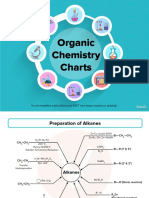
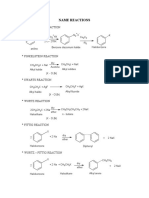
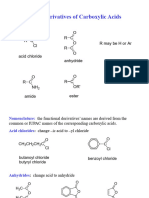
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tips For Conversion
Uploaded by
rairishveshOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tips For Conversion
Uploaded by
rairishveshCopyright:
Available Formats
KEY FOR CONVERSIONS
Sl Reagent Group Out Group In Remark
No
1 KMnO4 / H+ -CH2OH -COOH Strong Oxidation (2 alc ketone)
0
2 LiAlH4 -COOH -CH2OH Strong Reduction (ketone 2 alc)
0
3 Cu / 573 K or CrO3 -CH2OH -CHO Dehydrogenation
4 PCl5 or SOCl2 -OH -Cl
5 Cl2 / Δ or Cl2 / UV -H -Cl Free radical substitution
6 Aq NaOH / KOH -X -OH Nucleophilic substitution
7 KCN -X -CN Step Up
8 AgCN -X -NC
9 Alcoholic KOH -HX = Dehydrohalogenation (Stzf)
10 Mg / dry ether Mg R-X R-MgX
11 HBr >=< H, Br Merkovnikov
12 H2 / Pd-BaSO4 -COCl -CHO Rosenmund Reduction
13 Zn-Hg / HCl >C=O -CH2- Clemmension Reduction
14 NH3 / Δ -COOH -CONH2 -COOH + NH3 -COONH4
15 Br2 / NaOH or NaOBr -CONH2 -NH2 Step Down ( Hoffmann)
16 HNO2 or NaNO2/HCl -NH2 -OH HONO
17 CHCl3 / alc KOH -NH2 -NC Carbyl amine
18 P2O5 -CONH2 -CN Dehydration
19 H3O+ -CN -COOH Hydrolysis
20 OH- -CN -CONH2
21 LiAlH4 -CN -CH2NH2 Reduction
22 Red P / Cl2 α-H of acid -Cl HVZ Reaction
In benzene ring
23 Fe / X2 /dark -H -X Halogination
24 CH3Cl / AlCl3(anhyd) -H -CH3 Friedel Craft alkylation
25 CH3COCl / AlCl3(anhyd) -H -COCH3 Friedel Craft acylation
26 Conc.HNO3/con.H2SO4 -H -NO2 Nitration
27 Conc H2SO4 -H -SO3H Sulphonation
28 KMnO4 / H+ -R -COOH Oxidation
29 CrO2Cl2 / H+ -CH3 -CHO Mild oxidation(Etard Reaction)
30 Sn / HCl or Fe/HCl -NO2 -NH2 Reduction
31 NaOH / 623K / 300 atm -Cl -OH
32 Zn dust / Δ -OH -H
33 NaNO2 / dil HCl / 273-278 K -NH2 -N2+Cl- Diazo reaction
34 CuCl / HCl or Cu/HCl -N2+Cl- -Cl Sandmeyer or Gattermann
35 CuBr / HBr or Cu/HBr -N2+Cl- -Br Sandmeyer or Gattermann
36 CuCN / KCN -N2+Cl- -CN Sandmeyer
37 KI -N2+Cl- -I
38 HBF4 / Δ -N2+Cl- -F
39 H3PO2 or CH3CH2OH -N2+Cl- -H
40 H2O / 283 K -N2+Cl- -OH
41 HBF4/ NaNO2, Cu / Δ -N2+Cl- -NO2
42 C6H5-OH -N2+Cl- -N=N-C6H5-OH Coupling ( p-hydroxy)
43 C6H5-NH2 -N2+Cl- -N=N-C6H5-NH2 Coupling ( p-amino)
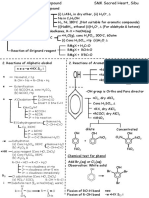
Reactions of Grignard Reagent
Grignard reagent + Any one below + H2O Product
H2O or ROH or RNH2 R-H
H-CHO R-CH2-OH (10 alc)
R-CHO R-CH(OH)-R (20 alc)
R-CO-R R2C(OH)-R (30 alc)
R-MgX
CO2 R-COOH
R-CN R-CO-R
HCOOR Aldehyde
RCOOR Ketone
NB: i) During reaction generally changes take place in the functional group only so see the functional
group very carefully.
