Energy Final Kinetic Energy 1750 1750 17 500 17 500 450 1750 16 200 17 500
Uploaded by
Ziauddin TaposhCopyright:
Available Formats
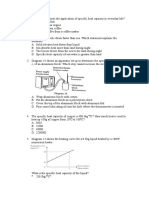
1.
A child slides down a slide
The weight of the child is 250 N. The height of the slide is 7.0 m. The work done against friction as the
child travels down the slide is 1300 J.
What is the change in gravitational potential energy and what is the final kinetic energy of the child?
change in final kinetic
gravitational energy
potential energy
A 1750 450
B 1750 1750
C 17 500 16 200
D 17 500 17 500
2 What uses non-renewable energy?
A a geothermal heating system B a nuclear power station
C a solar panel D a wind turbine
3 Which process in the Sun produces energy?
A burning B nuclear fission C nuclear fusion D radiation
4 A 300 N force is applied to a box to move it up a ramp, as shown.
How much work is done by the force when moving the box from X to Y?
A 900 J B 1200 J C 1500 J D 3000 J
5 A cyclist travels along a horizontal track at constant speed.
The work done by the cyclist is equal to
A the change in kinetic energy. B the force of air resistance.
C the force of friction in the bicycle. D the thermal energy (heat) produced.
6 A crane lifts a load of 6000 N through a vertical distance of 15 m in 30 s.
What is the average useful power during this operation?
A 200 W B 400 W C 3000 W D 12 000 W
7 Which statement about thermal radiation is correct?
A In a vacuum, thermal radiation travels at the speed of light.
B Thermal radiation is a longitudinal wave.
C Thermal radiation travels as an ultra-violet wave.
D White surfaces are better emitters of thermal radiation than black surfaces.
MAMUN SIR, Head of Physics, GGIS. 1 Phone: 01817750750.
8 A slice of bread is placed under a red-hot electric grill to make toast.
How does heat energy reach the bread?
A conduction and convection B conduction only
C convection and radiation D radiation only
9 A saucepan is used to heat up some water.
How is heat transferred through the aluminium pan and through the plastic handle?
10 A silver cup is filled with boiling water from a kettle. A man touches the outside surface of the cup and
finds that it is extremely hot. Why is the surface so hot?
A Convection takes place in the boiling water.
B Silver is a good conductor of heat.
C The boiling water gives out latent heat.
D The shiny surface is a good emitter of infra-red radiation.
11 A rod of metal is heated at one end. Which statement best describes the conduction of heat through the
metal?
A Atoms move from the hot end and hit electrons at the cold end.
B Atoms vibrate and hit atoms at the cold end.
C Free electrons move from the hot end and hit atoms further along the rod.
D Free electrons vibrate and pass energy to free electrons further along the rod.
12 To raise the temperature of a 2.0 kg block of metal by 20 °C, energy of 5.2 kJ is needed.
What is the value of the specific heat capacity of the metal?
A 0.13 J / (kg °C) B 52 J / (kg °C) C 130 J / (kg °C) D 52 000 J / (kg
°C)
13 In hot weather, people use electric fans to keep cool. Why do the fans make them feel cool?
A They change one form of energy into another. B They cool the air in the room.
C They increase the rate of evaporation from the skin. D They speed up the vibration of air molecules.
MAMUN SIR, Head of Physics, GGIS. 2 Phone: 01817750750.
14 Why is there a constriction in a clinical thermometer?
A to give the thermometer a smaller temperature range
B to make the thermometer more sensitive
C to prevent the mercury breaking the bulb when it expands
D to stop the mercury from going back to the bulb
15 In a liquid-in-glass thermometer, the liquid column is 2.0 cm long at 0 °C and it expands 10.0 cm when
heated to 100 °C.
Measuring from P, how long is the liquid column at 30 °C?
A 2.3 cm B 3.0 cm C 5.0 cm D 7.0 cm
16 The diagrams represent four thermometers.
Which thermometer has the greatest sensitivity and which thermometer has the greatest range?
greatest greatest
sensitivity range
A P R
B P S
C Q R
D Q S
17 The diagram shows a clinical thermometer.
Which factor affects the sensitivity of the thermometer?
A the constriction B the diameter of the bore
C the length of the glass tube D the thickness of the glass tube
18 A liquid-in-glass thermometer contains mercury.
Which physical property of the mercury varies with temperature, enabling the thermometer to operate?