ii) Remember structural formula of all the common organic compounds ( with their IUPAC and common
names)
iii) Wurtz Reaction and Aldol Condensation are not included in the table although they are
very important for conversions so study them .
iv) By taking examples practice all the above cases ( from 1 to 43 and Grignard)
v) Practice only from NCERT book.
vi) Start practicing NOW !
How to use the table? See below.
Example : See no 7 in the table
Directional Properties of groups in benzene ring for electrophilic substitution
Ortho-para directing group: -R , -OH, -NH2, -X, -OR, -NHR, -NR2, -NHCOCH3, -CH2Cl, -SH, - Ph
Meta-directing group: -NO2 , -CHO , -COOH , COOR , -CN , -SO3H , -COCH3 , -CCl3 , -NH3+ ,
You might also like
- Tips For ConversionDocument2 pagesTips For ConversionPratham ZalaNo ratings yet
- Reagent Group Out Group in Remark: Key For ConversionsDocument2 pagesReagent Group Out Group in Remark: Key For ConversionsChetan KumarNo ratings yet
- ConversionDocument5 pagesConversionPrathamesh SabaleNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 738616703organic ConversionDocument8 pages738616703organic ConversionSakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- Newer Redox Titrants: International Series of Monographs in Analytical ChemistryFrom EverandNewer Redox Titrants: International Series of Monographs in Analytical ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Important Reagents TreDocument3 pagesImportant Reagents Treraghava123456No ratings yet
- XXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973From EverandXXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973No ratings yet
- Best Chemistry Conversion TricksDocument7 pagesBest Chemistry Conversion TricksShiglu Habibti100% (1)
- Coordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972From EverandCoordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972A. B. P. LeverNo ratings yet
- Organic ConversionsDocument1 pageOrganic ConversionsMahmoud LotfyNo ratings yet
- Advances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookFrom EverandAdvances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookArmando J. L. PombeiroRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Acfrogcxqpd3dqml GQHMZQ B0c089di81vpcrvgphrwcu4gh Bzezvshldjt4clxztdrke4cieuxds1wlvk6scla 0byn2rmeu4btdaq8ckybm0chweegnztu7u2olcnli2lia5txmf386nyikuDocument6 pagesAcfrogcxqpd3dqml GQHMZQ B0c089di81vpcrvgphrwcu4gh Bzezvshldjt4clxztdrke4cieuxds1wlvk6scla 0byn2rmeu4btdaq8ckybm0chweegnztu7u2olcnli2lia5txmf386nyikuAchal ParekhNo ratings yet
- Organic Reactions and Reagents TableDocument3 pagesOrganic Reactions and Reagents TablePoornima RaviNo ratings yet
- Day 14 PDFDocument85 pagesDay 14 PDFAman9692No ratings yet
- ReductionDocument36 pagesReductionSayed Newaj ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- ReductionDocument7 pagesReductionPranayNo ratings yet
- GRIGNARD REAGENTS, REDUCTION & ALKANESDocument52 pagesGRIGNARD REAGENTS, REDUCTION & ALKANESPRIYANSHU KUMARNo ratings yet
- Dhoom # 9 Haloalkane & Haloarene in One Shot (10.6.2020)Document156 pagesDhoom # 9 Haloalkane & Haloarene in One Shot (10.6.2020)Jeet RathodNo ratings yet
- Hydroxyl at I OnDocument60 pagesHydroxyl at I OngbgbkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ChartsDocument84 pagesOrganic Chemistry ChartsHarish100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry ChartsDocument84 pagesOrganic Chemistry ChartsPRIYANSHU KUMARNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ChartsDocument84 pagesOrganic Chemistry ChartsPRIYANSHU KUMARNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ChartsDocument84 pagesOrganic Chemistry ChartsPRIYANSHU KUMARNo ratings yet
- Important Name Reactions by Vineet Khatri SirDocument4 pagesImportant Name Reactions by Vineet Khatri SirVishalNo ratings yet