A mass B melting point C resistance D volume
MAMUN SIR, Head of Physics, GGIS. 3 Phone: 01817750750.
19 The temperature shown by a mercury-in-glass thermometer increases.
Which of the following is constant?
A the density of the mercury B the internal energy of the mercury
C the mass of the mercury D the volume of the mercury
20 What makes a clinical thermometer suitable for measuring small changes in body temperature?
A The amount of mercury in the bulb is small. B The bore of the capillary tube is narrow.
C The capillary tube is long. D The glass bulb has a thin wall.
21 The diagram shows two liquid-in-glass thermometers P and Q.
The thermometers are identical except that Q has a capillary tube with a larger internal diameter than P.
Which thermometer has the larger range and which thermometer has the greater sensitivity?
22 A n electrical heater is placed in a beaker of cold oil, as shown.
The heater is switched on. What happens to the liquid at X?
A It becomes less dense and falls. B It becomes less dense and rises.
C It becomes more dense and falls. D It becomes more dense and rises.
23 A pupil adds 37 g of ice at 0 °C to 100 g of water at 30 °C. The final temperature of the water and
melted ice is 0 °C. No heat is lost to, or gained from, the surroundings. The specific heat capacity of water
is 4.2 J / (g °C).
What is the specific latent heat of ice?
A 47 J / g B 341 J / g C 4700 J / g D 12 600 J / g
24 The heat capacity of an object, of mass 2.0 kg, is C. The energy needed to
A increase the temperature of the whole object by ⵠt is Cⵠt.
B increase the temperature of unit mass of the object by ⵠt is Cⵠt.
C melt the whole object is C.
D melt unit mass of the object is C.
MAMUN SIR, Head of Physics, GGIS. 4 Phone: 01817750750.
25 An insulated beaker contains 300 g of water, initially at 30 °C. Water at 100 °C is added until the
temperature of the mixture reaches 50 °C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.2 J / (g °C).
How much water is added?
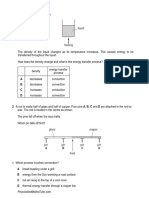
A 60 g B 120 g C 180 g D 750 g
26 A hot liquid is poured into a beaker. The graph shows how the temperature of the liquid changes as it
cools towards room temperature.
What is occurring at region X?
A boiling and evaporation B condensation only
C evaporation only D solidification and evaporation
27 An ice pack is used to cool 0.25 kg of water. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.2 kJ / (kg ℃).
How much thermal energy (heat) must the ice pack extract from the water to reduce the water temperature
by 15 ℃?
A 0.070 kJ B 1.1 kJ C 16 kJ D 250 kJ
28 Four cars are driven along a road. The table shows the work done by the engine in each car and the time
taken by each car. Which engine produces the most power?
29 Thermal energy is transferred to a solid. First it melts and then it boils to produce a gas. Which
statement about the temperature is correct?
A When melting and boiling the temperature does not change.
B When melting and boiling the temperature increases.
C When melting the temperature increases but when boiling the temperature stays the same.
D When melting the temperature stays the same but when boiling the temperature increases.
MAMUN SIR, Head of Physics, GGIS. 5 Phone: 01817750750.
30 Steam at 100 °C is passed into some water in a beaker. All the steam condenses in the water.
The mass of water in the beaker rises from 120.0 g to 122.0 g. The specific latent heat of vaporisation of
water is 2250 J / g. How much thermal energy is lost by the steam as it condenses?
A 8.9 × 10–4J B 1.1 × 103J C 4.5 × 103J D 2.7 × 105 J
31 A gas in a container of fixed volume is heated. What happens to the molecules of the gas?
A They collide less frequently. B They expand.
C They move faster. D They move further apart.
32 In a liquid, some energetic molecules break free from the surface even when the liquid is too cold for
bubbles to form. What is the name of this process?
A boiling B condensation C convection D evaporation
33 The diagram shows the inside of a refrigerator.
When the refrigerator is first switched on, what happens to the air near the cooling unit?
34 Some gas is trapped in a closed container. The gas is cooled and the volume of the container is kept
constant. What happens to the gas molecules?
A They collide with the walls more often. B They contract.
C They get closer together. D They move more slowly.
35 Some of the liquid in a dish evaporates, as shown in the diagrams.
Which molecules leave the liquid and which molecules in the liquid have greater average kinetic energy?
MAMUN SIR, Head of Physics, GGIS. 6 Phone: 01817750750.
36 The diagram shows a flask containing air. The air is trapped by a drop of oil in a narrow tube.
When the flask is heated the oil drop rises up the tube.
Which statement is not correct?
A The air molecules each get larger. B The air molecules hit the container with greater force.
C The air molecules move faster. D The air molecules move further apart.
37 When a gas in a container of fixed volume is heated, the pressure of the gas increases.
Which statement explains this?
A The molecules expand and get heavier, so they hit each other harder.
B The molecules have less room to move, so they collide with each other more frequently.
C The molecules hit the walls harder and less frequently.
D The molecules move faster, so they collide with the walls more frequently.
38 A crane moves its load diagonally, as shown.
By what distance is the weight of the load multiplied in order to calculate the increase in gravitational
potential energy of the load?
39 The efficiency of an electrical generator is 65 %.
Which useful output can be expected if the energy input to the generator is 12 kJ?
A 4.2 kJ B 7.8 kJ C 19 kJ D 780 kJ
40 In a hydroelectric power station, water from a reservoir falls down a long pipe before entering the
turbines. The turbines then turn the generator. What is the overall energy conversion?
A electrical energy into kinetic energy B electrical energy into potential energy
C kinetic energy into chemical energy D potential energy into electrical energy
MAMUN SIR, Head of Physics, GGIS. 7 Phone: 01817750750.
You might also like
- Thermal physics worksheetDocument15 pagesThermal physics worksheetilyasheee901100% (2)
- Spring balance graph load readingDocument5 pagesSpring balance graph load readingayeayeNo ratings yet
- Hasil Ujian Putri Apriliani JAK2 FIS SMA TD Thermal Physics & Ideal Gas PDFDocument21 pagesHasil Ujian Putri Apriliani JAK2 FIS SMA TD Thermal Physics & Ideal Gas PDFIrnawati KarubiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 2.0 - Thermal Physics - Test 2018Document9 pagesIGCSE 2.0 - Thermal Physics - Test 2018Brandeice BarrettNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ii Unit 1 Paper 1Document6 pagesChemistry Ii Unit 1 Paper 1maxime namaNo ratings yet
- Olp Igcse Heat & Electromagnetism CT 5 - Jan 2012Document17 pagesOlp Igcse Heat & Electromagnetism CT 5 - Jan 2012Shabbir H. KhanNo ratings yet
- UP Paper1 S1 SECOND TERM 2024Document9 pagesUP Paper1 S1 SECOND TERM 2024erumriaz.1995No ratings yet
- Form 4 Ujian OgosDocument3 pagesForm 4 Ujian Ogosjesunathan44@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesThermal Physics Multiple Choice QuestionsSameer Abu MunsharNo ratings yet
- SUBJECT - PHYSICS ss2Document6 pagesSUBJECT - PHYSICS ss2mark okorieNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Igcse Physics Grade 10 Sem 1 2014 Soal - RevisiDocument10 pagesMid Term Igcse Physics Grade 10 Sem 1 2014 Soal - RevisiJoshuaUntungNo ratings yet
- CE80Document26 pagesCE80Law Jing SeeNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam ThermodynamicsDocument10 pagesMidterm Exam ThermodynamicsRoselyn BenavidezNo ratings yet
- Physics IX WORKSHEETDocument8 pagesPhysics IX WORKSHEETShahidul Hassan MontiNo ratings yet
- International Education Centre Worksheet for Vacation Class VIII Physics MCQsDocument8 pagesInternational Education Centre Worksheet for Vacation Class VIII Physics MCQsShahidul Hassan MontiNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document14 pagesCH 11UbadahNo ratings yet
- IB Thermo (2016)Document7 pagesIB Thermo (2016)Hiroki Nose100% (1)
- Questionnaire For Elimination RoundDocument7 pagesQuestionnaire For Elimination RoundJV CustodioNo ratings yet
- Al-Azhhar Islamic Junior High School Competence TestDocument4 pagesAl-Azhhar Islamic Junior High School Competence TestbenyNo ratings yet