- WS - 19 - Alcohol Ether - 6 PageDocument6 pagesWS - 19 - Alcohol Ether - 6 Pageashish3229255No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Haloalkanes, Haloarenes, Alcohols, Phenols, and EthersDocument56 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Haloalkanes, Haloarenes, Alcohols, Phenols, and EthersArnav AdarshNo ratings yet
- Reduction, Oxidation - Hydrolysis Theory PDFDocument14 pagesReduction, Oxidation - Hydrolysis Theory PDFGOURISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes MADDocument31 pagesHaloalkanes MADggdfjkkvvNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Name Reactions of All Organic ChaptersDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Name Reactions of All Organic ChaptersRanit Mukherjee67% (3)
- R-Che: DMF (Mecc - E-H)Document9 pagesR-Che: DMF (Mecc - E-H)Janardhan BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - PPT Aldehyde Ketone Corboxilic AcidDocument33 pagesClass 12 - PPT Aldehyde Ketone Corboxilic AcidRidhi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Amines - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024Document3 pagesAmines - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024subhamwork2006No ratings yet
- 45 Hydrocarbons AlkanesDocument7 pages45 Hydrocarbons Alkanessujalgupta0123456789No ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry (Amino Acids) Part 2Document10 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Amino Acids) Part 2ridwanNo ratings yet
- Name ReactionDocument15 pagesName Reactionnirbhay shukla100% (1)
- RADHA SWAMI ACADEMY: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument10 pagesRADHA SWAMI ACADEMY: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsVishal KushwahNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenol ND EthersDocument16 pagesAlcohol Phenol ND Ethersbhawnam.1995No ratings yet
- Flow Chart - HydrocarbonsDocument77 pagesFlow Chart - HydrocarbonsKalyan Reddt100% (2)
- Reagent Chemistry Jeet Sir FinalDocument217 pagesReagent Chemistry Jeet Sir Finalallenclass11workNo ratings yet
- Amines, Reactions: Basic NucleophilicDocument37 pagesAmines, Reactions: Basic NucleophilicM. MoizNo ratings yet
- AminaDocument31 pagesAminaRedyNo ratings yet
- Lab Preparations and ReactionsDocument45 pagesLab Preparations and ReactionsSUYOG K.C.No ratings yet
- Undergraduate organic reactions summaryDocument41 pagesUndergraduate organic reactions summaryKathyNo ratings yet
- AldehydeDocument8 pagesAldehydecbs123abcNo ratings yet
- Name Reactions: Sandmeyer'S ReactionDocument9 pagesName Reactions: Sandmeyer'S ReactionSai Krishnan100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Fiitjee Flowcharts PDFDocument12 pagesOrganic Chemistry Fiitjee Flowcharts PDFAkshit Sharma50% (4)
- Full NCERT Organic Reactions ch10 to ch14 - इसे करके जाओगे तो 65+ Score पक्का (25.2.2021)Document89 pagesFull NCERT Organic Reactions ch10 to ch14 - इसे करके जाओगे तो 65+ Score पक्का (25.2.2021)Sameer Narula100% (1)
- Alkyl Halides: R-X (X F, CL, BR, I)Document40 pagesAlkyl Halides: R-X (X F, CL, BR, I)ranjit singh randhawaNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde (12th) of Chemistry For JEE 2019Document9 pagesAldehyde (12th) of Chemistry For JEE 2019misostudyNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 12Document20 pages12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 12sangam patraNo ratings yet
- Flow Charts in Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesFlow Charts in Organic ChemistryJessie McCartney85% (27)
- Alkanes: Methods of PreparationDocument16 pagesAlkanes: Methods of PreparationayushNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes1Document15 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes1Poorni RenuNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid DerivativesDocument38 pagesCarboxylic Acid DerivativesshaikmguNo ratings yet