- Text 9Document9 pagesText 9Debela mendaraNo ratings yet
- Analyze math problems instructionsDocument5 pagesAnalyze math problems instructionsJan Ebenezer MorionesNo ratings yet
- Specific heat capacity concept explained through everyday examplesDocument4 pagesSpecific heat capacity concept explained through everyday exampleskenenathNo ratings yet
- 2019 1st Sec80Document8 pages2019 1st Sec80Aboahmed Ali0% (1)
- I. MULTIPLE CHOICE: Blacken The Letter of The Correct Answer On A Separate Answer Sheet ProvidedDocument3 pagesI. MULTIPLE CHOICE: Blacken The Letter of The Correct Answer On A Separate Answer Sheet ProvidedMJ LizadaNo ratings yet
- 73 Summer 1st LE Set A With AnswersDocument12 pages73 Summer 1st LE Set A With AnswersNikkei Pfeiffer TadiliNo ratings yet
- L-1.2: Thermal Energy Section A: Choose The Best AnswerDocument17 pagesL-1.2: Thermal Energy Section A: Choose The Best AnswerDani BaderNo ratings yet
- Heat QuizDocument3 pagesHeat QuizI Putu Yoga Widi LaksanaNo ratings yet
- S4 Physics Paper 1-Resourceful Mock Examinations 2019ADocument11 pagesS4 Physics Paper 1-Resourceful Mock Examinations 2019ATwinomujuniNo ratings yet
- 11 Thermal Properties of MatterDocument8 pages11 Thermal Properties of MatterGIENo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Calorimetry QuestionsDocument14 pagesThermodynamics and Calorimetry QuestionsutikNo ratings yet
- Physics Heat and Thermodynamics Study Guide: True/FalseDocument5 pagesPhysics Heat and Thermodynamics Study Guide: True/FalseRB100% (1)
- Level 3 6090-30 502 ST Ver 1.0 Sep 2017Document19 pagesLevel 3 6090-30 502 ST Ver 1.0 Sep 2017e4erkNo ratings yet
- TDocument12 pagesTholdonpainendsNo ratings yet
- Thermometry: T/s T/KDocument9 pagesThermometry: T/s T/KJing Yu VoonNo ratings yet
- Test Chapter 17Document18 pagesTest Chapter 17damonchooNo ratings yet
- Thermal Processes (Multiple Choice) QPDocument26 pagesThermal Processes (Multiple Choice) QPFernando SalimNo ratings yet
- Chapter: ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesChapter: ThermodynamicsJaideep GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Hapter: Conceptual ProblemsDocument17 pagesHapter: Conceptual ProblemsMalek AqlanNo ratings yet
- Heat 1Document5 pagesHeat 1christian mooreNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 First Six Weeks TestDocument7 pagesGrade 11 First Six Weeks TestTanieka PowellNo ratings yet
- Physics Test 4Document2 pagesPhysics Test 4RaphaelNo ratings yet
- Heat & Gases Chapter 2 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument19 pagesHeat & Gases Chapter 2 Multiple Choice QuestionsLaw Jing SeeNo ratings yet
- Physics Thermodynamics MCQsDocument2 pagesPhysics Thermodynamics MCQsMohammad Umair100% (1)
- NMAT PRACTICE SET 0619 - Rationale - TEST B. PhysicsDocument10 pagesNMAT PRACTICE SET 0619 - Rationale - TEST B. PhysicsMianella Rosales100% (1)
- CalorDocument4 pagesCalorcesar jimenezNo ratings yet
- 2006 Form 3 Physics Half-Yearly Exam (Dec 2006)Document4 pages2006 Form 3 Physics Half-Yearly Exam (Dec 2006)Raistlin Chan Ching KitNo ratings yet
- Probset 1bDocument12 pagesProbset 1bRegina Marie MaximoNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Chapter 7Document10 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 7Angie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- PAPER-1 Mock Paper 2015Document10 pagesPAPER-1 Mock Paper 2015Ishtiyaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Final BookDocument160 pagesFinal BookSreekar GaliNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 01 Mastery TestDocument1 pageThermodynamics 01 Mastery TestKarl Christian SupnetNo ratings yet
- CalorDocument4 pagesCalorAlex AngelNo ratings yet
- SampleDocument5 pagesSampleMark Anthony RazonNo ratings yet