- Ald&Ketone IIDocument51 pagesAld&Ketone IIheraldas2421No ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Topic 17 Hydroxyl Compound (Short Notes)Document1 pageSTPM Chemistry Topic 17 Hydroxyl Compound (Short Notes)Chris Lau100% (1)
- Organic Named Reactions PDFDocument8 pagesOrganic Named Reactions PDFAshis BisoyiNo ratings yet
- Important Chemical Reactions For Class 12 Chemistry With MechanismDocument7 pagesImportant Chemical Reactions For Class 12 Chemistry With MechanismSatish YadavNo ratings yet
- Chem Ch-10 DPPDocument36 pagesChem Ch-10 DPPDummy dumNo ratings yet
- (L2) - (JLD 3.0) - Haloalkane & Haloarenes - 08 SeptDocument49 pages(L2) - (JLD 3.0) - Haloalkane & Haloarenes - 08 Septfunnyvideos. comNo ratings yet
- Important Chemical Reactions For Class 12 Chemistry With MechanismDocument9 pagesImportant Chemical Reactions For Class 12 Chemistry With MechanismSoma SahaNo ratings yet
- Important Chemical Reactions For Class 12 Chemistry: Classes Competitive Exams Buy A Course +919243500460Document10 pagesImportant Chemical Reactions For Class 12 Chemistry: Classes Competitive Exams Buy A Course +919243500460sssNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument53 pagesAminesasheethio4No ratings yet
- All Name Reactions of Chemistry Class 12th Cbse & Isc PDFDocument11 pagesAll Name Reactions of Chemistry Class 12th Cbse & Isc PDFzakiya100% (2)
- IzatinDocument141 pagesIzatinthamizh555No ratings yet
- All Name Reactions of Chemistry Class 12th Cbse & Isc PDFDocument11 pagesAll Name Reactions of Chemistry Class 12th Cbse & Isc PDFprabs2006917881% (145)
- 202003291608409191arun Sethi Diazonium CompoundsDocument12 pages202003291608409191arun Sethi Diazonium CompoundsMarwan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Amines: Pre-Medical: Chemistry Allen 3.1 AnilineDocument10 pagesAmines: Pre-Medical: Chemistry Allen 3.1 AnilineJK JHANo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Aldol Condensation ExplainedDocument30 pagesMechanism of Aldol Condensation ExplainedParameshwari kumar100% (1)
- Ch19 Wade ChemistryDocument58 pagesCh19 Wade ChemistrySunnyd1013No ratings yet
- Formal Lab ReportDocument5 pagesFormal Lab ReportAlfred ContadoNo ratings yet
- Amines WordDocument25 pagesAmines Wordnvmohankumar85No ratings yet
- Sandmeyer Isatin Synthesis 2010 PDFDocument4 pagesSandmeyer Isatin Synthesis 2010 PDFSamrat MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Organic Reactions and MechanismDocument51 pagesOrganic Reactions and MechanismAbhay Kumar Nayak75% (8)
- Organic Chemistry Reactions and MechanismsDocument160 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reactions and MechanismsRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- MiniRevOrgChem2015 127 PDFDocument23 pagesMiniRevOrgChem2015 127 PDFShashank SinghNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Name Reactions ExplainedDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry Name Reactions ExplainedTedoh RajNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Revision NotesDocument99 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Revision NotesTECH STOVENo ratings yet
- Name ReactionsDocument10 pagesName ReactionsMUKUL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument1 pageHaloalkanes and HaloarenesSneha Yadav0% (1)
- PCM Encyclopedia Organic ReactionsDocument10 pagesPCM Encyclopedia Organic ReactionsAbhinav SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Amines Important QuestionsDocument34 pagesAmines Important QuestionsK KANNANNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry ReactionsDocument10 pagesClass 12 Chemistry ReactionsRitishNo ratings yet
- Name ReactionDocument15 pagesName Reactionnirbhay shukla100% (1)