- Liquid Helium Technology: Proceedings of the International Institute of Refrigeration Commission 1, Boulder (U.S.A.) 1966From EverandLiquid Helium Technology: Proceedings of the International Institute of Refrigeration Commission 1, Boulder (U.S.A.) 1966No ratings yet
- Snow ProcessDocument1 pageSnow ProcessRaihan RasyidNo ratings yet
- Phase Change: Asynchronous Lesson Science Teacher: Mr. Robert Jay M. Lopez Grade 8-Science 8-PaulDocument3 pagesPhase Change: Asynchronous Lesson Science Teacher: Mr. Robert Jay M. Lopez Grade 8-Science 8-PauljemNo ratings yet
- Birch ReductionDocument5 pagesBirch ReductionShane Pike100% (1)
- Chan Thomas - The Adam and Eve Story - TextDocument57 pagesChan Thomas - The Adam and Eve Story - Textalfsborg83% (6)
- The Frozen TombDocument4 pagesThe Frozen TombAnonymous E91WVGPNo ratings yet
- Is The Earth Getting WarmerDocument9 pagesIs The Earth Getting Warmersalmanq_1850% (2)
- KS3 Chemistry Baseline TestDocument14 pagesKS3 Chemistry Baseline Testfadua barakatNo ratings yet
- Whirlpool Refrigerator - G2IXEFMWQ01Document32 pagesWhirlpool Refrigerator - G2IXEFMWQ01multivactNo ratings yet
- Assessment - 3: Participate in Safe Food Handling PracticesDocument47 pagesAssessment - 3: Participate in Safe Food Handling PracticesNidhi Gupta100% (1)
- Warming World Impacts by DegreeDocument40 pagesWarming World Impacts by DegreeCliffhangerNo ratings yet
- Thaung Shan HtetDocument19 pagesThaung Shan HtetThaungShanHtet PalatarNo ratings yet
- How To Build With CobDocument33 pagesHow To Build With CobmandritsopoulosNo ratings yet
- Earth and Space KES: by The End of The Grade, Students Will Be Able ToDocument10 pagesEarth and Space KES: by The End of The Grade, Students Will Be Able Toapi-307635338No ratings yet
- Ratio and Proportion: by Jay MehtaDocument20 pagesRatio and Proportion: by Jay MehtaJay MehtaNo ratings yet
- Ice Detection With Thermal ImagingDocument3 pagesIce Detection With Thermal ImagingayviwurbayviwurbNo ratings yet
- Ice Slurry Tech Cold Chain. APCpptxDocument16 pagesIce Slurry Tech Cold Chain. APCpptxmahendrapratNo ratings yet
- Inclined Plane Group Lever Group: Simple MachinesDocument6 pagesInclined Plane Group Lever Group: Simple MachinesgreyolNo ratings yet
- Jig 1 Issue 12 PDFDocument117 pagesJig 1 Issue 12 PDFHoàng Thuý Trang100% (7)
- An Inconvenient Truth WorksheetDocument3 pagesAn Inconvenient Truth WorksheetYashrajsing LuckkanaNo ratings yet
- 19405Document402 pages19405mohammed raidNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ LUYỆN 31.1.2023Document12 pagesĐỀ LUYỆN 31.1.2023Hoàng Như MaiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Week 1Document4 pagesWorksheet Week 1Leyana Katriel T BeltranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Rain, Thunder and LightningDocument3 pagesChapter 13 Rain, Thunder and Lightningbittuchintu100% (1)
- HomeswsDocument3 pagesHomeswsHegeNo ratings yet
- Physics Problems SolvedDocument345 pagesPhysics Problems Solvedvpo1673No ratings yet
- Full Solution Manual For Fundamentals of Hydraulic Engineering Systems 4Th Edition by Houghtalen PDF Docx Full Chapter ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Solution Manual For Fundamentals of Hydraulic Engineering Systems 4Th Edition by Houghtalen PDF Docx Full Chapter Chaptertimaline.episodalstgd8g100% (11)
- Class-X English Study Material 2020-21Document279 pagesClass-X English Study Material 2020-21Pratishtha Mishra100% (2)
- PEMERINTAH KOTA PALANGKA RAYA DINAS PENDIDIKAN ULANGAN SEMESTERDocument9 pagesPEMERINTAH KOTA PALANGKA RAYA DINAS PENDIDIKAN ULANGAN SEMESTERGkjbcdNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE FAIR - Which Shape of Ice Cube Melts The FastestDocument11 pagesSCIENCE FAIR - Which Shape of Ice Cube Melts The Fastestobx4everNo ratings yet
- Q1-W7-Activity - SheetDocument9 pagesQ1-W7-Activity - SheetBeth DomantayNo ratings yet